当前位置:网站首页>Detailed explanation of file operation (2)
Detailed explanation of file operation (2)
2022-04-23 16:32:00 【The mountain stream is clear and blue】
Catalog
3. Determination of the end of file reading
1. Random reading of files
1.1 fseek
The default reading of files starts from the first element
for example :
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
FILE* pf = fopen("test.txt", "r");// In the way of reading
if (pf == NULL)
{
perror("fopen");
return 1;
}
char ch = fgetc(pf);// Read a character and put it in ch in , After reading, the pointing position will be shifted backward
printf("%c\n", ch);
ch = fgetc(pf);
printf("%c\n", ch);
fclose(pf);
pf = NULL;
return 0;
}test.txt The contents of the document :

Running results :
![]()
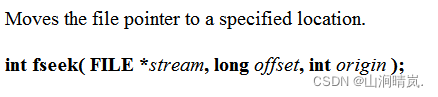
The first parameter is the file pointer , The second parameter is the offset , The initial position of the third parameter ( as follows )
SEEK_CUR// The current location of the file pointer
SEEK_END// The position at the end of the file
SEEK_SET// Where the file starts #include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
FILE* pf = fopen("test.txt", "r");// In the way of reading
if (pf == NULL)
{
perror("fopen");
return 1;
}
char ch = fgetc(pf);// Read a character and put it in ch in
printf("%c\n", ch);
ch = fgetc(pf);
printf("%c\n", ch);
fseek(pf, 2, SEEK_CUR);// from c Start to shift back 2 Characters
ch = fgetc(pf);
printf("%c\n", ch);
fseek(pf, 0, SEEK_END);// The character of the current position is '\0'
ch=fgetc(pf);
printf("%c\n", ch);
fclose(pf);
pf = NULL;
return 0;
}Running results :
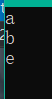

#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
FILE* pf = fopen("test.txt", "w");// In writing
if (pf == NULL)
{
perror("fopen");
return 1;
}
fputc('a', pf);
fputc('b', pf);
fputc('c', pf);
fputc('d', pf);
fseek(pf, -3, SEEK_CUR);// The current position is offset forward 3 A place
fputc('e', pf);
fclose(pf);
pf = NULL;
return 0;
}Running results :
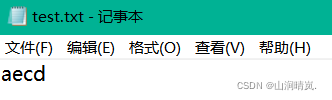
1.2 ftell
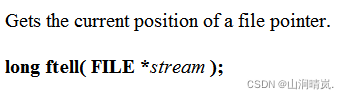
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
FILE* pf = fopen("test.txt", "w");// In writing
if (pf == NULL)
{
perror("fopen");
return 1;
}
fputc('a', pf);
fputc('b', pf);
fputc('c', pf);
fputc('d', pf);
fseek(pf, -3, SEEK_CUR);// The current position is offset forward 3 A place
fputc('e', pf);
long pos = ftell(pf);// The return type of this function is long type
printf("%ld\n", pos);
fclose(pf);
pf = NULL;
return 0;
}Running results :
![]()
1.3 rewind

#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
FILE* pf = fopen("test.txt", "w");// In the way of reading
if (pf == NULL)
{
perror("fopen");
return 1;
}
fputc('a', pf);
fputc('b', pf);
fputc('c', pf);
fputc('d', pf);
fseek(pf, -3, SEEK_CUR);// The current position is offset forward 3 A place
fputc('e', pf);
long pos = ftell(pf);
printf("%ld\n", pos);
rewind(pf);// Return to the starting position
pos = ftell(pf);
printf("%ld\n", pos);
fclose(pf);
pf = NULL;
return 0;
}Running results :
![]()
2. Text files and binaries
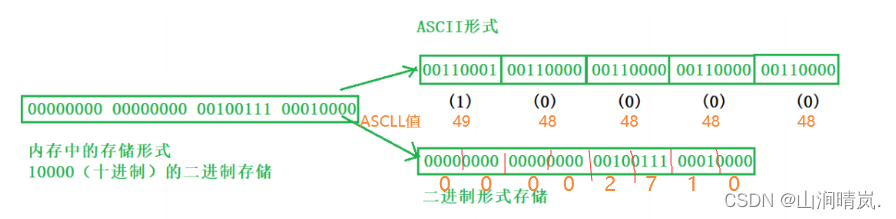
According to the organization of data , Data files are called text file perhaps Binary .The data is stored in memory as Binary system Form storage of , If the output without conversion is to external memory , Namely Binary .If it's required to use ASCII code Form storage of , You need to convert before storing . With ASCII The file stored in the form of characters is writing This document
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 10000;
FILE* pf = fopen("test.txt", "wb");
fwrite(&a, 4, 1, pf);// The binary form is written to the file
fclose(pf);
pf = NULL;
return 0;
}The contents of this file are binary files

Add to source file

Right click to select the opening method , With Binary editor Open up

It's about 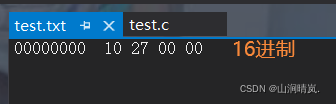
because VS2019 With Small end storage So the result is 10 27 00 00
3. Determination of the end of file reading
During file reading , You can't use feof The return value of the function is directly used to determine whether the end of the file .
feof function Apply when the file reading is finished , The judgment is that the read failed and ended , Or end of file .
1. Whether the reading of text file is finished , Determine whether the return value is EOF ( fgetc ), perhaps NULL ( fgets )for example :fgetc Judge whether it is EOF .fgets Determine whether the return value is NULL .2. Judgment of reading end of binary file , Judge whether the return value is less than the actual number to be read .for example :fread Determine the return value Whether it is less than the actual number to be read .
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void) {
int c; // Be careful :int, Not char, Ask to deal with EOF
FILE* fp = fopen("test.txt", "r");
if (!fp) {
perror("File opening failed");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
//fgetc When reading fails or the end of the file is encountered , Will return to EOF
while ((c = fgetc(fp)) != EOF) // standard C I/O Read file cycle
{
putchar(c);
}
putchar('\n');
// Judge why it ended
if (ferror(fp))
puts("I/O error when reading");
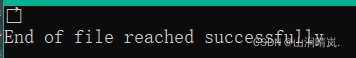
else if (feof(fp))
puts("End of file reached successfully");
fclose(fp);
}Running results :
4. File buffer
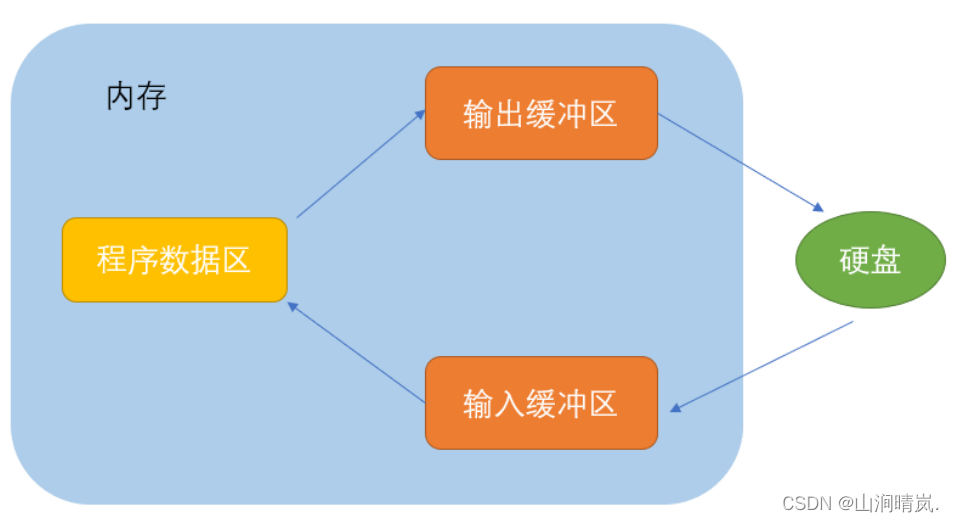
ANSIC The standard is “ Buffer file system ” Processing of data files , The so-called buffer file system means that the system automatically opens up a block in memory for each file being used in the program “ File buffer ” . Data output from memory to disk is first sent to a buffer in memory , pack full The buffer is then sent to disk together . If you read data from disk to computer , Then read the data from the disk file and input it into the memory buffer ( Full buffer ), And then send the data from the buffer to the program data area one by one ( Program variables, etc ). The size of the buffer depends on C The compiler system decides .
for example :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
int main()
{
FILE* pf = fopen("test.txt", "w");
fputs("abcdef", pf);// Put the code in the output buffer first
printf(" sleep 10 second - The data has been written , open test.txt file , Found no content in the file \n");
Sleep(10000);
printf(" Refresh buffer \n");
fflush(pf);// When the buffer is flushed , Write the data in the output buffer to a file ( disk )
// notes :fflush In high version VS It can't be used on
printf(" Sleep again 10 second - here , Open again test.txt file , There's something in the file \n");
Sleep(10000);
fclose(pf);
// notes :fclose When closing a file , It also flushes the buffer
pf = NULL;
return 0;
}Running results :
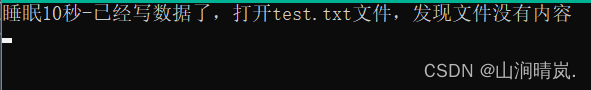

10 Seconds later
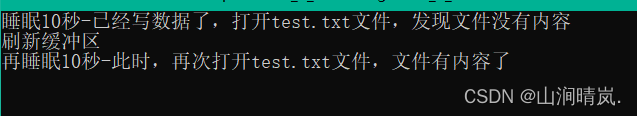

Conclusion :Because there is a buffer , C Language when operating files , Need to do Refresh buffer perhaps Close the file at the end of the file operation .If you don't do , May cause problems in reading and writing files .
版权声明
本文为[The mountain stream is clear and blue]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204231630298829.html
边栏推荐
- 最詳細的背包問題!!!
- Grbl learning (I)
- MySQL的btree索引和hash索引区别
- About background image gradient()!
- Sort by character occurrence frequency 451
- Vim使用Vundle安装代码补全插件(YouCompleteMe)
- 捡起MATLAB的第(7)天
- About JMeter startup flash back
- Ali developed three sides, and the interviewer's set of combined punches made me confused on the spot
- 下载并安装MongoDB
猜你喜欢

Interview question 17.10 Main elements
G008-hwy-cc-estor-04 Huawei Dorado V6 storage simulator configuration
Ali developed three sides, and the interviewer's set of combined punches made me confused on the spot
Day (4) of picking up matlab

安装及管理程序
捡起MATLAB的第(9)天
ESP32编译环境的搭建
Gartner 發布新興技術研究:深入洞悉元宇宙

捡起MATLAB的第(4)天
建站常用软件PhpStudy V8.1图文安装教程(Windows版)超详细
随机推荐
Hypermotion cloud migration helped China Unicom. Qingyun completed the cloud project of a central enterprise and accelerated the cloud process of the group's core business system
Es common query, sorting and aggregation statements
力扣-198.打家劫舍
Disk management and file system
How to quickly batch create text documents?
The first line and the last two lines are frozen when paging
Set the color change of interlaced lines in cells in the sail software and the font becomes larger and red when the number is greater than 100
Database dbvisualizer Pro reported file error, resulting in data connection failure
如何进行应用安全测试(AST)
The solution of not displaying a whole line when the total value needs to be set to 0 in sail software
RecyclerView advanced use - to realize drag and drop function of imitation Alipay menu edit page
How magical is the unsafe class used by all major frameworks?
The most detailed Backpack issues!!!
VMware Workstation cannot connect to the virtual machine. The system cannot find the specified file
Cloud migration practice in the financial industry Ping An financial cloud integrates hypermotion cloud migration solution to provide migration services for customers in the financial industry
JMeter installation tutorial and solutions to the problems I encountered
Server log analysis tool (identify, extract, merge, and count exception information)
Qipengyuan horizon credible meta universe social system meets diversified consumption and social needs
Algorithem_ ReverseLinkedList
Oracle data pump usage