当前位置:网站首页>PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL
2022-04-23 19:12:00 【Blocking rain G】
SQL standard
- ISO/IEC 9075:1992, abbreviation SQL92, It's the most versatile SQL standard .
- PostgreSQL Very close to SQL92 standard .
SQL Command type
- DML:Data Manipulation Language, Data operation language :. Additions and deletions .
- DDL:Data Definition Language, Data definition language . Structural control .
- DCL:Data Control Language, Data control language . Access control .
ordinary SQL command
- Build table
create table test_table(
id serial,
name varchar(64)
);
- Insert
insert into test_table (id, name) values (1,'lanluyu');
insert into test_table values (1,'lanluyu');
- Delete
delete from tableName where columnName= 'value';
-- Delete all table data , Can't recover
truncate table tableName;
- modify
update tableName set column1 = 'newValue1',column2='newValue2' where columnN = 'valueN'
- Inquire about
select id, name from test_table;
Catalog
What this document covers :
- data type
- Multi meter operation
- Business
- Modify table structure
-
jurisdiction
- Foreign key constraints
data type
- bool Boolean
- 1 byte
- integer integer
- serial Automatically set to a unique number
- char Fixed length character array
- varchar Variable length character array
- date date
- numeric Positioning numbers
- numeric(7,2) Will store 7 Digit number ,2 Decimal place .
- PostgreSQL Extension type
- Binary big object (BLOB)
- Can be defined as bytea type (byte array)
bit
- bit(n)
- bit varying(n)
bool
drop table if exists test_bool;
create table test_bool(
val varchar(8),
flag bool
);
| Translated into true( Case insensitive ) | Translated into false |
|---|---|
| ‘1’ | ‘0’ |
| ‘yes’ | ‘no’ |
| ‘y’ | ‘n’ |
| ‘true’ | ‘false’ |
| ‘t’ | ‘f’ |
- Self testing
insert into test_bool values ('true',true);
insert into test_bool values ('1','1');
insert into test_bool values ('t','t');
insert into test_bool values ('Y','Y');
insert into test_bool values ('no','no');
insert into test_bool values ('f','f');
insert into test_bool values ('NULL',NULL);
insert into test_bool values ('FALSE','FALSE');
insert into test_bool values ('0','0');
insert into test_bool values ('n','n');
insert into test_bool values ('N','N');
-- If other values are inserted, an error will be reported
insert into test_bool values ('x','x');-- Report errors
Return results
| val (varchar) | flag (bool) |
|---|---|
| TRUE | TRUE |
| 1 | TRUE |
| t | TRUE |
| Y | TRUE |
| no | FALSE |
| f | FALSE |
| NULL | NULL |
| FALSE | FALSE |
| 0 | FALSE |
| n | FALSE |
| N | FALSE |
- bool operation (AND, OR,NOT)
select 'true'::bool and 'false'::bool aa;
value type
- smallint
- 2 byte
- int
- 4 byte
- bigint
- 8 byte
- numeric
- Lengthening
- real
- 4 byte
- double precision
- 8 byte
- serial
- int
- bigserial
- bigint
character ( Maximum 1GB)
-
char Single character
-
char(n) n Fixed length characters
-
varchar(n) n Variable length characters
-
text An unlimited length string
-
Numeric type
| subtypes | Standard name | describe |
|---|---|---|
| Small Integer | Smallint | 2 Byte sign integer ,-32768~32767 |
| Integer | Int | 2 Byte sign integer ,-2147483648~2147483647 |
| Serial | and int equally | |
| float | float(n) | The minimum accuracy supported is n, Store the most 8 Floating point number of bytes |
| float8 | real | Double precision (8 byte ) Floating point number |
| numeric | numeric(p,s) | Have p A real number ,s Decimal place , Always an exact number , Less efficient than floating point numbers |
| decimal | ||
| money | numeric(9,2) | pg Unique type , In the later version, it has been cancelled |
numeric(5,2) It can only store 999.99
Time type
| Definition | significance |
|---|---|
| date | Store date information |
| time | Store time information |
| timestamp | Store date and time |
| interval | Storage timestamp The difference between |
| timestamptz | Store the data that contains the time zone timestamp |
Special data types
| Definition | significance |
|---|---|
| box | rectangular |
| line | A set of points |
| point | A pair of geometric numbers |
| lseg | A line segment |
| polygon | A closed geometric line |
| cidr or inet | One IPv4 The address of , entry 192.168.0.1 |
| macaddr | MAC Address |
Array
create table test_array(
label varchar(32),
val int[]
);
insert into test_array values
('val01','{1,0,2,4}');
insert into test_array values
('val02','{1,0,2,4,5}');
select * from test_array;
-- result
-- label val
-- val01 {1,0,2,4}
-- val02 {1,0,2,4,5}
select val[3] from test_array where label='val02';
select val[1:2] from test_array where label='val02';
Be careful pg The subscript of is from 1 At the beginning , instead of 0;
- Two ways of strong rotation
select cast(val[3] as varchar(8)) from test_array where label='val02';
select val[3]::varchar(8) from test_array where label='val02';
Magic variable
- CURRENT_DATE
- CURRENT_TIME
- CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
- CURRENT_USER
select current_date,current_time,current_timestamp,current_user;
Return results
| current_date | current_time | current_timestamp | current_user |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2021/7/10 | 13:56:18.853743+08:00 | 2021-07-10 13:56:18.853743+08 | postgres |
Blob type
create table test_blob(
id varchar(64),
image bytea
);
The compound type ( Custom type )
-- Custom type
create type inventory_item as (
name varchar(64),
id int,
price numeric
);
create table on_hand(
item inventory_item,
count int
);
insert into on_hand values (
'("lanluyu",28,1.1)', 1
);
select (item).name from on_hand;
Enumeration type
create type data_source_item as enum (
'MIMC_MobileNetWork',
'MIMC_FixedLineNetWork'
);
date
- PostgreSQL The use of date Output standard
- ISO-8601 Style output
- Output format :YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss.ssTZD
- for example : 2021-07-08 17:05:30.23+5 Express 2021 year 7 month 8 At 5:05 p.m. on the th 30.23 second , Time zone in UTC Five hours ago .
- Input
- String form
- for example :2005 year 2 month 1 Japan
- ‘2005-02-01’、‘2005/02/01’、‘2005 02 01’、‘2005|02|01’、‘2005.02.01’
- ‘February 1,2005’
- Set the date format
create table test_date(
day date
);
insert into test_date values ('2005-02-01');
insert into test_date values ('2005/02/01');
insert into test_date values ('2005 02 01');
insert into test_date values ('2005|02|01');
select cast('2021-07-08 12:00:11:30.23+5' as date);
select cast('2021-07-08' as date);
// timestamp type
select cast('2021-07-08' as timestamp);
insert into test_date VALUES ('2021-06-08');
insert into test_date VALUES ('2021-07-08');
select * from test_date where date_part('month', day)=7;
-- result :2021-07-08
-- Comparison date
select * from test_date where day <> cast('2021-07-08' as date);
-- result :2021-06-08
insert into test_date VALUES (DATE'01/02/03');
-- 2001-02-03
show datestyle;
-- ISO, YMD
set datestyle = MDY;
insert into test_date VALUES (DATE'01/02/03');
-- 2003-01-02
insert into test_time VALUES (TIME'10:20:02');
insert into test_time VALUES (TIMESTAMP'01/02/03 10:20:02');
The part that can be extracted (date_part The first parameter )
- Year
- Month
- Day
- Hour
- Minute
- Second
select now(),CURRENT_TIMESTAMP;
Subtracting time will get days
select now() - day from test_date
-- 32 days 09:55:20.966894
Multi meter operation
Table correlation
select columns from tableA a, tableB b where a.id = b.id
-- tableName as t perhaps tableName t Alias the table
Can also be transformed into :
select columns from tableA a Join tableB b on (a.id = b.id)
Union and Union all
-- union all No weight removal
-- union duplicate removal
select columns from tableA
union( perhaps union all)
select columns from tableB
In general use union all
Self join
-- Self test environment
create table part(
id int,
name varchar(32),
part_id int
);
insert into part values(1, 'table and chairs',null);
insert into part values(2, 'table',1);
insert into part values(3, 'chair',1);
-- Self join
select p1.name as name1, p2.name as name2 from part p1, part p2
where p1.id = p2.part_id;
Table joins
- Left connection
left join- return : Left table and common part
- The right connection
right join- return : Right table and public part
- Internal connection
inner join- return : Common part
intersect Return to the same line
select empno,ename,job,sal,deptno
from emp
where (ename,job,sal) in (
select ename,job,sal from emp
intersect
select ename,job,sal from V
)
Find a value that is not in another table
select deptno from dept
except
select deptno from emp;
select deptno from dept where deptno not in (select deptno from emp)
to update
update emp
set sal = sal * 1.2
where exists ( select 1
from emp_bonus
where emp.empno = emp_bonus.empno
)
Above select null and select * stay exists Have a consistent role in
Data interaction
Insert special characters
insert into tableName values ('O\'Rourke','Street A\\33');
-- Insert O'Rourke,Street A\33
Check all table names
select * from pg_tables;
Create sequence
create sequence test_seq;
Production value
select nextval('test_seq');
select nextval('test_seq');
-- 1
-- 2
Set the value
select setval('test_seq',1);
copy command (psql The command does not need to add “;”)
\copy tableName from 'filePath'
\copy tableName from 'filePath' using delimiter ','
Update through another table
update tableA set columnA = b.columnB from tableB b
Business
A unit consisting of a finite sequence of database operations
- Purpose
- Recover from failure ;
- Multi client isolation .
- Properties of the transaction (ACID)
- Atomicity (Atomicity): The transaction is executed as a whole , The operations on the database contained in it are either all performed , Either not .
- Uniformity (Consistency): Transactions should ensure that the state of the database changes from one consistent state to another . Consistent state means that the data in the database should meet the integrity constraints .
- Isolation, (Isolation): When multiple transactions are executed concurrently , The execution of one transaction should not affect the execution of other transactions .
- persistence (Durability): Changes made to the database by committed transactions should be persisted in the database .
select * from test_date;
-- Start a transaction , perhaps BEGIN TRANSACTION;
begin;
-- Limited operations
delete from test_date where day='2021-02-03';
-- Transaction confirmation
commit;
-- Transaction rollback
ROLLBACK;
- Use the dwell point
begin;
-- Use the dwell point
SAVEPOINT savepoint_name; -- Make a statement savepoint
-- Limited operations
delete from test_date where day='2021-02-03';
ROLLBACK TO savepoint_name; -- Roll back to savepoint
RELEASE SAVEPOINT savepoint_name; -- Delete the specified retention point
-- Transaction confirmation
commit;
-- Transaction rollback
ROLLBACK;
When an error occurs during the execution of a limited number of transactions , The database operation cannot continue , Can only commit perhaps rollback.
lock
Prevent users from damaging the consistency of the database
- Exclusive lock EXCLUSIVE
- Other transactions cannot be on it
ReadAndmodify
- Other transactions cannot be on it
- Shared lock SHARE
- Can be read by other transactions , But it can't be modified
-- Grammatical form
LOCK [ TABLE ]
name
IN
lock_mode
- lock_mode
- ACCESS SHARE
- Only with Access Exclusive Lock mode conflict .
- Query command (Select command) Will get... On the table it queries Access Shared lock , In a general way , Any read-only query operation on the table will acquire this type of lock .
- ROW SHARE
- And Exclusive and Access Exclusive Lock mode conflict .
- Select for update and Select for share Command will get this type of lock , And all are quoted but not for update I'll add... To my watch Access Shared lock .
- ROW EXCLUSIVE
- And Share,Shared Row Exclusive,Exclusive,Access Exclusive Pattern conflict .
- Update/Delete/Insert Command will obtain this type of lock on the target table , And add... To other referenced tables Access Share lock , In a general way , Commands to change table data will be obtained on this table Row Exclusive lock .
- SHARE UPDATE EXCLUSIVE
- Share Update Exclusive,Share,Share Row Exclusive,Exclusive,Access exclusive Pattern conflict , This pattern protects a table from concurrent schema changes and changes Vacuum.
- Vacuum(without full),Analyze and Create index concur-ently Command will get this type of lock .
- SHARE
- And Row Exclusive,Shared Update Exclusive,Share Row Exclusive,Exclusive,Access exclusive Lock mode conflict , This mode protects the data of a table from concurrent changes .
- Create index Command will get this lock mode .
- SHARE ROW EXCLUSIVE
- And Row Exclusive,Share Update Exclusive,Shared,Shared Row Exclusive,Exclusive,Access Exclusive Lock mode conflict .
- whatever PostgreSQL The command does not automatically acquire this type of lock .
- EXCLUSIVE
- And ROW Share , Row Exclusive, Share Update Exclusive, Share , Share Row Exclusive, Exclusive, Access Exclusive Pattern conflict , This lock mode can only be used with Access Share Mode concurrency , let me put it another way , Only read operations can and hold Exclusive Lock transaction parallelism .
- whatever PostgreSQL The command does not automatically acquire this type of lock .
- ACCESS EXCLUSIVE
- Conflicts with all mode locks (Access Share,Row Share,Row Exclusive,Share Update Exclusive,Share , Share Row Exclusive,Exclusive,Access Exclusive), This mode ensures that only one person currently accesses this table ;ALTER TABLE,DROP TABLE,TRUNCATE,REINDEX,CLUSTER,VACUUM FULL Command will get this type of lock , stay Lock table In command , If no other mode is declared , It is also the default mode .
- ACCESS SHARE
Detailed view :https://blog.csdn.net/greywolf0824/article/details/85072530
begin;
-- The lock will not be released until the transaction ends
LOCK TABLE test_date IN EXCLUSIVE MODE;
Modify table structure
- Add fields
alter table tableName add column columnName columnType;
- Delete fields
alter table tableName drop column columnName;
- Change the field name
alter table tableName rename column oldColumnName to newColumnName;
- Change field type
alter table tableName columnName type newType[using expression];
- Change the default value
alter table tableName alter column [set DEFAULT value | drop default];
- Change constraint
alter table tableName alter column [set not null | drop not null];
alter table tableName add check check_express;
alter table tableName add constraint name constraint_define;
- Modify the distribution key
alter table tablename set DISTRIBUTED BY (columnname);
- View primary key
select pg_constraint.conname as pk_name from pg_constraint;
- Delete primary key
alter table tablename drop constraint primaryname
- Add a new primary key
alter table dic_protocol_info add constraint dic_protocol_info_pkey primary key (no);
- Combined the primary key
alter table rds_source_define add constraint rds_source_define_pkey PRIMARY KEY ("sourceno", "field_name");
- Change the name of the watch
alter table oldTableName rename to newTableName;
- Delete table
drop table tableName;
jurisdiction
stay PostgreSQL in , Permissions are divided into the following categories :
- SELECT
- INSERT
- UPDATE
- DELETE
- TRUNCATE
- REFERENCES
- TRIGGER
- CREATE
- CONNECT
- TEMPORARY
- EXECUTE
- USAGE
GRANT grammar
GRANT The basic syntax of the command is as follows :
GRANT privilege [, ...]
ON object [, ...]
TO { PUBLIC | GROUP group | username }
- privilege − The value can be :SELECT,INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE, RULE,ALL.
- object − The name of the object to grant access to . Possible objects are : table, view,sequence.
- PUBLIC − Represents all users .
- GROUP group − Grant permissions to user groups .
- username − User name to grant permission .PUBLIC Is a short form representing all users .
in addition , We can use REVOKE Command to cancel permission ,REVOKE grammar :
REVOKE privilege [, ...]
ON object [, ...]
FROM { PUBLIC | GROUP groupname | username }
-- Create user
CREATE USER lanluyu WITH PASSWORD 'password';
-- Assign permissions
GRANT ALL ON test_date TO lanluyu;
-- Revocation of authority
REVOKE ALL ON test_date FROM lanluyu;
-- Delete user
DROP USER lanluyu;
Foreign key constraints
create table test_names(
id serial,
name varchar(32),
constraint names_pk primary key (id)
);
create table test_references(
no serial,
id integer,
constraint ref_id_fk foreign key (id) references test_names(id)
);
insert into test_names values (default, '1');
insert into test_names values (default, '2');
select * from test_names;
insert into test_references values (default, 1);
-- error : stay "test_names" The update or delete operation on violates the "test_references" Foreign key constraints on "ref_id_fk"
-- DETAIL: Key value pair (id)=(1) Still from the table "test_references" Refer to the .
delete from test_names where id=1;
-- success
delete from test_names where id=2;
Delay constraint
Allow violations of foreign key constraints
create table test_references(
no serial,
id integer,
constraint ref_id_fk foreign key (id) references test_names(id) initially deferred
);
ON UPDATE and ON DELETE
Delete primary key , The corresponding foreign key line will also be deleted
create table test_references(
no serial,
id integer,
constraint ref_id_fk foreign key (id) references test_names(id) on delete cascade
);
Delete primary key , The foreign key column will be set to null
create table test_references(
no serial,
id integer,
constraint ref_id_fk foreign key (id) references test_names(id) on update set null
);
Use a combination of
create table test_references(
no serial,
id integer,
constraint ref_id_fk foreign key (id) references test_names(id) on delete cascade on update set null
);
View
Definition : A virtual table exported from one or more tables ;
View( View ) It's a fake watch , It's just one that's stored in the database by the relevant name PostgreSQL sentence .
-
advantage :
-
- Simplified operation ;
- Security , Only the specified data can be seen ;
- Logical independence .
-
-
shortcoming :
- Poor performance
- Modify restrictions
-
Create view
create view viewName as select-statement;
- Use view
select * from viewName;
\d viewNameYou can view the view description
- Delete view
drop view viewName;
- Replace view
create or replace view viewName as select-statement;
Window function
SELECT depname, empno, salary,
rank() OVER (PARTITION BY depname ORDER BY salary DESC)
FROM empsalary;
pg Window command
| command | describe |
|---|---|
| ? | Get help messages |
| \do | List operation types |
| \dt | List tables |
| \dT | List types |
| \h | List SQL The order of |
| \i | Execute... In the file sql |
| \r | Reset buffer ( Ignore any input ) |
| \q | sign out psql |
| \c databaseName | Switch database |
| \d+ tableName | Table structure |
| \! | stay pg Window execution shell command |
版权声明
本文为[Blocking rain G]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204210601215436.html
边栏推荐
- SQL常用的命令
- Accessing private members using templates
- MySQL restores or rolls back data through binlog
- Customize the non slidable viewpage and how to use it
- Tencent cloud GPU best practices - remote development training using jupyter pycharm
- Scrollto and scrollby
- MySQL学习第五弹——事务及其操作特性详解
- c#:泛型反射
- SQL of contention for system time plus time in ocrale database
- 微搭低代码零基础入门课(第三课)
猜你喜欢
redis优化系列(三)解决主从配置后的常见问题
![[报告] Microsoft :Application of deep learning methods in speech enhancement](/img/29/2d2addd826359fdb0920e06ebedd29.png)
[报告] Microsoft :Application of deep learning methods in speech enhancement
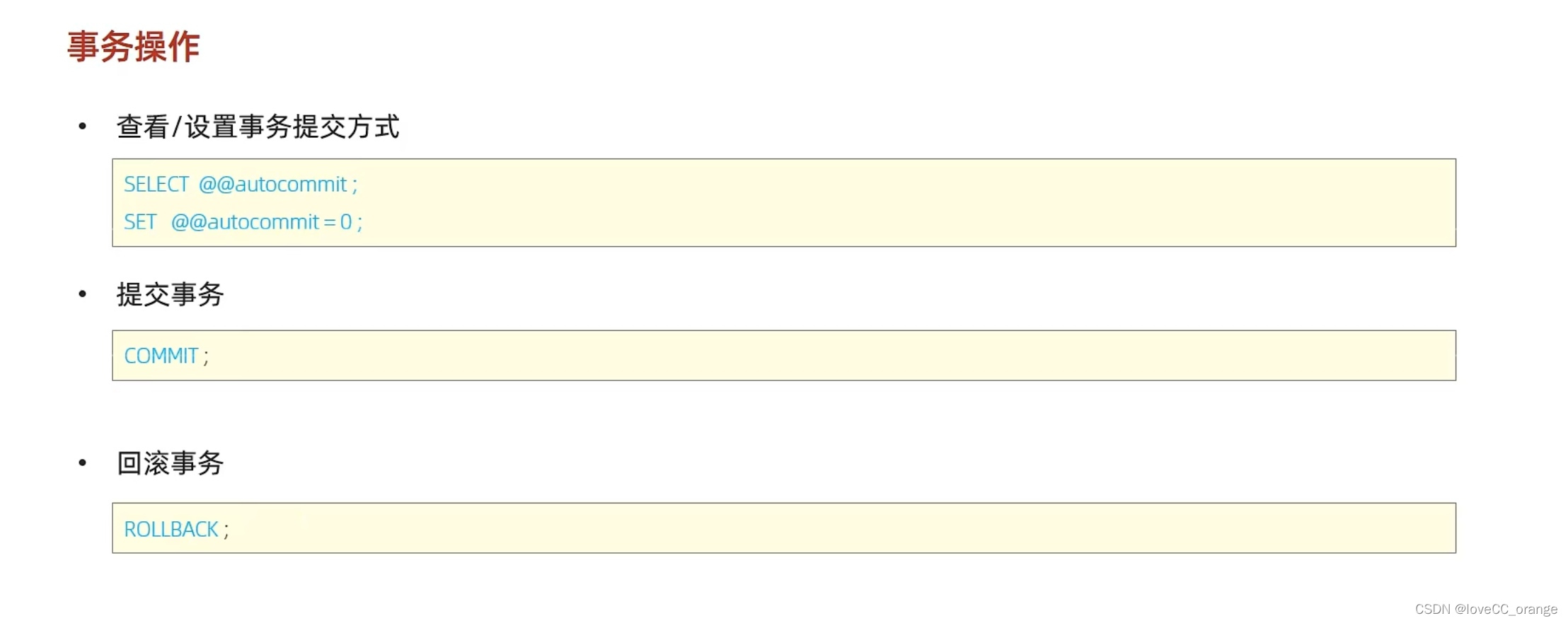
The fifth bullet of MySQL learning -- detailed explanation of transaction and its operation characteristics
浅谈c语言指针的强制转换

MySQL restores or rolls back data through binlog

为何PostgreSQL即将超越SQL Server?
Simple use of navigation in jetpack
Solutions such as unknown or garbled code or certificate problem prompt in Charles's mobile phone packet capture, actual measurement.
ArcMap连接 arcgis server
Partage de la conception de l'alimentation électrique de commutation et illustration des compétences en conception de l'alimentation électrique
随机推荐
I just want to leave a note for myself
为何PostgreSQL即将超越SQL Server?
Using Visual Studio code to develop Arduino
openlayers 5.0 热力图
[today in history] April 23: the first video uploaded on YouTube; Netease cloud music officially launched; The inventor of digital audio player was born
【历史上的今天】4 月 23 日:YouTube 上传第一个视频;网易云音乐正式上线;数字音频播放器的发明者出生
简化路径(力扣71)
On the forced conversion of C language pointer
binlog2sql 工具安装使用及问题汇总
Use of fluent custom fonts and pictures
Click the input box to pop up the keyboard layout and move up
WebView opens H5 video and displays gray background or black triangle button. Problem solved
开关电源设计分享及电源设计技巧图解
[record] typeerror: this getOptions is not a function
The type initializer for ‘Gdip‘ threw an exception
OpenHarmony开源开发者成长计划,寻找改变世界的开源新生力!
Get a list of recent apps
[report] Microsoft: application of deep learning methods in speech enhancement
MySQL restores or rolls back data through binlog
Download xshell 6 and xftp6 official websites