当前位置:网站首页>Shell script -- shell programming specification and variables
Shell script -- shell programming specification and variables
2022-04-23 16:57:00 【Kiro Jun】
Shell Programming specifications and variables
One 、Shell Script Overview
1.1.1 Shell Basic concepts
- Save the commands to be executed in order to a text file
- Give the file executable permissions
- It can combine all kinds of Shell Control statements to perform more complex operations
1.1.2 Shell Script application scenarios
- Repetitive operations
- Interactive tasks
- Batch transactions
- Service running status monitoring
- Scheduled task execution
1.1.3 Shell effect —— The interpreter
shell It's a special application , It lies between the operating system kernel and the user , Acting as a “ command interpreter ” Role , Be responsible for receiving and interpreting the operation instructions input by the user , Pass the operation to be performed to the kernel for execution , And output the execution result .
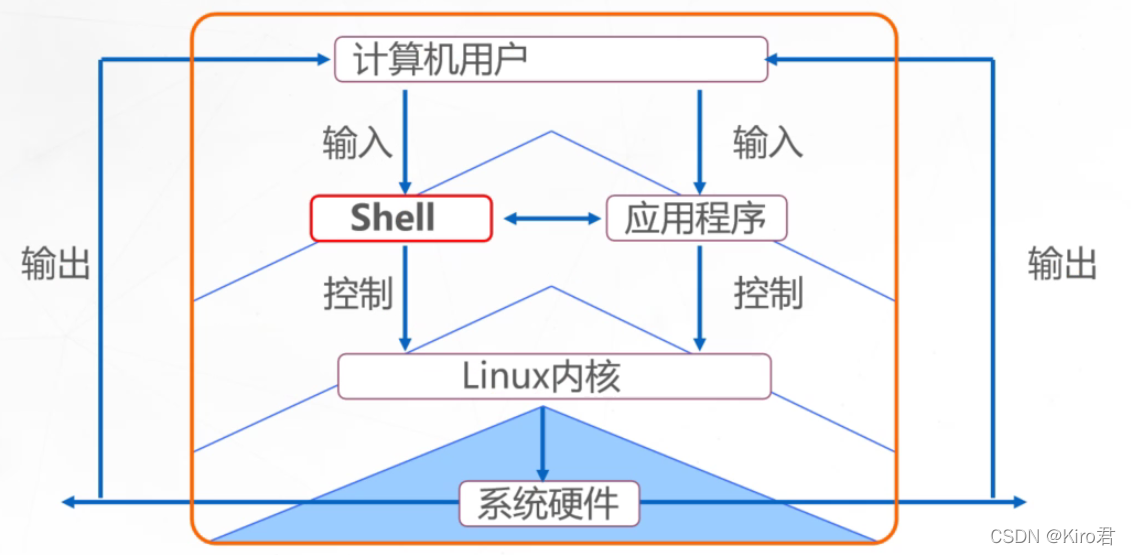
Two 、shell Programming specification
2.1 The user login shell
- After logging in, the default shell Program , It's usually /bin/bash
- Different shell The internal instructions of 、 The operating environment will be different

| shell | explain |
|---|---|
| bash | $ Base on GNU Developed under the framework of shell |
| csh | The grammar is a bit similar to C Linguistic shell |
| tcsh | Integrated csh, More features ( Enhanced version ) |
| sh | Has been bash Replaced by ( Soft link ) |
| nologin | strange shell, This shell It can prevent users from logging in to the host |
2.2 shell The composition of the script
- Script statement ( Interpreter ): If the first act “#!/bin/bash”, Indicates that the code statement below this line is passed /bin/bash Program to execute ,#!/bin/bash Is the default interpreter , There are other types of interpreters , such as #!/usr/bin/python、#!/usr/bin/expect.
- Annotation information : With “#” The opening statement is expressed as a comment message , The annotated statement will not be executed when the script is run .
- Executable statement : such as echo command , For output “ ” String between .

2.3 shell How to execute the script
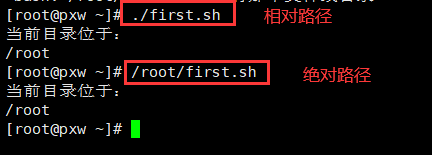
Method 1 : Command to specify the path , It is required that the document must have x jurisdiction
- Specify the absolute path :/root/first.sh
- Specify the relative path :./first.sh
Method 2 : Appoint shell To explain the script , It is not required that the document must have x jurisdiction
- sh Script path :sh first.sh
- source Script path :.first.sh perhaps source first.sh
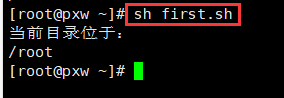
Method 3 :source Script path execution shell Script

2.4 Script error
Wrong command : Command error will not affect the next command to continue
Grammar mistakes : Will affect the next command to continue
Logic error : You can only screen yourself
Find the correct code :
bash -n Script name ( Do not add an absolute path to the current directory ) Check for grammatical errors
bash -x Script name ( Do not add an absolute path to the current directory ) Check for logic errors
2.5 Redirect
Interactive hardware devices
The standard input : Receiving data input from the user from the device
standard output : Output data to the user through the device
The standard error : Report execution error information through this device
| type | Device file | Document description number | Default device |
|---|---|---|---|
| The standard input | /dev/stdin | 0 | keyboard |
| standard output | /dev/stdout | 1 | Monitor |
| Standard error output | /dev/stderr | 2 | Monitor |
Redirection operation
| type | operation | purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Redirect input | < | Read data from the specified file |
| Redirect output | > | Save the standard output results to the specified file , And overwrite the original file |
| >> | Appends the standard output to the end of the specified file , Don't cover the original content | |
| Standard error output | 2> | Save the error message to the specified file , And overwrite the original file |
| 2>> | Append the error message to the end of the specified file , Don't cover the original content | |
| Mixed output | &> and 2>&1 | Standard output , The standard error is saved to the same — In file |
Case a
Put the standard output result “132456” Save to file passwd.txt; Then enter the standard password to niangao When , From the specified file passwd.txt Read data from :

Case 2
“>” It will cover the original file
“>>” The original file will not be overwritten

Case three :& usage
2>/dev/null ## Output the error to the black hole
>/dev/null 2>&1 ## Redirect standard output to black hole , Error output 2 Redirect to standard output ( Both standard output and error output go to black hole )
2>&1>/dev/null ## Error output redirected to standard output , Standard output into black hole


Add

2.6 Pipeline operation
The pipe symbol “|” The command output on the left , As input to the command on the right ( Deal with people ), Multiple pipes can be used in the same command line
Use format :
cmd1 command 1 | cmd2 command 2[… | cmdn command n]
Pipeline operation

awk -F: '{print $1,$3}' ## It means to force the output of information and print the first and third Columns

3、 ... and 、Shell Script variables
Various Shell It is used in the environment “ Variable ” The concept of .Shell Variables are used to store specific parameter values that the system and users need to use .
Role of variables
It is used to store specific parameters that the system and users need to use ( value )
Variable name : Use a fixed name , Preset by the system or defined by the user
A variable's value : According to the user settings 、 The system changes with the change of environment
The type of variable
Custom variable : Customized by user 、 Modify and use
Special variables : environment variable , A read-only variable , Positional variable , Predefined variables
environment variable : Maintained by system , Used to set up the work environment
A read-only variable : Used when the variable value cannot be modified
Positional variable : Pass parameters to the script through the command line
Predefined variables :bash A class of variables built into , Cannot be modified directly
3.1 Custom variable
1. Define new variables :
Format : Variable name = A variable's value
[root@pxw ~]# product=c++
2. View the value of the defined variable :
Format :echo $ Variable name
[root@pxw ~]# version=3.5.1

3. Special operation of variable assignment
| quotes | explain |
|---|---|
| Double quotes | Allowed to pass through $ Symbols refer to other variables |
| Single quotation marks | Do not reference other variable values ,$ Treat as normal characters |
| Apostrophe | Command substitution , Extract the output of the command after execution |

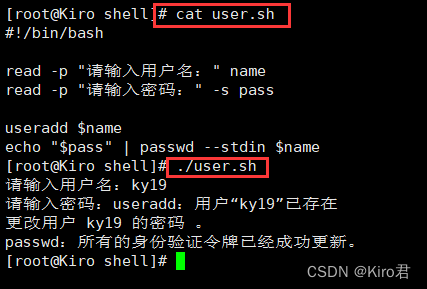
4.read command
-------- Method 1 :read Command to get input ---------
read [-p " Prompt information "] Variable name
echo $ Variable name
[root@pxw ~]# echo 192.168.61.128 > ip.txt
[root@pxw ~]# read -p "input your IP" < ip.txt
[root@pxw ~]# echo $IP
192.168.100.10
-------- Method 2 : Write... In a script , Implement... On the command line read obtain ---------
read Variable name
echo $ Variable name
Method 1 :
Method 2 :


5. Set the scope of the variable
export Variable name = Variable

3.1.1 Operation of numerical variables
Operator :+ Add 、- Subtraction 、* Multiplication 、/ division 、% Remainder
expr Variable 1 Operator Variable 2
var=$(expr Variable 1 Operator Variable 2)
var=$(( Variable 1 Operator Variable 2))
var=$[ Variable 1 Operator Variable 2]
let var= Variable 1 Operator Variable 2
i++ amount to i=$[$i + 1],i++ Is the assignment first , Re operation
i-- amount to i=$[$i - 1],++i Is to calculate first and then assign value
i+=1 amount to i=$[$i + 1]
---- expand -----
[root@Kiro shell]# expr $[2 * 2] ## You can use the normal operator directly in brackets
Case a : The remainder only needs the remainder after division
# Law 1
[root@localhost data]#expr 3 % 2
1
# Law two : Defining variables , Use the apostrophe
[root@Kiro shell]# sum=`expr $X + $X + $Y`
[root@Kiro shell]# echo $sum
301

Case 2 : Extension of multiplication sign


Case three : Script

3.2 environment variable
Environment variable refers to the environment variable generated by Linux A type of variable created by the system in advance , It is mainly used to set the user's working environment , Include user host Directory 、 Command to find the path 、 User current directory 、 Login terminal, etc . The environment variable consists of Linux Automatic system maintenance , It will change with the change of user state :
- If after modification ,(uname) , Restart to restore the original ;
- Or copy the previous one and assign the variable directly
adopt env Command to view , It's all set :
HOSTNAME=Kiro
SHELL=/bin/bash
HISTSIZE=1000
USER=root
PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin
PWD=/root/shell

Case study :

3.3 Positional variable
In order to use Shell Script program , It is convenient to provide parameters through the command behavior program ,bash The concept of position variable is introduced .
[root@Kiro shell]# cat vars.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo $1
echo $2
echo $3
[root@Kiro shell]# ./vars.sh 11 22 cc
11
22
cc
Case study :

3.4 Predefined variables
And defining variables is bash A special class of pre-defined variables , Can only be used and cannot create new :
$# : Indicates the number of positional parameters in the command line
$*: Represents the contents of all unknown parameters
$?: Indicates the return status after the execution of the previous command , by 0 The execution is correct , Not 0 Indicates an exception occurred during execution ;
$0: Indicates the name of the currently executing script or program
$$: Indicates the process number of the current script
Case study :

3.5 Use awk Value extraction IP value
[root@Kiro shell]# ip=`ifconfig ens33|awk /netmask/'{print $2}'`
[root@Kiro shell]# echo $ip
192.168.61.100
3.6 Global and local variables
- Global variables
For global variables export
[root@Kiro ~]# export Y=22
[root@Kiro ~]# echo $Y
22

- Local variables
Local variables are only currently valid
[root@Kiro ~]# a=100
[root@Kiro ~]# echo $a
100
[root@Kiro ~]# exit
exit
[root@Kiro ~]# echo $a

Can be found in pstree Look at the sub variables in
【 expand 】
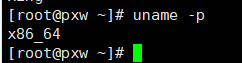
- uname -p ## Query processor model
- /dev/null ## empty , Error output can be put in
- Command line input “bc”==Linux The computer


- permanent /etc/profile

版权声明
本文为[Kiro Jun]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204231652526221.html
边栏推荐
- 批量制造测试数据的思路,附源码
- Calculation formula related to tolerance analysis
- Introduction to new functions of camtasia2022 software
- 【题解】[SHOI2012] 随机树
- PHP高效读大文件处理数据
- Blue Bridge Cup provincial road 06 -- the second game of the 12th provincial competition
- 面试百分百问到的进程,你究竟了解多少
- 信息摘要、数字签名、数字证书、对称加密与非对称加密详解
- Expression "func" tSource, object "to expression" func "tSource, object" []
- Grpc gateway based on Ocelot
猜你喜欢
Use itextpdf to intercept the page to page of PDF document and divide it into pieces

ACL 2022 | dialogved: a pre trained implicit variable encoding decoding model for dialogue reply generation
Nacos + aspnetcore + Ocelot actual combat code
Path environment variable

TypeError: set_ figure_ params() got an unexpected keyword argument ‘figsize‘
![[pimf] openharmony paper Club - what is the experience of wandering in ACM survey](/img/b6/3df53baafb9aad3024d10cf9b56230.png)
[pimf] openharmony paper Club - what is the experience of wandering in ACM survey
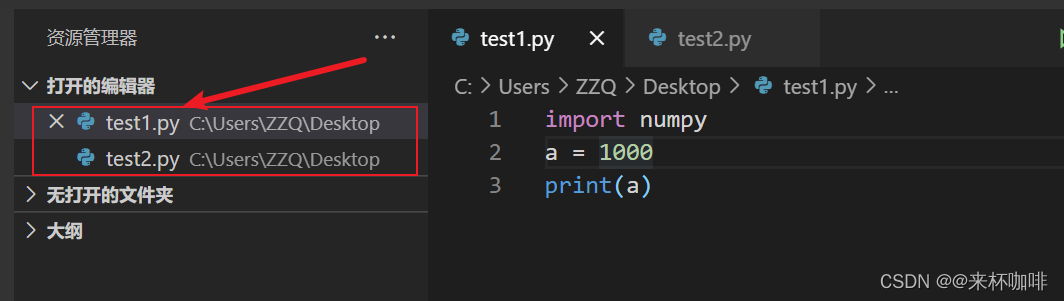
How vscode compares the similarities and differences between two files

Installation and management procedures
SQL database
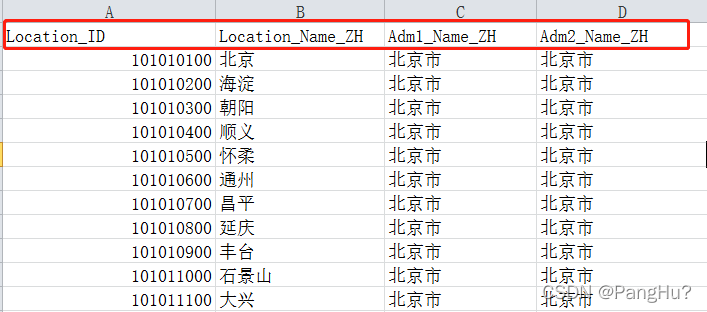
Easyexcel reads the geographical location data in the excel table and sorts them according to Chinese pinyin
随机推荐
First knowledge of go language
Paging the list collection
STM32__03—初识定时器
自定义my_strcpy与库strcpy【模拟实现字符串相关函数】
Sub database and sub table & shardingsphere
ACL 2022 | dialogved: a pre trained implicit variable encoding decoding model for dialogue reply generation
Zhimeng dedecms security setup Guide
How vscode compares the similarities and differences between two files
计算饼状图百分比
UWA Pipeline 功能详解|可视化配置自动测试
Do you really understand the principle of code scanning login?
Real time operation of vim editor
Node access to Alipay open platform sandbox to achieve payment function
Server log analysis tool (identify, extract, merge, and count exception information)
扫码登录的原理你真的了解吗?
SQL database
Decimal format decimal / datetime conversion processing
Encapsulating the logging module
Paging SQL
Disk management and file system