当前位置:网站首页>Bottom processing of stack memory in browser
Bottom processing of stack memory in browser
2022-04-23 16:58:00 【Endless cake】
Execution stack
JS The engine wants to execute code , An execution stack will be created , That's what we call :
Stack memory (ECstackl) Execution context stack
The first function of stack memory :
Used to execute code
JS in , Code execution under a domain , Each has its own execution context . Compress the created execution context to js This process is performed in stack memory in , There is a professional term : Into the stack
Created execution context , There are two kinds of :
overall situation EC(G) there G refer to global Abbreviation
function EC (…)
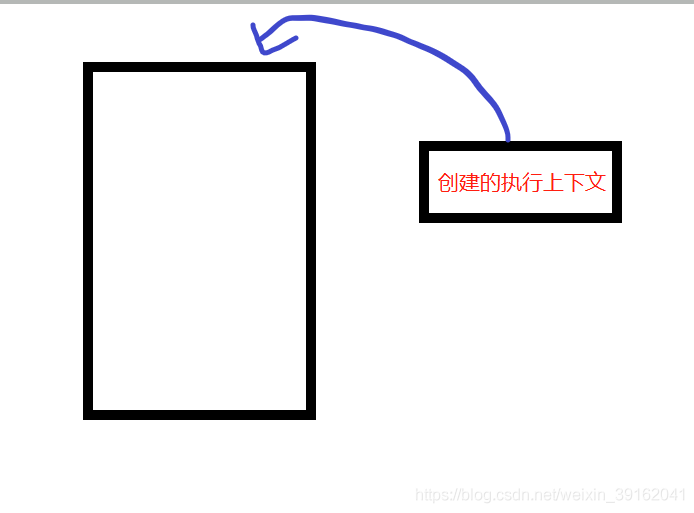
When some context is executed , It's useless. . We call it : Out of the stack .
However , Some ask up and down after the execution , It's also useful , Will compress it to the bottom of the stack , Wait for the next call ,( That is, the top and bottom questions have not been destroyed ), This mechanism also has a professional term called : Closure
Inside this , It also involves a professional term called global object (GO) globla obeject On the browser side , Will assign the global object to window . All in our global execution context , It must contain GO( Global object )
The second function of stack memory
Store basic type values ( For example, global object, we create a variable , Will be stored in the stack )
There is a very important concept , Look at the example
let a = 10;
// This variable will be stored in the stack by us
We define a variable, which is very simple , So let's see , How does he realize the assignment and creation of variables .
The assignment of all variables is divided into three steps to create ( If it has been created, it will not be created again )
Three step operation of variable assignment :
(1) Create variables ( Statement declare)
(2) Create values : The basic values can be directly created and stored in the stack memory
(3) Associate variables with values ( assignment ) defined Definition
therefore , We usually only declare variables, but if we don't define them ,js You're going to report a mistake undefined ( Undefined )
let a = 10;
let b =a;
This is the time , Let's create another variable b, because b=a,a Has been created . So you don't have to create values anymore , Just associate ,b=a Will go through it directly Pointer to a Value , That is to say 10. therefore b be equal to 10
Here I mentioned an important concept , The pointer . In fact, the underlying data processing mechanism of programming language , Pointer to variable , Are implemented through pointers . The concept of pointer is , The association of a variable with a value , It's called Association The pointer .
let a = 10;
let b =a;
b = 13;
This is the time , We assign b=13, This is the time b Has been declared . So there is no need to restate , This is to prevent the browser from redefining A process of . Then you need to create a new value 13, Put it in the stack ( therefore , As long as this mechanism is followed , Values will be created , Even if the value is the same )
js A variable in can only point to one value , Yes b Reassign , It doesn't affect a Of . therefore ,b=13, that a Is equal to 10.
A digression , Namely js in , There are two ways to define values , You can define variables and constants
The essential difference between variables and constants is , The direction of the variable can be changed , And constant , Each value is separate . The pointer cannot be changed , If you change, you will report an error .
ES6 In the const, It's not called a real constant , Its specialized syntax is called immutable variables , Or a variable whose pointer cannot be changed .
Create reference types
let a = {
n:12
}
let b = a;
b['n'] = 13;
console.log(a.n)
The creation of reference values is different , Because reference values are complex deconstructions , So special treatment .
Handle reference values :
(1) Open up a key value pair in the storage object ( Store the code in the function ) Of memory space , Namely “ Heap memory ”.
So heap memory has only one function , Store values of reference types .
(2) All heap memory has one that can be searched later 16 Base address
(3) So when assigning values to subsequent associations , Is to give the heap memory address to the variable operation .
That's why we call it a reference type , Because it operates on reference addresses .
Back to the example above , adopt b[‘n’] = 13 It will directly affect a.n Value , because a and b Bound is an address .
Reference type operation
let a = {
n:12
}
let b = a;
b={
n:13
}
console.log(a.n)
Because it's the reference type , So it must have recreated a heap .
a The heap address of is equal to a1.
then b be equal to a, therefore b The heap address of is also equal to a1
b={} therefore b Recreated a reference value , And generates a new heap b1. This is the time b The point is b1.
This is the time ,a and b All have their own direction , therefore a.n be equal to 12.
Knowledge point : Once heap memory is created , Can't be destroyed . If you want to destroy, you can make the reference type directly equal to null.
null: An empty object . By pointing the pointer to a null pointer , To release some memory .
On a daily basis , We define a variable , If you want to assign a value later , We define its value as null. Because if you only declare , If you don't create a value, it will be equal to undefined. I've seen a lot of people who are equal to 0 Of , In fact, this operation is not recommended , Because it is equal to 0, It will also open memory in the stack . and null It doesn't open memory .
版权声明
本文为[Endless cake]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204230554520092.html
边栏推荐
- New keyword learning and summary
- Nifi fast installation and file synchronization
- Grpc gateway based on Ocelot
- 织梦DEDECMS安全设置指南
- Website_ Collection
- About stream flow, write it down briefly------
- Feign report 400 processing
- Decimal format decimal / datetime conversion processing
- 【PIMF】OpenHarmony啃论文俱乐部—在ACM Survey闲逛是什么体验
- 手写事件发布订阅框架
猜你喜欢
Shell脚本——Shell编程规范及变量
英语 | Day15、16 x 句句真研每日一句(从句断开、修饰)
True math problems in 1959 college entrance examination
ByteVCharts可视化图表库,你想要的我都有
详解牛客----手套
RTKLIB 2.4.3源码笔记

Project framework of robot framework
NVIDIA graphics card driver error

English | day15, 16 x sentence true research daily sentence (clause disconnection, modification)

ACL 2022 | dialogved: a pre trained implicit variable encoding decoding model for dialogue reply generation
随机推荐
groutine
Installation and management procedures
Redis docker installation
Detailed explanation of Niuke - Gloves
◰GL-阴影贴图核心步骤
AIOT产业技术全景结构-数字化架构设计(8)
Linux MySQL data timing dump
Dlib of face recognition framework
org. apache. parquet. schema. InvalidSchemaException: A group type can not be empty. Parquet does not su
博士申请 | 厦门大学信息学院郭诗辉老师团队招收全奖博士/博后/实习生
Installing labellmg tutorial in Windows
STM32__03—初识定时器
Copy constructor shallow copy and deep copy
∑GL-透视投影矩阵的推导
正则过滤内网地址和网段
Detailed explanation of the penetration of network security in the shooting range
JSON deserialize anonymous array / object
Aiot industrial technology panoramic structure - Digital Architecture Design (8)
Paging SQL
Idea of batch manufacturing test data, with source code