当前位置:网站首页>Fundamentals of programming language (2)
Fundamentals of programming language (2)
2022-04-23 19:43:00 【flysh05】
3. Basic principles of compiler
The function of the compiler is to translate the source program written in a high-level language into an equivalent target program ( Assembly language Speech or machine language ). The working process of compiler is divided into 6 Stages , As shown in the figure below :
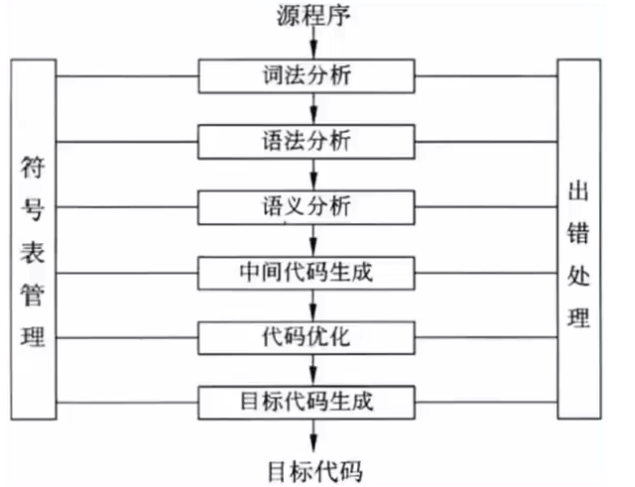
Lexical analysis : Is the first stage of the compilation process paragraph . The task of this stage is from left to right Read character by character into the source program , That is to scan the character stream constituting the source program Then recognize the word according to the word formation rules ( Also known as single A word or symbol ).
Syntax analysis : Is a logical phase of the compilation process . The task of grammar analysis is to combine word sequences into various types on the basis of lexical analysis Grammatical phrases , Such as “ Program ”,“ sentence ”, “ expression ” wait . The parser judges the source Whether the program is structurally correct
Semantic analysis : Is a logical phase of the compilation process . The task of semantic analysis is to analyze the structurally correct source program Conduct a review of a context sensitive nature , Conduct type review . Such as type matching 、 The divisor of division is not 0 etc. . It is also divided into static semantic errors ( It can be found in the compilation stage ) And dynamic semantic errors ( Can only be issued at run time present ).
Intermediate code and object code generation : Intermediate code is generated according to semantic analysis , Need optimized Links , Finally generate executable object code . The purpose of introducing intermediate code is to optimize the code independent of the machine . The commonly used intermediate code has suffix ( Reverse Polish )、 Ternary form ( Three address codes )、 Quaternions and trees . Three questions need to be considered ( One is how to generate shorter object code ; The second is how to make full use of Computing Registers in the machine , Reduce the number of accesses to the storage unit ; The third is how to make full use of computer instructions Characteristics of the system , To improve the quality of object code ).
To master the above three expressions , In fact, it is three kinds of traversal of trees , Generally, the normal expression is middle order traversal Infix expression , Construct a tree based on it , Then according to the requirements of the topic, find the prefix or suffix .
Simple solution : The suffix expression starts from left to right , First put the expression in parentheses , Then add the operators to the brackets of this level in turn .
3. Grammar defines
A formal grammar is an ordered quadruple G=(V,T,S,P), among :
1)V: non-terminal . Not part of language , Not the end result , Can be understood as placeholder .
2)T: Terminator . Is an integral part of language , Is the end result .V⌒T=θ
3)S: Start character . Is the beginning symbol of language .
4)P: Generative formula . The rule of replacing a nonterminal with a Terminator . Form like α->β
Terminator : final result , Other elements cannot be derived .
non-terminal : Can deduce other elements .
Generative formula : That is, the formula of the terminator derived from the non Terminator .
Closure , The concept is as follows , Generally, the closure can be 0 The case of is substituted into the operation :
Regular closure :A+=A1UA2UA3U…UAn U…( That is, the combination of all powers ).
Closure :A*=A0UA+( On the basis of regular closure , add A0={ε}).
for example a={a,aa,aaa,…,ε}, and (ab)*={ab,abab,ababab,.,ε}
4. Grammar type

5. Normal form
For the alphabet ∑, The normal expression on it and the normal set it represents can be recursively defined as follows .
(1) ε It's a normal form , It represents a collection L( ε)={ ε}.
(2) if a yes ∑ Characters on , be a It's a normal form , The normal set it represents is {a}.
(3) If normal r and s Represent normal set respectively L and L(s), be :
①r|s It's normal , Represents a collection L U L(s).
②r·s It's normal , Represents a collection LL(s).
③r’ It's normal , Represents a collection (L(r)).
④ It's normal , Represents a collection L.
6. Finite automaton
Deterministic finite automata and uncertain finite automata : Enter a character , Look yes Whether we can get the only successor , If you can , Is certain , Otherwise, it is uncertain if multiple successors are obtained
7. Grammar analysis method
Top down parsing : Leftmost inference , From left to right . A given grammar G And source program string r. from G The start sign of S set out , By way of anti Use production to replace the non terminator in the sentence pattern ( deduction ), Gradually deduce r.
Recursive descent thought : The principle is to use recursive calls between functions to simulate the top-down construction process of syntax tree , It's a top-down Grammar analysis method .
Bottom up parsing : Rightmost derivation , right to left . Start with the given input string , Keep looking for substrings and grammar G A certain property in Life style P Match the candidates of , And use P Replace the left part of ( reduction ) And , Gradually reduce to the starting symbol S.
Move into conventional thinking : A stack setting , Move the input symbols into the stack one by one , When the top of the stack forms the right part of a production , Just use the left to Instead of , It's called reduction . Obviously , The idea is to deduce the left from the right , Therefore, it is the core idea of bottom-up grammar analysis .
版权声明
本文为[flysh05]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204231941311726.html
边栏推荐
- Zero base to build profit taking away CPS platform official account
- Deep learning -- Summary of Feature Engineering
- 【h264】libvlc 老版本的 hevc h264 解析,帧率设定
- 山大网安靶场实验平台项目—个人记录(四)
- Executor、ExecutorService、Executors、ThreadPoolExecutor、Future、Runnable、Callable
- Steps to build a deep learning environment GPU
- Building googlenet neural network based on pytorch for flower recognition
- C6748 software simulation and hardware test - with detailed FFT hardware measurement time
- Data analysis learning directory
- PHP reference manual string (7.2000 words)
猜你喜欢
C6748 software simulation and hardware test - with detailed FFT hardware measurement time
【数值预测案例】(3) LSTM 时间序列电量预测,附Tensorflow完整代码
Pdf reference learning notes
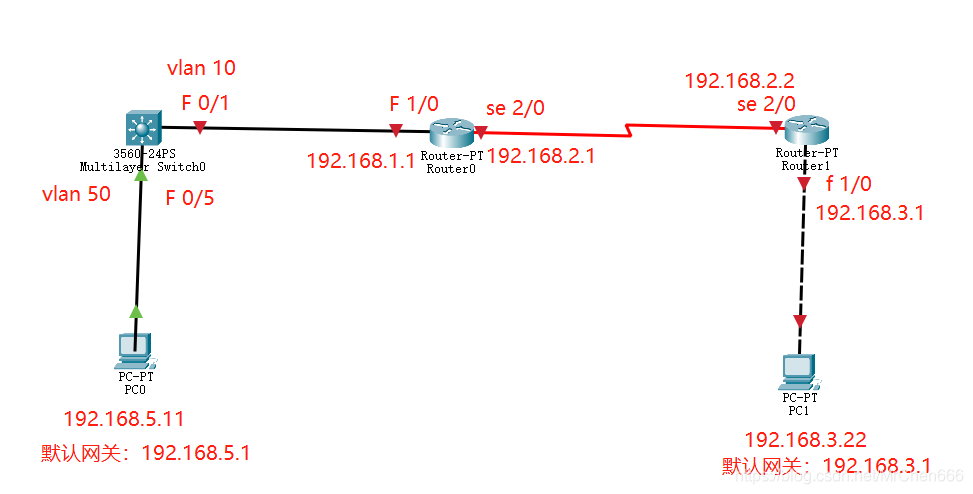
The most detailed network counting experiment in history (2) -- rip experiment of layer 3 switch
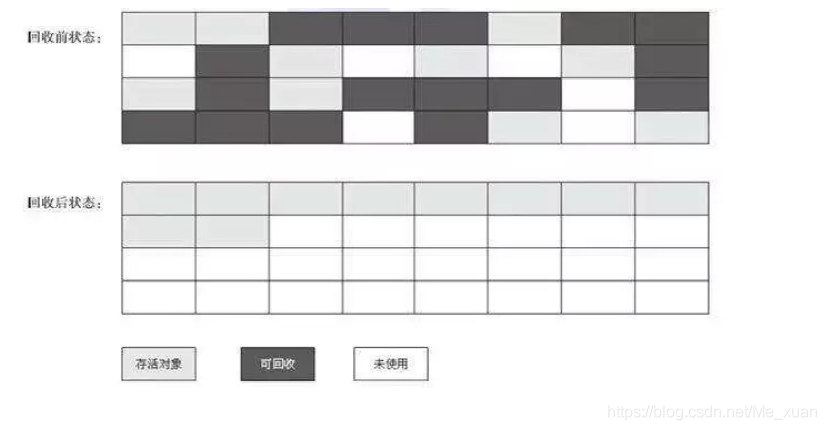
Garbage collector and memory allocation strategy
山东大学软件学院项目实训-创新实训-网络安全靶场实验平台(八)

@MapperScan与@Mapper

Software College of Shandong University Project Training - Innovation Training - network security shooting range experimental platform (8)

深度分析数据恢复原理——那些数据可以恢复那些不可以数据恢复软件

MySQL syntax collation (5) -- functions, stored procedures and triggers
随机推荐
MySQL 进阶 锁 -- MySQL锁概述、MySQL锁的分类:全局锁(数据备份)、表级锁(表共享读锁、表独占写锁、元数据锁、意向锁)、行级锁(行锁、间隙锁、临键锁)
Unity general steps for creating a hyper realistic 3D scene
The textarea cursor cannot be controlled by the keyboard due to antd dropdown + modal + textarea
Go recursively loops through folders
对普通bean进行Autowired字段注入
Strange passion
山东大学软件学院项目实训-创新实训-网络安全靶场实验平台(八)
山大网安靶场实验平台项目-个人记录(五)
SRS 的部署
[report] Microsoft: application of deep learning methods in speech enhancement
Redis core technology and practice 1 - start with building a simple key value database simplekv
IIS data conversion problem: 16bit to 24bit
IIS数据转换问题16bit转24bit
Kubernetes入门到精通-在 Kubernetes 上安装 OpenELB
OpenHarmony开源开发者成长计划,寻找改变世界的开源新生力!
基于pytorch搭建GoogleNet神经网络用于花类识别
No, some people can't do the National Day avatar applet (you can open the traffic master and earn pocket money)
Mysql database - single table query (III)
Electron入门教程4 —— 切换应用的主题
Gossip: on greed