当前位置:网站首页>[STL]map与set
[STL]map与set
2022-08-10 03:27:00 【Protein_zmm】
目录
一、容器
序列式容器:vector、list等(没有stack与queue,他们是适配器)
关联式容器:map、set等
关联式容器
在初阶阶段,我们已经接触过STL中的部分容器,比如:vector、list、deque、forward_list(C++11)等,这些容器统称为序列式容器,因为其底层为线性序列的数据结构,里面存储的是元素本身。
那什么是关联式容器?它与序列式容器有什么区别?
关联式容器也是用来存储数据的,与序列式容器不同的是,其里面存储的是<key, value>结构的键值对,在数据检索时比序列式容器效率更高,相比序列式容器还增加了查找的功能。
二、 set与multiset
2.1 set
set实际上就是二叉搜索树的K模型
基本使用:


void test_set1()
{
set<int> s;
s.insert(3);
s.insert(1);
s.insert(5);
s.insert(8);
s.insert(2);
set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
// auto it = s.begin();
// 迭代器删除
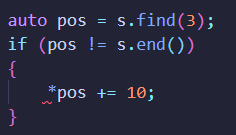
set<int>::iterator pos = s.find(3); // 删除3
if (pos != s.end())
{
// pos必须是一个有效位置的迭代器,否则会报错
s.erase(pos);
}
// 值删除
s.erase(30); // 没找到也不反馈
// erase是有返回值的,返回删除元素的数量,没有就是0—这里不是bool
cout << s.erase(30) << endl;
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
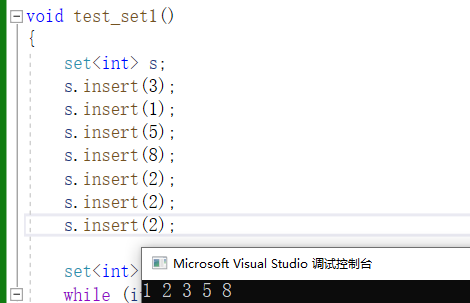
以上代码我们完成的是排序+去重,但是如果我们只想要排序,而不去去重怎么办?
2.2 multiset
基本用法与set一致,头文件也一致
multi可以不去重
void test_multiset()
{
multiset<int> s;
s.insert(3);
s.insert(1);
s.insert(5);
s.insert(8);
s.insert(2);
s.insert(2);
s.insert(2);
multiset<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
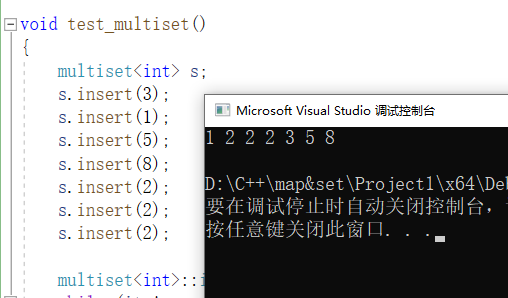
因此他可以完成排序而不去重
若find的val有多个值,返回中序的第一个val值所在节点的迭代器
删除所有的1
void test_multiset1()
{
multiset<int> s;
s.insert(3);
s.insert(1);
s.insert(5);
s.insert(8);
s.insert(2);
s.insert(1);
s.insert(1);
s.insert(2);
multiset<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
// 方式1
multiset<int>::iterator pos = s.find(1); // 有多个1找的是哪一个1?—找中序的第一个1
while (pos != s.end() && *pos == 1)
{
// 删除所有的1
// s.erase(pos);
// ++pos;
// 不能这样子,如果pos删除掉后,++pos就找不到下一个位置了
auto next = pos;
++next;
s.erase(pos);
pos = next;
}
// 方式2
cout << s.erase(1) << endl; // 有几个删除几个
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
不支持迭代器进行修改
三、 map与multimap
3.1 pair与make_pair
3.1.1 pair
map实际上就是二叉搜索树中的KV模型
每个结点的位置除了存储key还有value,把KV封装到了一个类结构pair,这个pair也叫作键值对
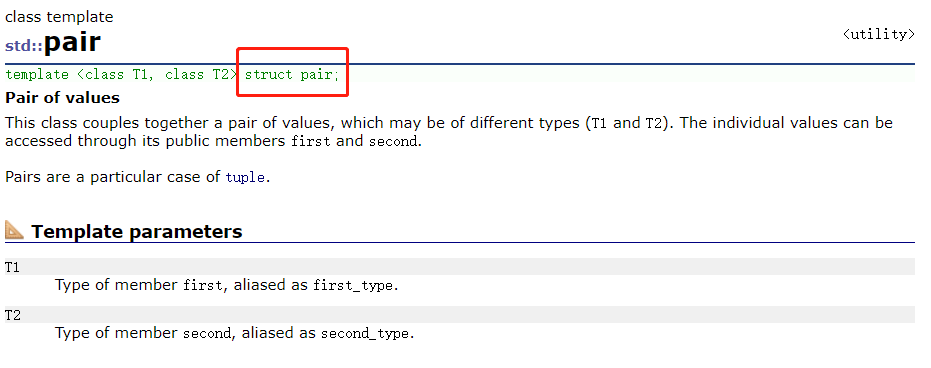
里面有两个成员,一个first,一个second
first就是第一个模板参数,一般就是K
second一般就是第二个模板参数,也就是V
3.1.2 make_pair

他是一个函数模板,本质是返回pair的匿名对象
自动推倒类型,因为是函数模板
实际上make_pair使用了更多一些
3.2 map
map可以按K进行排序,但是会去重
map文档中这里的T就是Value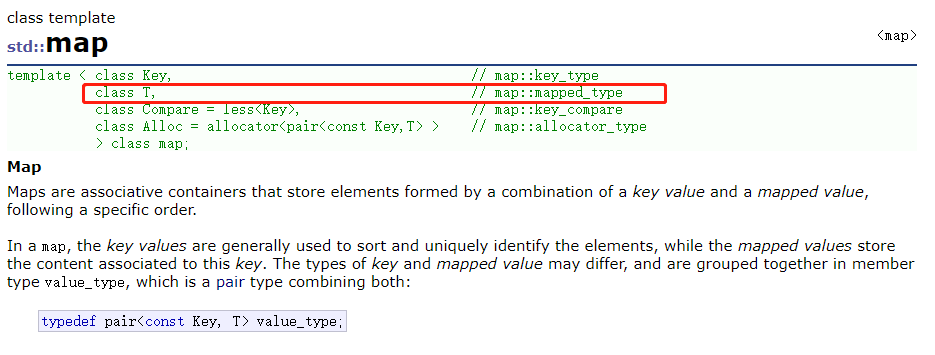
这里重载的[]并不是支持随机访问
插入
这里的插入是插入了value_type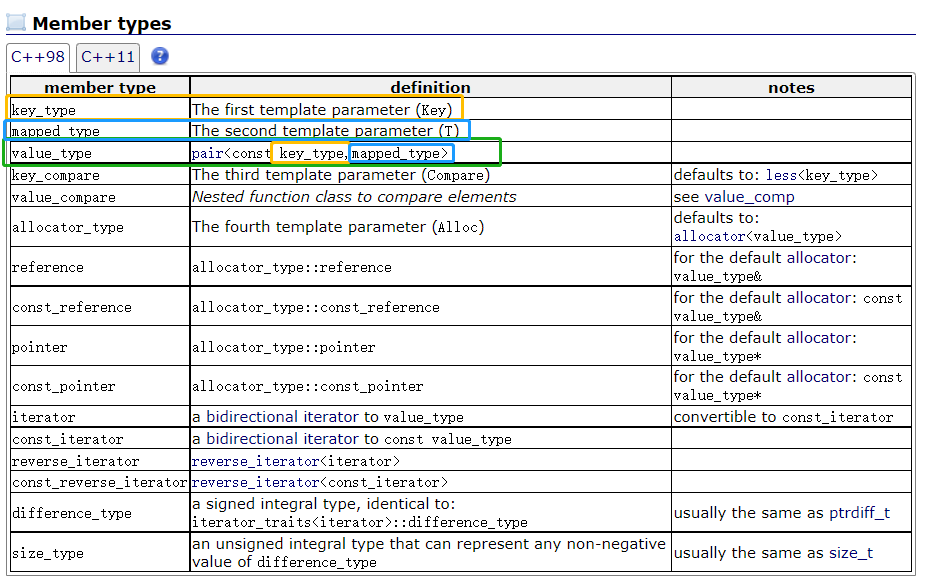
void test_map1()
{
// 定义一个中英互翻的字典
map<string, string> dict;
// insert第1种方法
pair<string, string> kv1("sort", "排序"); // pair也支持构造函数
dict.insert(kv1);
// insert第2种方法
dict.insert(pair<string, string>("string", "字符串")); // 构造一个匿名对象
// insert第3种方法——自动推倒类型,因为是函数模板,使用的次数是最多的
dict.insert(make_pair("test", "测试")); // 相当于是把第二个进行了封装
map<string, string>::iterator it = dict.begin();
while (it != dict.end())
{
// cout << (*it).first << " -> " << (*it).second << endl;
cout << it->first << " -> " << it->second << endl;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto& kv : dict) // pair里面又有string,最好加上引用,否则代价很大
{
// 相当于把*it赋值给了kv
cout << kv.first << " -> " << kv.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
// 依然会按照K进行排序进行输出
}
统计每个水果出现的次数
void test_map2()
{
// 统计次数
string arr[] = {
"苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "苹果", "苹果", "樱桃", "樱桃"};
map<string, int> countMap;
for (auto& str : arr)
{
// set不支持修改,map的value支持修改,但是key不支持修改,因为key修改会影响树的结构
auto ret = countMap.find(str);
if (ret == countMap.end())
{
// 找不到说明是第一次出现,就将他插入进去
countMap.insert(make_pair(str, 1));
}
else
{
// find返回的是迭代器 迭代器->会去调用operator->返回数据的指针,数据是pair,再调用一个->,但是编译器会省略一个->
ret->second++;
}
}
for (auto& kv : countMap)
{
cout << kv.first << " -> " << kv.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
在这里我们还可以去进行一些优化,因为find已经查找过一次了,在insert的时候还会在进行查找一次,就多余了

因此可以针对返回值进行优化
void test_map2()
{
// 统计次数
string arr[] = {
"苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "苹果", "苹果", "樱桃", "樱桃"};
map<string, int> countMap;
for (auto &str : arr)
{
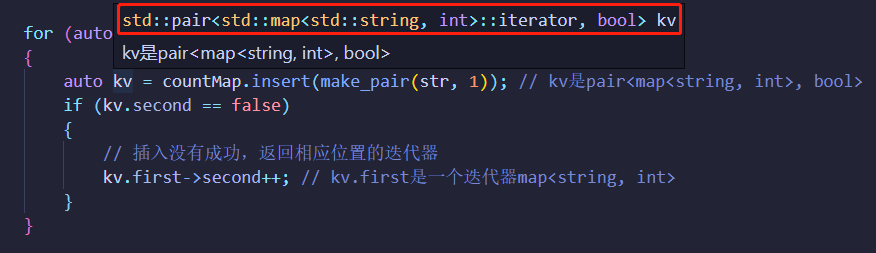
auto kv = countMap.insert(make_pair(str, 1)); // kv是pair<map<string, int>, bool>
if (kv.second == false)
{
// 插入没有成功,返回相应位置的迭代器
kv.first->second++; // kv.first是一个迭代器map<string, int>
}
}
for (auto &kv : countMap)
{
cout << kv.first << " -> " << kv.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
上述两种方法都可以完成统计,但实际中更常用的是下面这种
void test_map2()
{
// 统计次数
string arr[] = {
"苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "苹果", "苹果", "樱桃", "樱桃"};
map<string, int> countMap;
for (auto& str : arr)
{
countMap[str]++;
}
for (auto &kv : countMap)
{
cout << kv.first << " -> " << kv.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
在这里我们借助了operator[]
其中参数key_type是first,返回值是second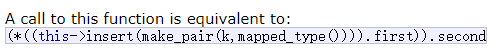
countMap[str]++;在上述代码中,返回值就是第二个参数也就是int
operator[]作用
1、插入
2、查找(value)
3、修改(value)
返回的是value的引用
void test_map3()
{
map<string, string> dict;
dict.insert(make_pair("sort", "排序"));
dict.insert(make_pair("left", "左边"));
dict.insert(make_pair("left", "剩余")); // map要求K不能重复,如果K有重复的时候,此时就插入不进去
dict["left"] = "剩余";
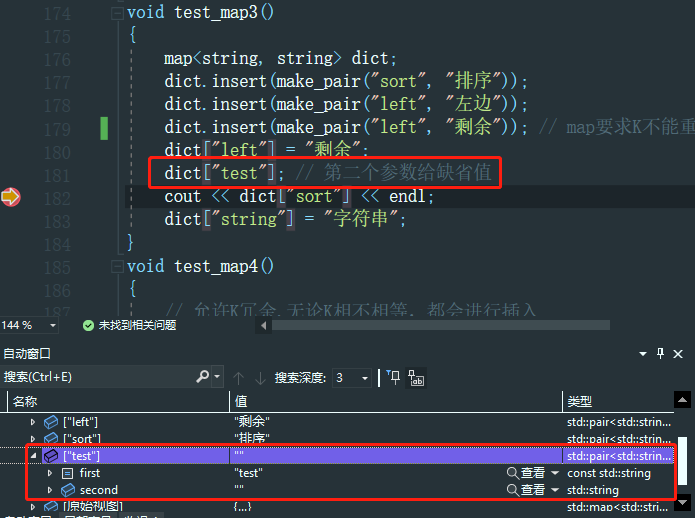
dict["test"]; // 第二个参数给缺省值
cout << dict["sort"] << endl;
dict["string"] = "字符串";
}
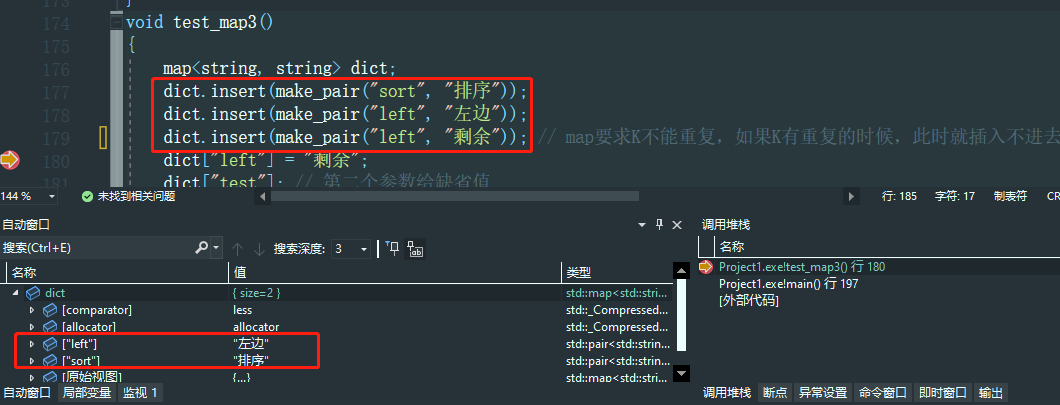
[]可以进行修改,指定了K,对V进行了修改(因为[]是返回value的引用)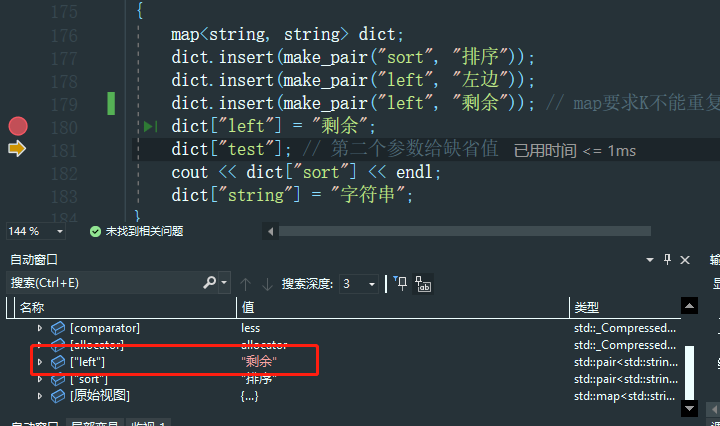
重载的[]实际上就是下面代码
mapped_type& operator[](const key_type& k) // mapped_type&就是value的引用
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(k, mapped_type())); // mapped_type()是匿名对象
// insert返回的是pair<iterator, bool>
return ret.first->second
}
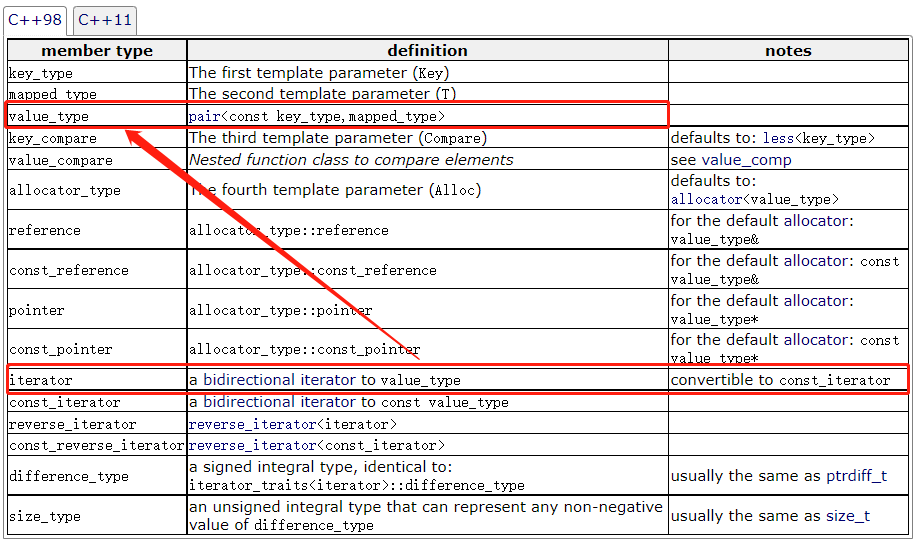
上述代码中ret.first就是iterator,之后指向value_type的第二个参数,也就是mapped_type(value),这样子就做到了返回value的引用
3.3 multimap
与map最大区别就是没有operator[]以及允许K冗余
count可以查找K有多少个,虽然也可以去判断在不在,但是判断在不在最好去用find
四、经典题目
4.1 统计最爱吃的前K种水果
方法1:利用sort(数据量不大的情况)
// 仿函数,为了让sort实现降序排列
struct countVal
{
bool operator()(const pair<string, int>& l, const pair<string, int>& r)
{
return l.second > r.second;
}
};
// topK问题
void GetFavoriteFruit(const vector<string>& fruits, size_t k)
{
// 方法1
// 先统计每种水果出现的次数(按K进行排序)
map<string, int> countMap;
for (auto& str : fruits)
{
countMap[str]++;
}
// 这里要求按V进行排序—sort
// sort要求传随机迭代器区间,map不是随机迭代器,应该先存入vector在进行排序
vector<pair<string, int>> sortv;
for (auto& kv : countMap)
{
sortv.push_back(kv);
}
sort(sortv.begin(), sortv.end(), countVal()); // 默认是升序排列,改为降序可以采用仿函数
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
{
cout << sortv[i].first << " -> " << sortv[i].second << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
vector<string> v = {
"苹果", "苹果", "香蕉", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "樱桃", "哈密瓜", "榴莲", "榴莲", "苹果" };
GetFavoriteFruit(v, 3);
return 0;
}
方法2:优化版本——迭代器
上述代码中for (auto& kv : countMap)把每一个KV中的pair(里面还包括string)赋值给kv,进行深拷贝,代价比较大,因为pair是自定义类型,所以我们可以进行改善
struct countIteratorVal
{
bool operator()(const map<string, int>::iterator& l, const map<string, int>::iterator& r)
{
return (l->second) > (r->second);
}
};
// topK问题
void GetFavoriteFruit(const vector<string>& fruits, size_t k)
{
// 先统计每种水果出现的次数(按K进行排序)
map<string, int> countMap;
for (auto& str : fruits)
{
countMap[str]++;
}
// 方法2,迭代器4/8字节,更小
vector<map<string, int>::iterator> sortv;
auto it = countMap.begin();
while (it != countMap.end())
{
sortv.push_back(it);
++it;
}
sort(sortv.begin(), sortv.end(), countIteratorVal());
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
{
// 上个版本sortv[i]是结构体,结构体.成员就可以访问内容
// 这个版本sortv[i]是迭代器,要使用->
cout << sortv[i]->first << " -> " << sortv[i]->second << endl;
}
}
方法3:使用仿函数
#include <functional> // 仿函数头文件,包含了less和greater
void GetFavoriteFruit(const vector<string>& fruits, size_t k)
{
// 先统计每种水果出现的次数(按K进行排序)
map<string, int> countMap;
for (auto& str : fruits)
{
countMap[str]++;
}
// 方法3 multimap
multimap<int, string, greater<int>> sortMap; // multimap默认第三个参数是less,greater后就会降序排列了
for (auto& kv : countMap)
{
sortMap.insert(make_pair(kv.second, kv.first)); // 这样子就不需要写仿函数
}
}
方法4:优先级队列
struct countVal
{
bool operator()(const pair<string, int>& l, const pair<string, int>& r)
{
return l.second < r.second; // 优先级队列给<是大堆
}
};
void GetFavoriteFruit(const vector<string>& fruits, size_t k)
{
// 先统计每种水果出现的次数(按K进行排序)
map<string, int> countMap;
for (auto& str : fruits)
{
countMap[str]++;
}
// 方法4:优先级队列
priority_queue<pair<string, int>, vector<pair<string, int>>, countVal> pq; // 这里传递类型—类模板传类型 函数模板传对象 这里是类模板,传递类型
for (auto& kv : countMap)
{
pq.push(kv);
}
while (k--)
{
cout << pq.top().first << " -> " << pq.top().second << endl;
pq.pop();
}
}
优先级队列也可以用迭代器进行优化
struct countIteratorVal
{
bool operator()(const map<string, int>::iterator& l, const map<string, int>::iterator& r)
{
return (l->second) < (r->second);
}
};
void GetFavoriteFruit(const vector<string>& fruits, size_t k)
{
// 先统计每种水果出现的次数(按K进行排序)
map<string, int> countMap;
for (auto& str : fruits)
{
countMap[str]++;
}
// 这里也可以传递迭代器
priority_queue<map<string, int>::iterator, vector<map<string, int>::iterator>, countIteratorVal> pq; // 这里传递类型—类模板传类型 函数模板传对象
auto it = countMap.begin();
while (it != countMap.end())
{
pq.push(it);
++it;
}
while (k--)
{
cout << pq.top()->first << " -> " << pq.top()->second << endl;
pq.pop();
}
}
4.2 前K个高频单词
692. 前K个高频单词
快排是不稳定的,这里不能保证i和love的顺序,所以不能用sort,想要用稳定的排序可以去使用stable_sort函数
在这里我们使用multimap去进行处理,思路与上一题相似
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> topKFrequent(vector<string>& words, int k) {
// 统计每一个单词出现的次数
map<string, int> countMap;
for (auto& str : words)
{
countMap[str]++;
}
// 按照次数进行排序,默认按K进行排序,因此把int写在第一个参数位置
multimap<int, string, greater<int>> sortMap;
for (auto& kv : countMap)
{
sortMap.insert(make_pair(kv.second, kv.first));
}
// 将排好序的答案存入vector
vector<string> v;
auto it = sortMap.begin();
while (k--)
{
v.push_back(it->second);
++it;
}
return v;
}
};
边栏推荐
- 什么是Jmeter?Jmeter使用的原理步骤是什么?
- The same is a primary test, why does he pay 5,000 yuan more than me?
- Basic understanding of network models
- @Autowired注解 --required a single bean, but 2 were found出现的原因以及解决方法
- leetcode 283:移动零
- Flink Table&Sql API使用遇到的问题总结
- 如何开启热部署Devtools
- js原型和原型链以及原型继承
- 笔试题记录
- Embedded Sharing Collection 32
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
超全面的Android面试题汇总
《天才基本法》:平行时空的第二次选择,小演员的表现意外出圈
金融财经翻译的行业前景如何
当我操作dms客户端的时候,我要操控好几个阿里云账号下的数据库,但是这边每次切换都会把我的登录记录删
一篇文章教你Pytest快速入门和基础讲解,一定要看
【Verilog数字系统设计(夏雨闻)6-------模块的结构、数据类型、变量和基本运算符号2】
TCP协议之《对端MSS值估算》
socket编程基础
Flink学习15:Flink自定义数据源
UDP协议之《套接口阻塞选项UDP_CORK》
Pen paper records
@Autowired注解 --required a single bean, but 2 were found出现的原因以及解决方法
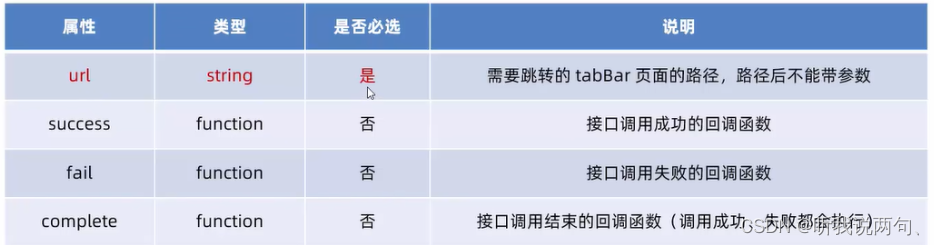
Mini Program Navigation and Navigation Parameters
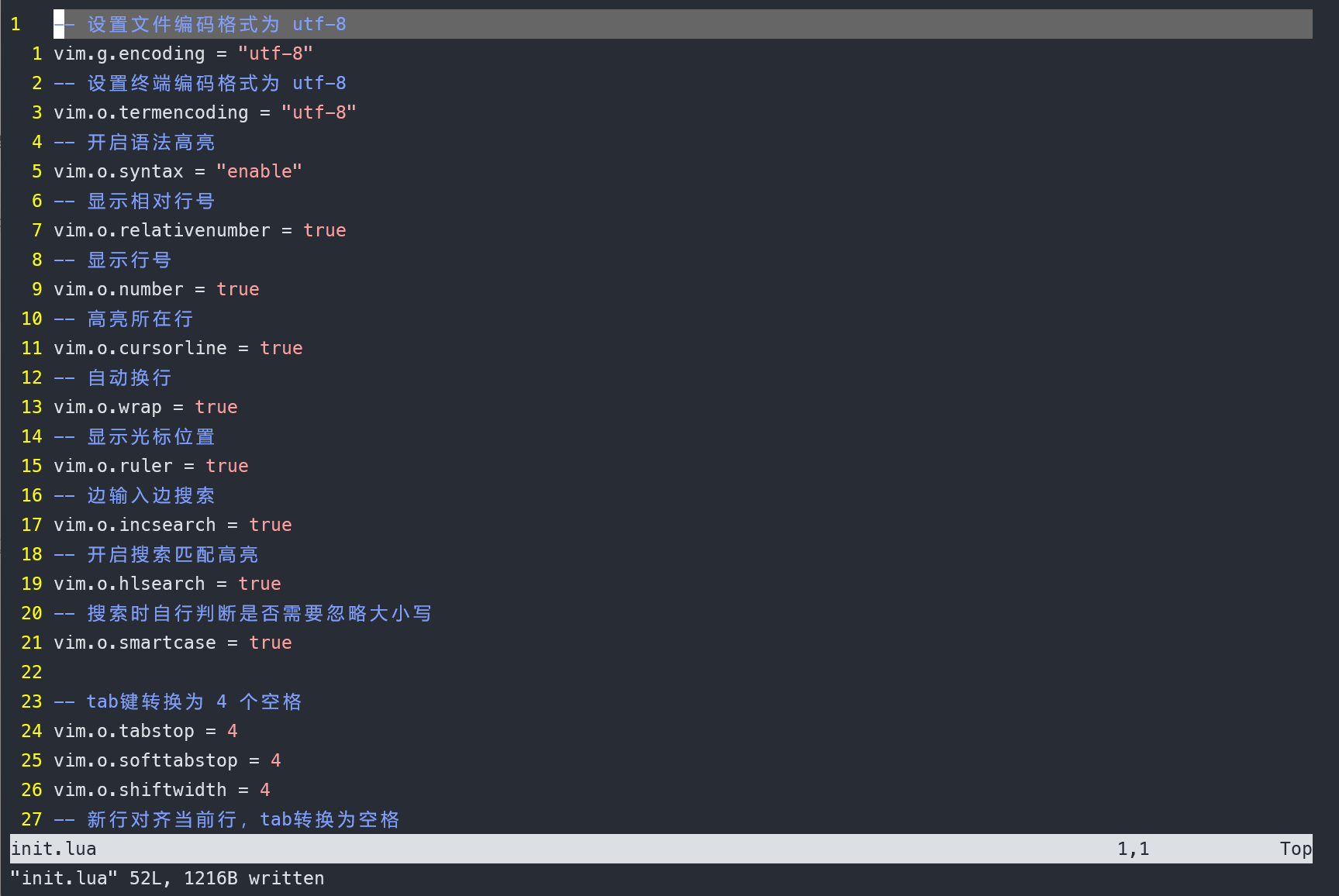
从零开始配置 vim(9)——初始配置
关于JWT 和Token(转)
Camera partial update
sql优化
什么是Jmeter?Jmeter使用的原理步骤是什么?
测试工作管理与规范
Do you know these basic types of software testing?