bitnami-docker-postgresql Warehouse
Source code :bitnami-docker-postgresql
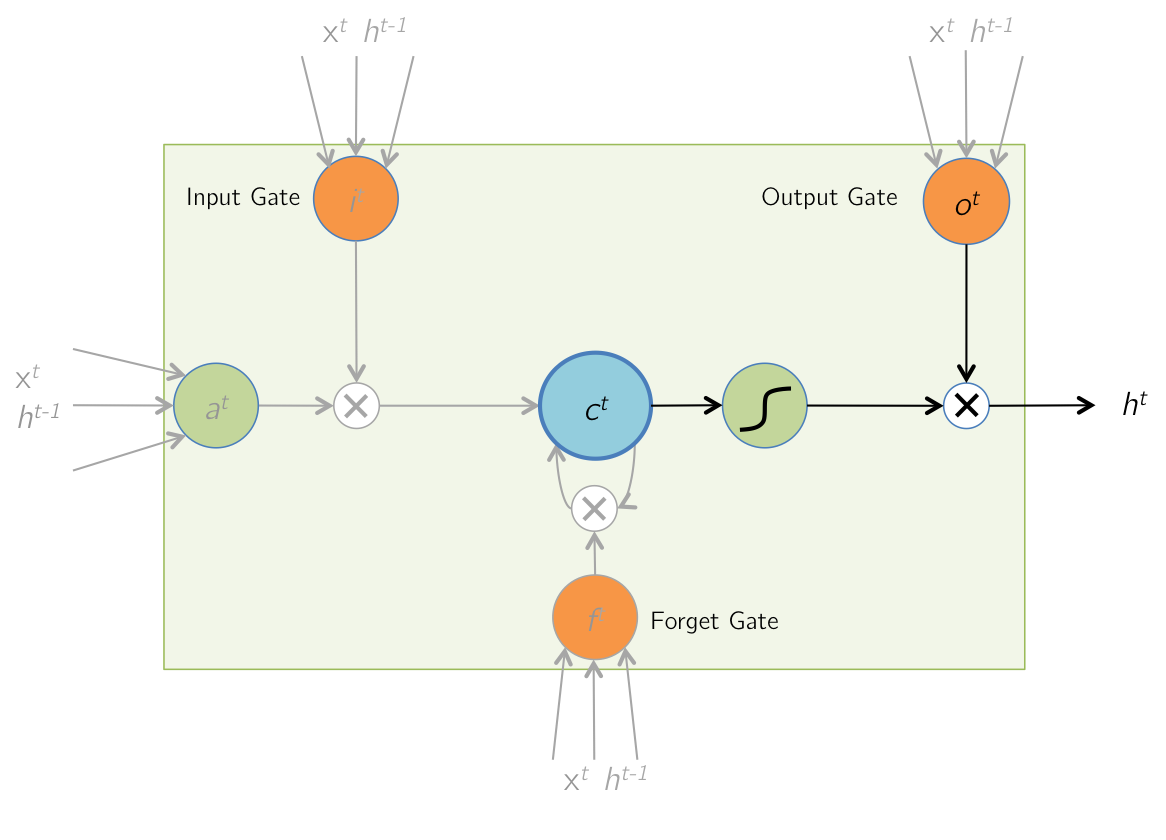
Stream replication related environment variables
Use the following environment variables , have access to Bitnami PostgreSQL Docker Mirror image Easy setup Stream replication colony :
POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_MODE: replication Pattern . Possible valuemaster/slave. No default .POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_USER: Created on the primary server at first run replication user . No default .POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_PASSWORD: replication User password . No default .POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_PASSWORD_FILE: contain replication The path to the user password file . This will coverPOSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_PASSWORDThe value specified in . No default .POSTGRESQL_MASTER_HOST: replication master(slave Parameters )Hostname/IP. No default .POSTGRESQL_MASTER_PORT_NUMBER: replication master Server port for (slave Parameters ). The default is5432.
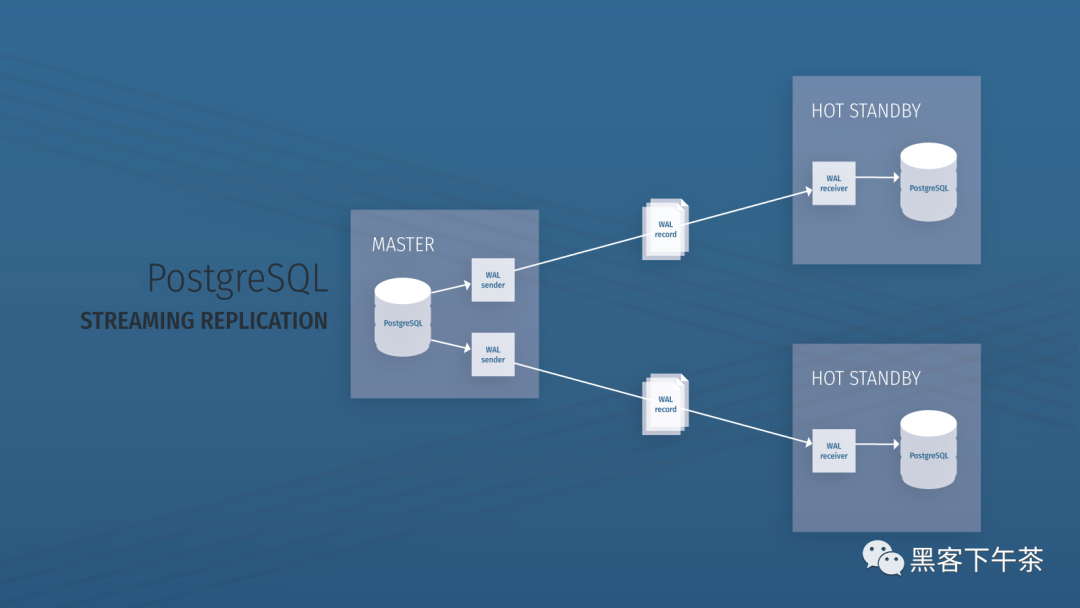
stay Copy (replication) In the cluster , You can have one Lord (master) Servers and zero or more from (slave) The server . When replication is enabled ,master The node is in read-write mode , and slave The node is in read-only mode . For optimal performance , It is recommended to limit reading to slave On .
The first 1 Step : establish replication master
The first step is to start master.
$ docker run --name postgresql-master \
-e POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_MODE=master \
-e POSTGRESQL_USERNAME=my_user \
-e POSTGRESQL_PASSWORD=password123 \
-e POSTGRESQL_DATABASE=my_database \
-e POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_USER=my_repl_user \
-e POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_PASSWORD=my_repl_password \
bitnami/postgresql:latest In this order , We use POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_MODE=master Parameter configures the container to master Containers . Use POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_USER and POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_PASSWORD Parameter assignment replication user .
step 2: establish replication slave
Next we launch a replication slave Containers .
$ docker run --name postgresql-slave \
--link postgresql-master:master \
-e POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_MODE=slave \
-e POSTGRESQL_MASTER_HOST=master \
-e POSTGRESQL_MASTER_PORT_NUMBER=5432 \
-e POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_USER=my_repl_user \
-e POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_PASSWORD=my_repl_password \
bitnami/postgresql:latest In the above order , Use POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_MODE Parameter configures the container to slave. stay replication slave Before starting ,slave Container usage POSTGRESQL_MASTER_HOST and POSTGRESQL_MASTER_PORT_NUMBER Parameters are connected to master And from master Copy the initial database .POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_USER and POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_PASSWORD The voucher is used to send to master Authentication . To change pg_hba.conf Default Settings ,slave You need to know if you have set POSTGRESQL_PASSWORD.
Use these two commands , You can now start and run a two node PostgreSQL Master-slave (master-slave) Stream replication cluster . You can do this by adding / Delete from (slave) Server to expand the cluster , Without causing any downtime .
Note: The cluster replicates completely master The server , Including all users and databases .
If master Server down , You can reconfigure a slave Server as master Server and create trigger file /tmp/postgresql.trigger.5432 Start accepting writes . for example , The following command will postgresql-slave Reconfigure to master The server :
$ docker exec postgresql-slave touch /tmp/postgresql.trigger.5432Note: Other nodes in the cluster need to be updated
slaveServer configuration , So they know the newmasterThe server . This will require you to use... Based on our example--link postgresql-slave:masterRestart otherslaveThe server .
Use Docker Compose, You can set up master-slave replication in the following ways :
version: '2'
services:
postgresql-master:
image: 'bitnami/postgresql:latest'
ports:
- '5432'
volumes:
- 'postgresql_master_data:/bitnami/postgresql'
environment:
- POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_MODE=master
- POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_USER=repl_user
- POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_PASSWORD=repl_password
- POSTGRESQL_USERNAME=my_user
- POSTGRESQL_PASSWORD=my_password
- POSTGRESQL_DATABASE=my_database
postgresql-slave:
image: 'bitnami/postgresql:latest'
ports:
- '5432'
depends_on:
- postgresql-master
environment:
- POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_MODE=slave
- POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_USER=repl_user
- POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_PASSWORD=repl_password
- POSTGRESQL_MASTER_HOST=postgresql-master
- POSTGRESQL_PASSWORD=my_password
- POSTGRESQL_MASTER_PORT_NUMBER=5432
volumes:
postgresql_master_data: Use the following methods to scale slave The number of :
$ docker-compose up --detach --scale postgresql-master=1 --scale postgresql-slave=3 The order above will slave The number of 3. You can shrink in the same way .
Note: You should not expand / Reduce the number of primary nodes . Always run only one primary node .
Synchronous commit
By default ,slave The instance is configured for asynchronous replication . In order to ensure higher data stability ( At the expense of some performance ), You can use the following environment variables to set the synchronization commit ( namely , Before committing a transaction to a set of replicas , Transaction commit will not return success to the client ).
POSTGRESQL_SYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT_MODE: Establish the type of synchronous submission . The available options are :on、remote_apply、remote_write、localandoff. The default value ison. For more information , Please check out official PostgreSQL file .POSTGRESQL_NUM_SYNCHRONOUS_REPLICAS: Determine the number of replicas that will enable synchronous replication . This number must not exceed the number you have configured in the clusterslaveThe number of .
Use Docker Compose, You can set up master-slave replication with synchronous commit as follows :
version: '2'
services:
postgresql-master:
image: 'bitnami/postgresql:latest'
ports:
- '5432'
volumes:
- 'postgresql_master_data:/bitnami/postgresql'
environment:
- POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_MODE=master
- POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_USER=repl_user
- POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_PASSWORD=repl_password
- POSTGRESQL_USERNAME=my_user
- POSTGRESQL_PASSWORD=my_password
- POSTGRESQL_DATABASE=my_database
- POSTGRESQL_SYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT_MODE=on
- POSTGRESQL_NUM_SYNCHRONOUS_REPLICAS=1
volumes:
- '/path/to/postgresql-persistence:/bitnami/postgresql'
postgresql-slave:
image: 'bitnami/postgresql:latest'
ports:
- '5432'
depends_on:
- postgresql-master
environment:
- POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_MODE=slave
- POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_USER=repl_user
- POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_PASSWORD=repl_password
- POSTGRESQL_MASTER_HOST=postgresql-master
- POSTGRESQL_MASTER_PORT_NUMBER=5432
postgresql-slave2:
image: 'bitnami/postgresql:latest'
ports:
- '5432'
depends_on:
- postgresql-master
environment:
- POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_MODE=slave
- POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_USER=repl_user
- POSTGRESQL_REPLICATION_PASSWORD=repl_password
- POSTGRESQL_MASTER_HOST=postgresql-master
- POSTGRESQL_MASTER_PORT_NUMBER=5432 In the example above , Submissions need to be written to both the master server and one of the slave servers to be accepted . the other one slave Will continue to use asynchronous replication . Use the following SQL Query to check it :
postgres=# select application_name as server, state,
postgres-# sync_priority as priority, sync_state
postgres-# from pg_stat_replication;
| server | state | priority | sync_state |
|-------------|-----------|----------|------------|
| walreceiver | streaming | 0 | sync |
| walreceiver | streaming | 0 | async |Note: For more advanced settings , You can set
POSTGRESQL_CLUSTER_APP_NAMEenvironment variable , Useapplication_nameParameters define different replication groups .