当前位置:网站首页>深度学习100例 | 第41天-卷积神经网络(CNN):UrbanSound8K音频分类(语音识别)
深度学习100例 | 第41天-卷积神经网络(CNN):UrbanSound8K音频分类(语音识别)
2022-04-23 16:13:00 【K同学啊】
- 运行环境:python3
- 作者:K同学啊
- 选自专栏:《深度学习100例》
- 精选专栏:《新手入门深度学习》
- 推荐专栏:《Matplotlib教程》
- 🧿 优秀专栏:《Python入门100题》
我的环境:
- 语言环境:Python3.6.5
- 编译器:jupyter notebook
- 深度学习环境:TensorFlow2.4.1
- 显卡(GPU):NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080
- 数据地址:【传送门】
我们的代码流程图如下所示:

一、准备工作
大家好,我是K同学啊!
今天给大家分享一个音频分类的实战案例。
使用的数据集为UrbanSound8K,该数据集包含来自 10 个类别的城市声音的 8732 个标记声音摘录 (<=4s):air_conditioner、car_horn、children_playing、dog_bark、drilling、enginge_idling、gun_shot、jackhammer、siren和 street_music,数据分别存在fold1-fold10等十个文件夹中。
除了声音摘录之外,还提供了一个 CSV 文件,其中包含有关每个摘录的元数据。
方法介绍
-
有 3 种从音频文件中提取特征的基本方法:
a) 使用音频文件的 mffcs 数据
b) 使用音频的频谱图图像,然后将其转换为数据点(就像对图像所做的那样)。这可以使用 Librosa 的 mel_spectogram 函数 轻松完成
c) 结合这两个特征来构建更好的模型。 (需要大量时间来读取和提取数据)。 -
我选择使用第二种方法。
-
标签已转换为分类数据以进行分类。
-
CNN 已被用作对数据进行分类的主要层
1. 导入所需的库
# Basic Libraries
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
pd.plotting.register_matplotlib_converters()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Conv2D, Flatten, Dense, MaxPool2D, Dropout
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
import os,glob,skimage,librosa
import librosa.display
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") #忽略警告信息
2. 分析数据类型及格式
分析CSV数据
df = pd.read_csv("./41-data/UrbanSound8K.csv")
df.head()
| slice_file_name | fsID | start | end | salience | fold | classID | class | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100032-3-0-0.wav | 100032 | 0.0 | 0.317551 | 1 | 5 | 3 | dog_bark |
| 1 | 100263-2-0-117.wav | 100263 | 58.5 | 62.500000 | 1 | 5 | 2 | children_playing |
| 2 | 100263-2-0-121.wav | 100263 | 60.5 | 64.500000 | 1 | 5 | 2 | children_playing |
| 3 | 100263-2-0-126.wav | 100263 | 63.0 | 67.000000 | 1 | 5 | 2 | children_playing |
| 4 | 100263-2-0-137.wav | 100263 | 68.5 | 72.500000 | 1 | 5 | 2 | children_playing |
列名
-
slice_file_name:音频文件名字. 命名格式为: [fsID]-[classID]-[occurrenceID]-[sliceID].wav
- [fsID]:从中提取摘录(片段)的录音的 Freesound ID
- [classID]:类别ID
- [occurrenceID]:一个数字标识符,用于区分原始录音中不同事件的声音
- [sliceID]:一个数字标识符,用于区分从同一事件中获取的不同切片
-
fsID:从中提取摘录(片段)的录音的 Freesound ID
-
start:原始 Freesound 录音中片段的开始时间
-
end:原始Freesound录音中切片的结束时间
-
salience:声音的(主观)显着性等级。 1 = 前景,2 = 背景。
-
fold:一共1-10,10个文件夹
-
classID:声音类别的数字标识符:
- 0 = air_conditioner
- 1 = car_horn
- 2 = children_playing
- 3 = dog_bark
- 4 = drilling
- 5 = engine_idling
- 6 = gun_shot
- 7 = jackhammer
- 8 = siren
- 9 = street_music
使用Librosa分析随机声音样本
a,b = librosa.load()返回值:
- a: 音频的信号值,类型是ndarray
- b: 采样率
3. 数据展示
import IPython.display as ipd
ipd.Audio('./41-data/fold5/100263-2-0-117.wav')

dataSample, sampling_rate = librosa.load('./41-data/fold5/100032-3-0-0.wav')
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 3))
D = librosa.amplitude_to_db(np.abs(librosa.stft(dataSample)), ref=np.max)
librosa.display.specshow(D, y_axis='linear')
plt.colorbar(format='%+2.0f dB')
plt.title('Linear-frequency power spectrogram')
plt.show()

arr = np.array(df["slice_file_name"])
fold = np.array(df["fold"])
cla = np.array(df["class"])
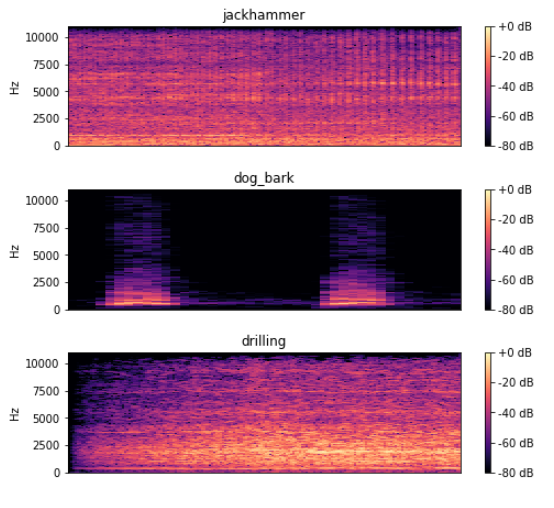
for i in range(192, 197, 2):
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 2))
path = './41-data/fold' + str(fold[i]) + '/' + arr[i]
data, sampling_rate = librosa.load(path)
D = librosa.amplitude_to_db(np.abs(librosa.stft(data)), ref=np.max)
librosa.display.specshow(D, y_axis='linear')
plt.colorbar(format='%+2.0f dB')
plt.title(cla[i])
二、特征提取与数据集构建
先看一下使用librosa.feature.melspectrogram()函数提取出来的数据shape
arr = librosa.feature.melspectrogram(y=data, sr=sampling_rate)
arr.shape
(128, 173)
1. 数据特征提取
feature = []
label = []
def parser():
# 加载文件并提取特征
for i in range(8732):
if i%1000 == 0:
print("已经提取%d份数据特征"%i)
file_name = './41-data/fold' + str(df["fold"][i]) + '/' + df["slice_file_name"][i]
X, sample_rate = librosa.load(file_name, res_type='kaiser_fast')
# 提取频谱图形成图像数组
mels = np.mean(librosa.feature.melspectrogram(y=X, sr=sample_rate).T,axis=0)
feature.append(mels)
label.append(df["classID"][i])
print("数据特征提取完成!")
return [feature, label]
temp = parser()
已经提取0份数据特征
已经提取1000份数据特征
已经提取2000份数据特征
已经提取3000份数据特征
已经提取4000份数据特征
已经提取5000份数据特征
已经提取6000份数据特征
已经提取7000份数据特征
已经提取8000份数据特征
数据特征提取完成!
temp_numpy = np.array(temp).transpose()
X_ = temp_numpy[:, 0]
Y_ = temp_numpy[:, 1]
X = np.array([X_[i] for i in range(8732)])
Y = to_categorical(Y_)
print(X.shape, Y.shape)
(8732, 128) (8732, 10)
2. 数据集构建
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, random_state = 1)
X_train = X_train.reshape(6549, 16, 8, 1)
X_test = X_test.reshape(2183, 16, 8, 1)
input_dim = (16, 8, 1)
三、构建模型并训练
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv2D(64, (3, 3), padding = "same", activation = "tanh", input_shape = input_dim))
model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
model.add(Conv2D(128, (3, 3), padding = "same", activation = "tanh"))
model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
model.add(Dropout(0.1))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(1024, activation = "tanh"))
model.add(Dense(10, activation = "softmax"))
model.compile(optimizer = 'adam', loss = 'categorical_crossentropy', metrics = ['accuracy'])
model.fit(X_train, Y_train, epochs = 90, batch_size = 50, validation_data = (X_test, Y_test))
Epoch 1/90
131/131 [==============================] - 3s 4ms/step - loss: 1.5368 - accuracy: 0.4717 - val_loss: 1.3617 - val_accuracy: 0.5144
Epoch 2/90
131/131 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 1.1502 - accuracy: 0.6091 - val_loss: 1.1119 - val_accuracy: 0.6326
......
131/131 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0481 - accuracy: 0.9835 - val_loss: 0.8535 - val_accuracy: 0.8653
Epoch 89/90
131/131 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0511 - accuracy: 0.9818 - val_loss: 0.7716 - val_accuracy: 0.8694
Epoch 90/90
131/131 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0502 - accuracy: 0.9829 - val_loss: 0.8673 - val_accuracy: 0.8630
model.summary()
Model: "sequential"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
conv2d (Conv2D) (None, 16, 8, 64) 640
_________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d (MaxPooling2D) (None, 8, 4, 64) 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_1 (Conv2D) (None, 8, 4, 128) 73856
_________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d_1 (MaxPooling2 (None, 4, 2, 128) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dropout (Dropout) (None, 4, 2, 128) 0
_________________________________________________________________
flatten (Flatten) (None, 1024) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense (Dense) (None, 1024) 1049600
_________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 10) 10250
=================================================================
Total params: 1,134,346
Trainable params: 1,134,346
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
predictions = model.predict(X_test)
score = model.evaluate(X_test, Y_test)
print(score)
69/69 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.8673 - accuracy: 0.8630
[0.8672816753387451, 0.8630325198173523]
版权声明
本文为[K同学啊]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://mtyjkh.blog.csdn.net/article/details/124347971
边栏推荐
- What does cloud disaster tolerance mean? What is the difference between cloud disaster tolerance and traditional disaster tolerance?
- You need to know about cloud disaster recovery
- Intersection, union and difference sets of spark operators
- The most detailed Backpack issues!!!
- Hyperbdr cloud disaster recovery v3 Release of version 3.0 | upgrade of disaster recovery function and optimization of resource group management function
- Day (3) of picking up matlab
- JMeter setting environment variable supports direct startup by entering JMeter in any terminal directory
- linux上啟動oracle服務
- 第九天 static 抽象类 接口
- 最詳細的背包問題!!!
猜你喜欢

Cloud migration practice in the financial industry Ping An financial cloud integrates hypermotion cloud migration solution to provide migration services for customers in the financial industry
Config learning notes component

What is cloud migration? The four modes of cloud migration are?
Day (6) of picking up matlab
Gartner predicts that the scale of cloud migration will increase significantly; What are the advantages of cloud migration?
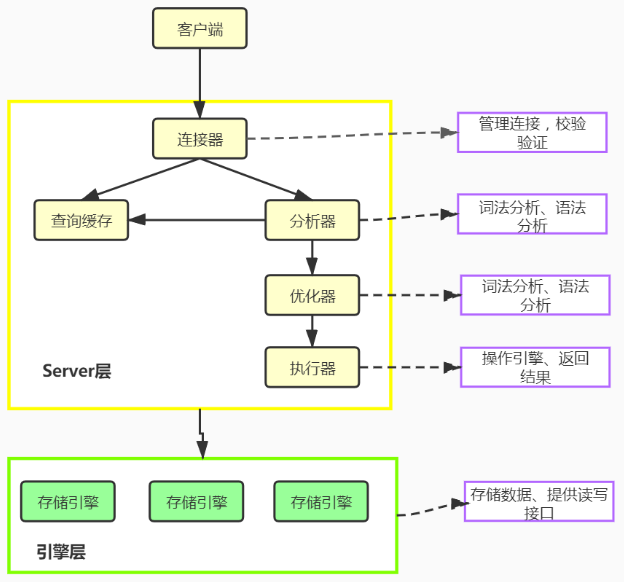
MySQL - execution process of MySQL query statement
Spark 算子之groupBy使用
Nanny Anaconda installation tutorial
JIRA screenshot
Day (9) of picking up matlab
随机推荐
G008-HWY-CC-ESTOR-04 华为 Dorado V6 存储仿真器配置
Meaning and usage of volatile
糖尿病眼底病变综述概要记录
Hypermotion cloud migration helped China Unicom. Qingyun completed the cloud project of a central enterprise and accelerated the cloud process of the group's core business system
Compile, connect -- Notes
Start Oracle service on Linux
451. 根据字符出现频率排序
Hypermotion cloud migration completes Alibaba cloud proprietary cloud product ecological integration certification
Homewbrew installation, common commands and installation path
Using JSON server to create server requests locally
leetcode-396 旋转函数
Distinct use of spark operator
Implement default page
299. 猜数字游戏
捡起MATLAB的第(2)天
How to quickly batch create text documents?
dlopen/dlsym/dlclose的简单用法
Spark 算子之coalesce与repartition
最详细的背包问题!!!
捡起MATLAB的第(3)天
