当前位置:网站首页>Solution to the trial of ycu Blue Bridge Cup programming competition in 2021
Solution to the trial of ycu Blue Bridge Cup programming competition in 2021
2022-04-23 06:29:00 【cornivores】
2021 year YCU Blue Bridge Cup programming competition tryout problem solution ( In order of difficulty )
It may be the last time in the training team to participate in the topic ~
A: Simple check-in question
The question :

practice : There are two situations , Odd positions are odd and even positions are odd . Then judge by violence . Um. … I wanted to finish this problem by backhand counting odd numbers , As a result, a false check-in was sent , There is a situation 0 1 0 1 1, There is only one case of this , Just line up 1 0 1 0 1, So we have to judge the number of odd numbers to decide which one to choose .
Code :
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6+10;
int main() {
int n; scanf("%d", &n);
int x = 0, y = 0, cntj = 0;
for(int i = 1, a; i <= n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &a);
if(a & 1) {
++cntj;
if(i&1) ++x;
else ++y;
}
}
int res;
if(cntj * 2 == n) res = min(x, y);
else if(cntj * 2 < n) res = x;
else res = y;
printf("%d\n", res);
return 0;
}
B: Fried chicken is simply added
The question :

practice : Small scale violence , Send out directly 70 branch . about 1e18 Data partition method , It is divided into 1e18 individual 1, Separate two boards , The number of schemes separated by these two boards is the answer . The first board has a total of (n+1) A place to put , The second board is based on the first board (n+2) A place to put , Divided by 2( The sequence of the first board and the second board may be repeated ). You can find the answer is C n + 2 2 = ( n + 1 ) ( n + 2 ) 2 C_{n+2}^2=\frac{(n+1)(n+2)}{2} Cn+22=2(n+1)(n+2), But the best thing is to find the law and push the formula , You have to be careful in the middle. Ow ~
Code :
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define fio ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
#define lson rt<<1, l, mid
#define rson rt<<1|1, mid+1, r
#define PI acos(-1)
#define eps 1e-5
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pli;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pll;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
typedef map<char, int> mci;
typedef map<string, int> msi;
template<class T>
void read(T &res) {
int f = 1; res = 0;
char c = getchar();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') {
if(c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar(); }
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
res = res * 10 + c - '0'; c = getchar(); }
res *= f;
}
const int N = 1003;
const LL Mod = 998244353;
int main() {
LL n; scanf("%lld", &n);
LL x = n + 1, y = n + 2;
if(x&1) y /= 2;
else x /= 2;
x %= Mod; y %= Mod;
printf("%lld\n", x * y % Mod);
return 0;
}
C: Can't you avoid the date of the Blue Bridge Cup this time
The question :

practice : Direct violence .
Code :
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <fstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <deque>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const double Pi = acos(-1);
namespace io{
template <typename T> inline void read(T &x) {
x = 0; T f = 1;char s = getchar();
for(; !isdigit(s); s = getchar()) if(s == '-') f = -1;
for(; isdigit(s); s = getchar()) x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (s ^ 48);
x *= f;
}
template <typename T> inline void write(T x) {
if(x < 0) putchar('-'), x = -x;
if(x > 9) write(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
};
#define fio ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
#define _for(n,m,i) for (int i = (n); i < (m); ++i)
#define _rep(n,m,i) for (int i = (n); i <= (m); ++i)
#define _srep(n,m,i)for (int i = (n); i >= (m); i--)
#define _sfor(n,m,i)for (int i = (n); i > (m); i--)
#define ef(u, i) for(int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].next)
#define lson rt << 1, l, mid
#define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r
#define lowbit(x) x & (-x)
#define pii pair<int,int>
#define fi first
#define se second
int yue[] = {
0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int rn(int x) {
return (x % 4 == 0 && x % 100 != 0) || x % 400 == 0;
}
int main() {
int n = 1937, y = 1, r = 1, w = 5, ans = 0;
while(1) {
r = r % yue[y] + 1;
if(r == 1) {
y = y % 12 + 1;
if(y == 1) n++;
if(y == 2) {
if(rn(n)) yue[2] = 29;
else yue[2] = 28;
}
}
w = w % 7 + 1;
if(w == 1) ans++;
if(n == 2021 && y == 3 && r == 20) break;
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
answer :4394
D:01 maze
The question :
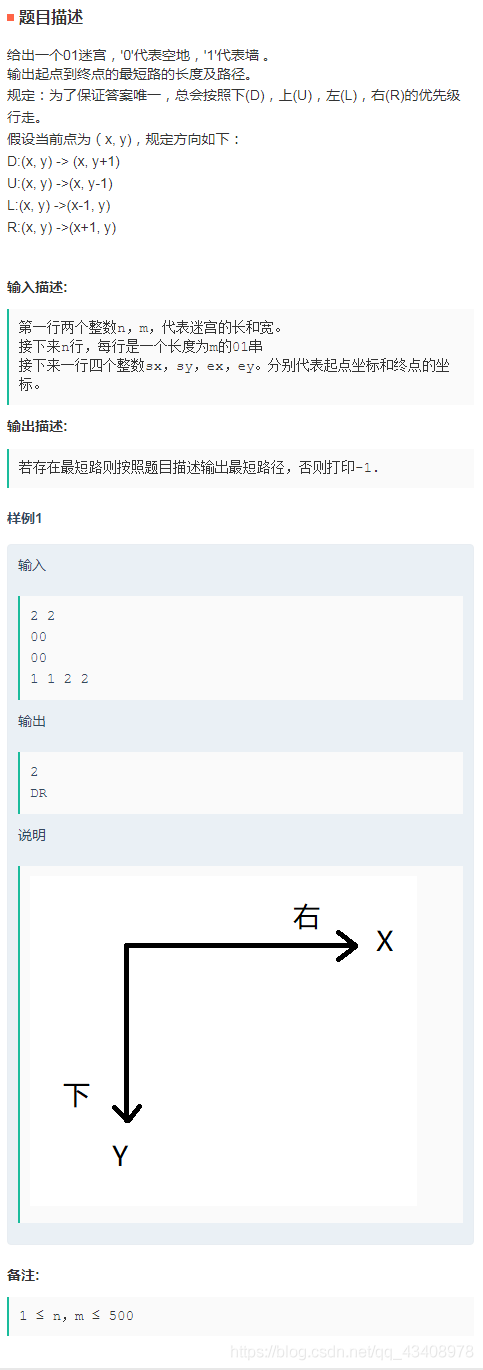
practice :BFS Search for + Path record . Maybe the starting point or the ending point is an obstacle , So direct output -1, Maybe the beginning is the end , Output 0 And an empty string .
Code :
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define fio ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
#define lson rt<<1, l, mid
#define rson rt<<1|1, mid+1, r
#define PI acos(-1)
#define eps 1e-5
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pli;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pll;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
typedef map<char, int> mci;
typedef map<string, int> msi;
template<class T>
void read(T &res) {
int f = 1; res = 0;
char c = getchar();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') {
if(c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar(); }
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
res = res * 10 + c - '0'; c = getchar(); }
res *= f;
}
const int N = 510;
const LL Mod = 998244353;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int ne[4][2] = {
0, 1, 0, -1, -1, 0, 1, 0};
string nec = "DULR";
int n, m;
char tu[N][N], pre[N][N];
int vis[N][N], dis = -INF;
int sx, sy, ex, ey, tx, ty;
struct xx {
int x, y, step; } u;
void bfs() {
if(tu[sx][sy] == '1') return;
queue<xx> q;
q.push(xx {
sx, sy, 0});
vis[sx][sy] = 1;
while(!q.empty()) {
u = q.front(); q.pop();
if(u.x == ex && u.y == ey) {
dis = u.step; break; }
for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
tx = u.x + ne[i][0]; ty = u.y + ne[i][1];
if(tx > 0 && tx <= n && ty > 0 && ty <= m && !vis[tx][ty] && tu[tx][ty] == '0') {
vis[tx][ty] = 1;
q.push(xx {
tx, ty, u.step+1});
pre[tx][ty] = nec[i];
}
}
}
}
void Print() {
// The output path
if(dis == -INF) {
puts("-1"); return ;
}
string res = "";
tx = ex; ty = ey;
int i;
while(tx != sx || ty != sy) {
res += pre[tx][ty];
i = nec.find(pre[tx][ty]);
tx -= ne[i][0]; ty -= ne[i][1];
}
reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
cout << dis << "\n" << res << "\n";
}
int main() {
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) scanf("%s", tu[i]+1);
scanf("%d %d %d %d", &sx, &sy, &ex, &ey);
memset(pre, '0', sizeof pre);
bfs(); Print();
return 0;
}
E: perseverance prevails
The question :

practice : The longest ascending subsequence template problem , There are three ways ,DP, Tree array , Two points , Can search in a small area .
Code :
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <climits>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
#define fio ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
#define _for(n,m,i) for (register int i = (n); i < (m); ++i)
#define _rep(n,m,i) for (register int i = (n); i <= (m); ++i)
#define lson rt<<1, l, mid
#define rson rt<<1|1, mid+1, r
#define PI acos(-1)
#define eps 1e-8
#define rint register int
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pli;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<double, int> pdi;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pll;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
typedef map<int, int> mii;
typedef map<char, int> mci;
typedef map<string, int> msi;
template<class T>
void read(T &res) {
int f = 1; res = 0;
char c = getchar();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') {
if(c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar(); }
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
res = res * 10 + c - '0'; c = getchar(); }
res *= f;
}
const int ne[8][2] = {
1, 0, -1, 0, 0, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1, -1, 1, 1, -1, 1, 1};
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 3e5+10;
const LL Mod = 1e9+7;
const int M = 1e6+10;
vector<int> a;
int main() {
int n; scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1, x, pos; i <= n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &x);
pos = lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin();
if(pos == a.size()) a.push_back(x);
else if(a[pos] > x) a[pos] = x;
}
printf("%d\n", a.size());
return 0;
}
F:Mex
The question :
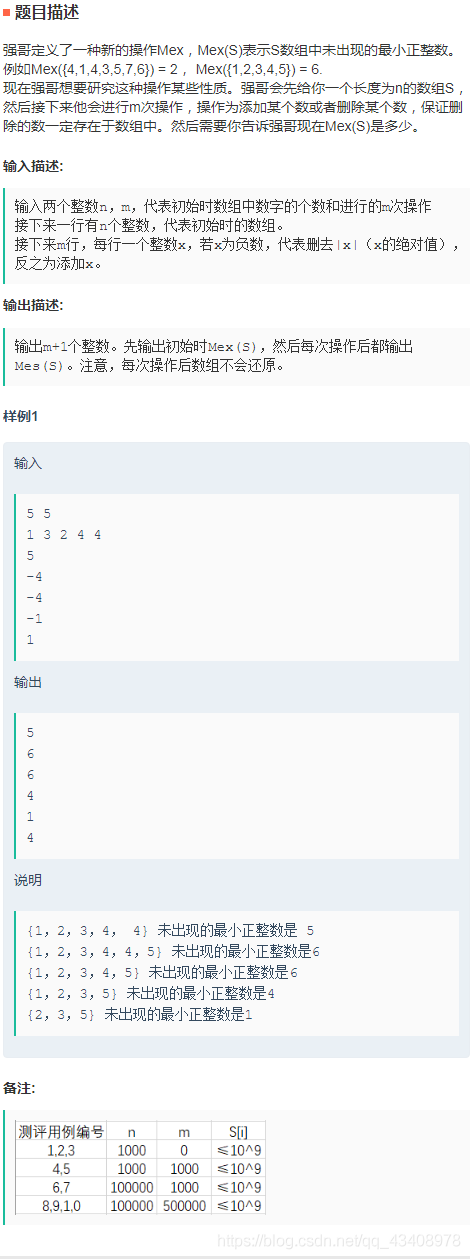
practice : Two points answer + Tree array . First, when this number is greater than or equal to n+m when , This number will be useless , So use a bucket , That is to say ton The array records less than or equal to n+m Number of occurrences of ,ton[x] representative x How many times has it appeared . According to the idea of reverse order of tree array , Tree array is used to maintain less than or equal to x How many different numbers are there , Then the answer can be divided into the following situations :
- Less than or equal to x-1 The different numbers are x-1 individual , So when ton[x] by 0 The answer is x.
- Less than or equal to x-1 The different numbers are x-1 individual , however ton[x] Not for 0, That is to say x( Include ) There have been numbers before , Then the answer must be x after .
- Less than or equal to x-1 There is no difference in numbers x-1 individual , That means the answer must appear in x front .
Code :
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <climits>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
#define fio ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
#define _for(n,m,i) for (register int i = (n); i < (m); ++i)
#define _rep(n,m,i) for (register int i = (n); i <= (m); ++i)
#define lson rt<<1, l, mid
#define rson rt<<1|1, mid+1, r
#define PI acos(-1)
#define eps 1e-8
#define rint register int
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pli;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<double, int> pdi;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pll;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
typedef map<int, int> mii;
typedef map<char, int> mci;
typedef map<string, int> msi;
template<class T>
void read(T &res) {
int f = 1; res = 0;
char c = getchar();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') {
if(c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar(); }
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
res = res * 10 + c - '0'; c = getchar(); }
res *= f;
}
const int ne[8][2] = {
1, 0, -1, 0, 0, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1, -1, 1, 1, -1, 1, 1};
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 6e5+10;
const LL Mod = 1e9+7;
const int M = 1e6+10;
int ton[N], b[N], n;
// Tree array
int lowbit(int x) {
return x&(-x); }
void Add(int p, int x) {
for(; p < N; p += lowbit(p)) b[p] += x;
}
int Sum(int p) {
int sum = 0;
for(; p; p -= lowbit(p)) sum += b[p];
return sum;
}
// Two points search
int binary_search() {
int l = 0, r = N, mid;
while(l <= r) {
mid = l + r >> 1;
if(Sum(mid-1) == mid-1) {
if(!ton[mid]) return mid;
else l = mid + 1;
} else r = mid - 1;
}
return N;
}
int main() {
int n, m, x;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &x);
if(x <= n + m) ++ton[x];
}
for(int i = 1; i < N; ++i) {
if(ton[i]) Add(i, 1);
}
printf("%d\n", binary_search());
while(m--) {
scanf("%d", &x);
if(x < 0) {
x = -x;
--ton[x];
if(!ton[x]) Add(x, -1);
} else {
++ton[x];
if(ton[x] == 1) Add(x, 1);
}
printf("%d\n", binary_search());
}
return 0;
}
G: Regular Fibonacci
The question :

practice : Matrix fast power .
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 3;
const int Mod = 998244353;
LL n, m;
struct Mar {
LL a[N][N];
Mar operator * (const Mar &m) {
Mar res;
res.init();
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < N; ++j) {
for(int k = 0; k < N; ++k) {
res.a[i][j] = (res.a[i][j] + this->a[i][k] * m.a[k][j] % Mod) % Mod;
}
}
}
return res;
}
void init(int f = 0) {
memset(a, 0, sizeof a);
// Initialize it to the identity matrix
if(f == 1) {
this->a[0][0] = this->a[1][1] = this->a[2][2] = 1;
}
// Initialize it as a construction matrix
if(f == 2) {
this->a[0][0] = this->a[0][1] = this->a[0][2] = this->a[1][0] = this->a[2][1] = 1;
}
// Initialize it to include Fibonacci matrix
if(f == 3) {
this->a[0][0] = 2;
this->a[2][0] = this->a[1][0] = 1;
}
}
};
Mar ksm(Mar m, LL k) {
Mar res;
res.init(1);
while(k) {
if(k & 1) res = res * m;
m = m * m;
k >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
int main() {
scanf("%lld", &n);
Mar m1, m2;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
scanf("%lld", &m);
m2.init(3);
if(m < 3) printf("%lld\n", m2.a[2-m][0]);
else {
m1.init(2);
printf("%lld\n", (ksm(m1, m-2)*m2).a[0][0]);
}
}
return 0;
}
版权声明
本文为[cornivores]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204210615591598.html
边栏推荐
- Cf6d lizards and fundamentals 2 problem solving
- H. Are You Safe? Convex hull naked problem
- Doomsday (simple computational geometry)
- 2. Average length of words
- Use of multithreaded executors
- Kibana search syntax
- 11.a==b?
- Troubleshooting of data deleted and reappeared problems
- Class loading and classloader understanding
- Rust 的多线程安全引用 Arc
猜你喜欢

Addition, deletion, query and modification of data
![[leetcode 401] binary Watch](/img/a5/538caf3a1a6143a47d79d947717554.png)
[leetcode 401] binary Watch
-- SQL query and return limit rows

SQL -- data definition
![Denoising paper - [noise2void, cvpr19] noise2void learning denoising from single noise images](/img/9d/487c77b5d25d3e37fb629164c804e2.png)
Denoising paper - [noise2void, cvpr19] noise2void learning denoising from single noise images

線性代數第一章-行列式

Database - sorting data
![Paper on Image Restoration - [red net, nips16] image restoration using very deep revolutionary encoder decoder networks wi](/img/1b/4eea05e2634780f45b44273d2764e3.png)
Paper on Image Restoration - [red net, nips16] image restoration using very deep revolutionary encoder decoder networks wi
![[leetcode 59] spiral matrix II](/img/6e/58e600272797563129d2b325a054b5.png)
[leetcode 59] spiral matrix II
Installation and usage skills of idea
随机推荐
Failure to deliver XID in Seata distributed transaction project
线程和进程的关系和区别是什么
scikit-learn sklearn 0.18 官方文档中文版
进程间通信的方式
Rainbow (DP)
MySQL table constraints and table design
Fundamentals of in-depth learning -- a simple understanding of meta learning (from Li Hongyi's course notes)
A general U-shaped transformer for image restoration
Algèbre linéaire chapitre 1 - déterminants
检测技术与原理
Explain of MySQL optimization
lambda expressions
Understanding and installing MySQL
JDBC operation transaction
[leetcode 202] happy number
Example of ticket selling with reentrant lock
Code neat way to learn
Consistent hash algorithm used for redis cache load balancing
Introduction to virtualization features
In depth understanding of the relationship between dncblevel and noise denoising in the paper