当前位置:网站首页>I just want to leave a note for myself
I just want to leave a note for myself
2022-04-23 19:08:00 【Gougouliang】
CSS
position: sticky
Viscous positioning , The positioning is based on the user's scrolling position .
It acts like position:relative; And when the page scrolls beyond the target area , It behaves like position:fixed;, It will be fixed in the target position .
Be careful : Internet Explorer, Edge 15 And earlier IE Version not supported sticky location . Safari Need to use -webkit- prefix.

.xiding{
position: sticky;
z-index: 1;
top: 100rpx;
width: 750rpx;
background-color: #FFF;
border: 2px solid #4CAF50;
}
Be careful :
- Parent element cannot have overflow:hidden perhaps overflow:auto attribute .
- The height of the parent element cannot be lower than sticky Height ,
- Must specify top、bottom、left、right4 One of the values .
overflow: hidden Property clear float
Browser support
All major browsers support overflow attribute .
overflow Property specifies what happens when content overflows the element box .
| value | explain |
|---|---|
| visible | The default value is . Content will not be trimmed , It will appear outside the element box . |
| hidden | The content will be trimmed , And the rest is invisible . |
| scroll | The content will be trimmed , But the browser will display scroll bars to see the rest of the content . |
| auto | If the content is trimmed , The browser will display scroll bars to view the rest of the content . |
| inherit | Rules should be inherited from the parent element overflow The value of the property . |
By adding overflow: hidden; Can achieve the effect of clearing floating .
advantage : The code is concise
shortcoming : When the content increases, it is easy to cause that the content will not automatically wrap and the content will be hidden , Cannot display element to overflow , But if you have only one line , Like a title , Add a little top and bottom margin style to make the height collapse , This attribute will be very convenient .
It is more recommended that the pseudo element method simulate the removal of additional tags
.clearfix:after,.clearfix:before{
content: "";
display: table;
}
.clearfix:after{
clear: both;
}
.clearfix{
*zoom: 1;
}
<div class="fahter clearfix">
<div class="big">big</div>
<div class="small">small</div>
</div>
<div class="footer"></div>
original text :https://blog.csdn.net/h_qingyi/article/details/81269667
JS
Complete the beginning and end of the string
Complete the beginning and end of the string
- ES6 Of padStart() Methods and padEnd() Method
- The first parameter is zero , Complete length , The second parameter is the complement value
'x'.padStart(5, 'ab') // 'ababx'
'x'.padStart(4, 'ab') // 'abax'
'x'.padEnd(5, 'ab') // 'xabab'
'x'.padEnd(4, 'ab') // 'xaba'
If the length of the original string , Equal to or greater than the specified complement length , Return the original string .
'xxx'.padStart(2, 'ab') // 'xxx'
'xxx'.padEnd(2, 'ab') // 'xxx'
The difference between function and method
- function (function) It's a piece of code , It needs to be called by name . It can take some data ( The parameters of the function ) Pass it in for processing , And then return some data ( The return value of the function ), You can also not return data .
- Method (method) It's called through an object javascript function . in other words , Methods are also functions , It's just a special function .
stay ECMAScript 6 after , Functions can be divided into three categories :
- class : Can only do new operation ;
- Method : You can only call “( )” operation ;
- General functions :( Except that some functions have special restrictions ,) At the same time can do new And call operations .
among , Typical “ Method ” When declaring internally , There are three main features :
- Has a name called “ The main object [[HomeObject]]” Internal groove of ;
- There is no name “ Constructors [[Construct]]” Internal groove of ;
- There is no name “prototype” Properties of .
function say(){
console.log(this,'say')
}
var a = {
say1:function(){
console.log(this,'say1')
},
say2:()=>{
console.log(this,'say2')
},
say3(){
console.log(this,'say3')
}
}
say() // window
a.say1() // a
a.say2() // window
a.say3() // a
new say()
new a.say1()
new a.say2() // a.say2 is not a constructor
new a.say3() // a.say3 is not a constructor
new Did four things
- Create an empty object
- Set up prototype chains
- Give Way Func Medium this Point to obj, And implement Func Function body .
- Judge Func Return value type of : If it's a value type , return obj. If it's a reference type , Just return the object of this reference type
parseInt Second parameter of
parseInt() Function to parse a string , And return an integer .
grammar :
parseInt(string, radix)
- string It's necessary . The string to be parsed .
- radix Optional . Represents the cardinality of the number to be resolved . The value is between 2 ~ 36 Between . If the parameter is omitted or its value is 0, Then the number will be in 10
Analyze... On the basis of . If it takes “0x” or “0X” start , Will be with 16 Cardinal number . If the parameter is less than 2 Or greater than 36, be parseInt() Will return NaN.
parseInt("17",8); // 15
parseInt("18",8); // 1
parseInt(021, 8) // 15 021 Number
parseInt('021', 8) // 17 021 String
Here is the second parameter 8, The meaning is not to change the first parameter 8 Hexadecimal conversion . At first I always thought so . notice parseInt(“18”,8); What is returned is 1.
first 17, The base number is 8
Personally, I think the process is based on 8 Judge on the basis of , First look at 17 Top ten 1, stay 8 within , It works , bits 7 Also in the 8 within , It works . The result is 1 + 7 , here 1 It's ten ,8 Cardinal number , full 8 Into the 1, amount to 18+7 = 15
the second 18, Based on 8
ten 1 It works , bits 8 Out of range , Invalid . The return value here is , It's just 1, Equivalent to a bit 1. The result is 1
021 and ‘021’ The return result is different
If as a number ,javascript Default 0 The first number is 8 Base number , in other words ,021 The corresponding decimal system is 17, So for 17 analysis , The result is 18+7 = 15
As string , Namely 0+ 2*8 + 1 = 17
Some implicit calls
// Convert string to numeric type
var a = '123456'
var b = +a
console.log(b) // 123456
// call toString Method .
function fun () {
return 585
}
fun.toString = ()=>{
return ' Called tostring Method '
}
console.log(fun) // Called tostring Method
var obj = {
a: 1,
toString: function () {
console.log('toString')
return '2'
},
valueOf: function () {
console.log('valueOf')
return 3
}
}
console.log(obj == '2'); // Output... In sequence 'valueOf' false
console.log(String(obj));// Output... In sequence 'toString' '2'
var obj = {
a: 1,
toString: function () {
console.log('toString')
return '2'
},
valueOf: function () {
console.log('valueOf')
return {} // Change to object
}
}
console.log(obj == '2'); // Output... In sequence 'valueOf' 'toString' true
console.log(Number(obj));// Output... In sequence 'valueOf' 'toString' 2
In the operation of the equality operator , Object will call first valueOf If the value returned is , Just compare directly , If an object is returned , Will call toSting, null With the exception of , Then compare with the returned value
async await
- async Used to state a function It's asynchronous
- async The function returns a Promise object
- await Used to wait for an asynchronous method execution to complete
- await Can only appear in async Function
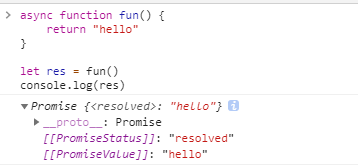

await Waiting is an expression , The result of this expression is Promise Objects or other values .
If it doesn't wait for one Promise object , that await The result of this expression is what it's waiting for .
If it waits for one Promise object ,await And he got busy , It blocks the rest of the code , Waiting for the Promise object resolve, Then get resolve Value , As await The result of an expression .
function fun() {
return new Promise((res,rej)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
res('hello')
},5000)
})
}
async function fun1(){
console.log(1)
let res = await fun()
console.log(res)
console.log(2)
}
fun1()
await After the order Promise object , The result of the run might be rejected, So it's better to await The order is placed in the try…catch Block of code
Sequence of events
console.log('sync1');
setTimeout(function () {
console.log('setTimeout1')
}, 0);
var promise = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function () {
console.log('setTimeoutPromise')
}, 0);
console.log('promise');
resolve();
});
promise.then(() => {
console.log('pro_then');
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('pro_timeout');
}, 0)
})
setTimeout(function () {
console.log('last_setTimeout')
}, 0);
console.log('sync2');
The output order of this code is
sync1
promise
sync2
pro_then
setTimeout1
setTimeoutPromise
last_setTimeout
pro_timeout
The order of execution of personal understanding :
Output sync1
Add the first macro task after the current macro task (‘setTimeout1’)
Add a second macro task after the current macro task (‘setTimeoutPromise’)
Output promise
.then() For micro task , At the end of the current macro task queue
Add a third macro task after the current macro task (‘last_setTimeout’)
Output sync2
end
The micro task that executes the current macro task .then()
Output pro_then
Add a fourth macro task after the current macro task (‘pro_timeout’)
The current macro task has finished executing , Start the next macro task (setTimeout1)
Output setTimeout1
The current macro task has finished executing , Start the next macro task (setTimeoutPromise)
Output setTimeoutPromise
The current macro task has finished executing , Start the next macro task (last_setTimeout)
Output last_setTimeout
The current macro task has finished executing , Start the next macro task (pro_timeout)
Output pro_timeout
- First, analyze how many macro tasks there are ;
- In each macro task , Analyze how many micro tasks there are ;
- According to the call order , Determine the execution order of micro tasks in macro tasks ;
- According to the trigger rules and call order of macro task , Determine the execution order of macro tasks ;
- Determine the whole sequence .
A statement in advance
JavaScript Before execution , It's about scripts 、 Preprocessing statements in modules and function bodies . The preprocessing process will be processed ahead of time var、 Function declaration 、class、const and let These statements , To determine the meaning of the variables .
var a = 1;
function foo() {
console.log(a);
var a = 2;
}
foo(); // undefined
The preprocessing process is performed before , There are function body level variables a, You won't access variables in the outer scope a 了 , And function body level variables a There is no assignment yet , So it is undefined. amount to
var a = 1;
function foo() {
var a;
console.log(a);
a = 2;
}
foo(); // undefined
example 2:
var a = 1;
function foo() {
console.log(a);
if(false) {
var a = 2;
}
}
foo(); //undefined
This code is better than the previous code in var a = 2 There is an extra paragraph if, We know if(false) The code in will never be executed , But the preprocessing phase doesn't care about this ,var The function of can penetrate all sentence structures , It only recognizes scripts 、 Module and function body . So the result here is exactly the same as the previous code , We will get undefined.
console.log(foo); // function
function foo(){
}
console.log(foo); // undefined
if(true) {
function foo(){
}
}
The first 2 This code gets undefined. If there is no function declaration , An error will be thrown . This explanation function It still works in the pretreatment phase , A variable is generated in the scope , No assignments are generated , The assignment behavior occurs in the execution phase .
console.log(c); // error :c is not defined
class c{
}
class Declare the global behavior with function and var Is not the same . stay class Use... Before declaring class name , Will report a mistake . This behavior is very much like class No preprocessing , But it's not .
var c = 1;
function foo(){
console.log(c); // error: 'c' has already been declared
class c {}
}
foo();
After execution , We see , Still threw an error , If you remove class Statement , Will print out 1, in other words , Appear in the back class The declaration affects the result of the previous statement . This explanation ,class Statements are also preprocessed , It creates variables in the scope , And an error is thrown when you ask to access it . also class The effect of the statement will not penetrate if And so on , So only when it is written in the global environment can it be declared .
ES6 Variable structure assignment
ES6 Allow to follow certain mode , Extract values from arrays and objects , Assign values to variables , This is called deconstruction .
let a = 1;
let b = 2;
let c = 3;
// ES6 You can write like this in let [a, b, c] = [1, 2, 3];
If the structure fails, it will return undefined
let [a, b, c] = [1, 2];
console.log(a,b,c) // 1 2 undefined
Object deconstruction can also specify default values
var {x, y = 5} = {x: 1};
x // 1
y // 5
The default value takes effect when , The property value of the object is exactly equal to undefined.
var {x = 3} = {x: undefined};
x // 3
var {x = 3} = {x: null};
x // null
String structure
const [a, b, c, d, e] = 'hello';
a // "h"
b // "e"
c // "l"
d // "l"
e // "o"
vue
this.$nextTick()
Today, my colleagues do a echart, stay mounted The request interface and echart Method . The request data returned , however echart The picture doesn't show . So I let him use async await To deal with it , Wait until the returned data is updated , Do it again echart, So it can be displayed normally . After the discovery this.$nextTick() Can also be handled .
“ The next time DOM A delayed callback is executed after the update loop is completed . Use this method immediately after modifying the data , Gets the updated DOM.”
A small example of someone else :

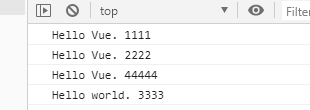
You can see msg change ,msg1 and msg3 No updates .msg2 Updated .Vue Updating DOM Time is executed asynchronously . Just listen for data changes ,Vue A queue will be opened , And buffer all data changes that occur in the same event cycle .
From the order of input , Maybe after the current macro task promise Add a micro task , It is also possible to add a macro task directly . Execute... After executing the current task nexttick The operation .
Give it a try , In the request echart In the method of data , After using the data nextTick Method callback , call echart Method , The diagram can also be displayed normally .
other
vscode Connect Night God Simulator
If vscode No nocturnal simulator detected
Find the night God Simulator bin Catalog , Copy path
win+R open cmd , Switch to this path
Input
nox_adb.exe connect 127.0.0.1:62001

Small exercise
Put a circle div According to the red 3 second , yellow 2 second , green 1 Second cycle changes background color

<view class="light" :style="'background:'+ colors">
changeColor(val,dur){
return new Promise((res,rej)=>{
this.colors = val
setTimeout(()=>res(),dur)
})
},
async getuser(){
while(true){
await this.changeColor('red',3000)
await this.changeColor('yellow',2000)
await this.changeColor('green',1000)
}
}
Local packaging blank
vue.config.js
module.exports = { publicPath: './', assetsDir: 'static', parallel: false }
Set Taobao image
npm config set registry https://registry.npm.taobao.org
nanoid only ID
npm install nanoid
import {
nanoid } from 'nanoid'
model.id = nanoid() //=> "V1StGXR8_Z5jdHi6B-myT"
版权声明
本文为[Gougouliang]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204210602029708.html
边栏推荐
- Eight bit binary multiplier VHDL
- Druid SQL和Security在美团点评的实践
- Disable Ctrl + Alt + Del
- The type initializer for ‘Gdip‘ threw an exception
- Xlslib use
- The first leg of the national tour of shengteng AI developer creation and enjoyment day was successfully held in Xi'an
- MVVM model
- The difference between ordinary inner class and static inner class
- static类变量快速入门
- Machine learning practice - naive Bayes
猜你喜欢
redis优化系列(三)解决主从配置后的常见问题

【历史上的今天】4 月 23 日:YouTube 上传第一个视频;网易云音乐正式上线;数字音频播放器的发明者出生
Class loading process of JVM
![[record] typeerror: this getOptions is not a function](/img/c9/0d92891b6beec3d6085bd3da516f00.png)
[record] typeerror: this getOptions is not a function
2022.04.23(LC_763_划分字母区间)
Résolution: cnpm: impossible de charger le fichier... Cnpm. PS1 parce que l'exécution de scripts est désactivée sur ce système
From technical system to business insight, the closing chapter of the practice of small and medium-sized R & D team structure
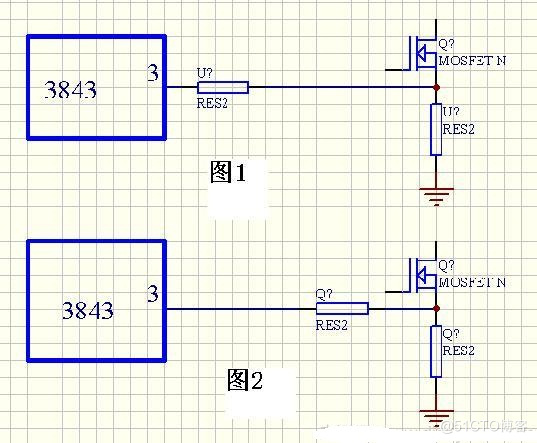
Partage de la conception de l'alimentation électrique de commutation et illustration des compétences en conception de l'alimentation électrique

2022.04.23 (lc_763_divided into letter interval)
![[popular science] CRC verification (I) what is CRC verification?](/img/80/a1fa10ce6781aebf1b53d91fba52f4.png)
[popular science] CRC verification (I) what is CRC verification?
随机推荐
Tencent cloud GPU best practices - remote development training using jupyter pycharm
Class loading process of JVM
ESP32 LVGL8. 1 - roller rolling (roller 24)
mysql_linux版本的下載及安裝詳解
Simplified path (force buckle 71)
Advanced transfer learning
Switching power supply design sharing and power supply design skills diagram
Sentinel rule persistence into Nacos
Sogou cell thesaurus analysis (only extract words and word frequency)
Use bitnami / PostgreSQL repmgr image to quickly set up PostgreSQL ha
PyGame tank battle
[popular science] CRC verification (I) what is CRC verification?
程序员如何快速开发高质量的代码?
Minesweeping II of souI instance
mysql通过binlog恢复或回滚数据
Is it safe to open an account in Bohai futures.
FTP、ssh远程访问及控制
特征选择feature_selection--SelectKBest
The fifth bullet of MySQL learning -- detailed explanation of transaction and its operation characteristics
c#:泛型反射