当前位置:网站首页>多线程与高并发(11)——经典面试题之实现一个容器,提供两个方法,add,size。
多线程与高并发(11)——经典面试题之实现一个容器,提供两个方法,add,size。
2022-08-10 17:13:00 【李王家的翠花】
实现一个容器,提供两个方法,add,size。写两个线程,线程 1 添加 10 个元素到容器中,线程 2 实现监控元素的个数,当个数到 5 个时,线程 2 给出提示并结束。
1、普通方法
public class Test_Container {
List list = new ArrayList<>();
private void add(Object o) {
list.add(o);
}
private Integer size() {
return list.size();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test_Container container = new Test_Container();
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("T1 开始");
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
container.add(new Object());
System.out.println("add + " + i);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("T1 结束");
}, "T1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("T2 开始");
while(true){
if(container.size()==5){
break;
}
}
System.out.println("T2 结束");
}, "T2").start();
}
}
赶早不如赶巧,一上来我就运行出了死循环的结果…
这是为什么呢?很简单,因为线程2开始的时候,线程1都执行到7了!
还有一种情况,如下图: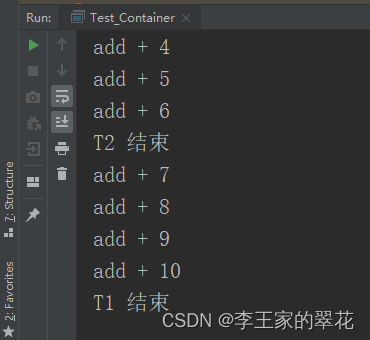
T2结束的时候,T1都执行到6了。
我们加volatile关键字尝试一下。
2、volatile关键字
public class Test_ContainerWithVolatile {
volatile List list = new ArrayList<>();
private void add(Object o) {
list.add(o);
}
private Integer size() {
return list.size();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test_ContainerWithVolatile container = new Test_ContainerWithVolatile();
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("T1 开始");
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
container.add(new Object());
System.out.println("add + " + i);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("T1 结束");
}, "T1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("T2 开始");
while(true){
if(container.size()==5){
break;
}
}
System.out.println("T2 结束");
}, "T2").start();
}
}
看上去没有死循环的问题:
但是,是因为我加了sleep的原因,如果不加sleep,还是不行。
所以,volatile关键字是不可以的,为什么不可以呢,volatile关键字禁止指令重排序,保证线程可见性,但是又保证不了原子性,更保证不了线程等待不运行。你想读到size=5的时候,他可能都变成6了。
我们用wait和notify实现尝试一下。
3、wait和notify实现
wait()方法的作用是释放锁,加入到等待队列。调用notify或者notifyAll方法不释放锁,只是让他参与锁的竞争中去。
public class Test_ContainerWithWait {
//及时可见
volatile List list = new ArrayList<>();
private void add(Object o) {
list.add(o);
}
private Integer size() {
return list.size();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test_ContainerWithWait container = new Test_ContainerWithWait();
//用来上锁的对象
Object o = new Object();
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("T2 开始");
if (container.size() != 5) {
try {
//wait()方法必须在同步关键字修饰的方法中才能调用。
synchronized (o) {
o.wait();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("T2 结束");
}, "T2").start();
//保证线程2先运行
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("T1 开始");
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
container.add(new Object());
System.out.println("add + " + i);
if (container.size() == 5) {
synchronized (o) {
//notify不释放锁
o.notify();
}
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("T1 结束");
}, "T1").start();
}
}
上面代码,执行结果如下,执行结果正常,但是,这是有问题的:
notify不释放锁,只是让对象去争这把锁,其中真正起作用的还是Thread.sleep(1000);这个,T2先去执行了。如果是以下写法:
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (o) {
System.out.println("T1 开始");
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
container.add(new Object());
System.out.println("add + " + i);
if (container.size() == 5) {
//notify不释放锁
o.notify();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("T1 结束");
}
}, "T1").start();
我们把锁加在代码逻辑的最外层,结果如下:
notify不释放锁,T2在5这个时候还是拿不到锁。怎么解决呢?正确写法如下;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test_ContainerWithWait container = new Test_ContainerWithWait();
//用来上锁的对象
Object o = new Object();
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (o) {
System.out.println("T2 开始");
if (container.size() != 5) {
try {
//wait()方法必须在同步关键字修饰的方法中才能调用。
o.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("T2 结束");
//唤醒锁让T1继续执行
o.notify();
}
}, "T2").start();
//保证线程2先运行
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (o) {
System.out.println("T1 开始");
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
container.add(new Object());
System.out.println("add + " + i);
if (container.size() == 5) {
//notify不释放锁
o.notify();
try {
//通过wait释放锁
o.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("T1 结束");
}
}, "T1").start();
}
两个地方,一个是在T1线程里通过wait释放锁,一个是在T2线程里notify让T1绩效执行。结果如下:
边栏推荐
- 建筑施工员证怎么考?报名条件及报考时间是什么?
- 如何构建一个自己的代理ip池
- DASCTF2022.07 empowerment competition WEB topic recurrence
- 神经网络全连接层的作用,各种神经网络的优缺点
- 强网杯2021final
- R语言使用ggpubr包的ggbarplot函数可视化柱状图、设置add参数为mean_se和jitter可视化不同水平均值的柱状图并为柱状图添加误差线(se标准误差)和抖动数据点分布
- #夏日挑战赛#【ELT.ZIP】啃论文俱乐部——学术科研方法论沉淀辑
- pytorch 模型GPU推理时间探讨3——正确计算模型推理时间
- 需求骤降,成本激增,PC行业再次入冬
- DGIOT平台实时展示OPC上报数据全流程代码剖析
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
神经网络全连接层的作用,各种神经网络的优缺点
kuangbin专题一 简单搜索
Polling and the principle of webSocket and socket.io
matsuri.icu 筛选单场直播中 指定用户的弹幕
router.afterEach()
Pytorch GPU模型推理时间探讨
PS2手柄通讯协议解析—附资料和源码「建议收藏」
取Json中的数组进行遍历
雷达人体存在感应器,人体感知控制应用,为客户提供真实的感知方案
ARM开发(三)ARM寻址方式,异常中断,异常向量表
长markdown文档的拆分与合并
浅析端口扫描原理
神经网络如何提高准确率,神经网络的求解方式
还在用 Xshell?你 out 了,推荐一个更现代的终端连接工具,好用到爆!
R语言ggplot2可视化:使用ggpubr包的text_grob函数和as_ggplot函数可视化文本段落(将指定文本段落可视化出来、指定文本段可视化为图像)、face参数指定文本的字体样式
mysql主主复制+keepalived高可用
未来5年的9大技术趋势
BalsnCTF2021
奥迪的极致高端属于一个大写的H?重塑时空,谁会是这个夜晚的主角?
「企业架构」企业架构师,解决方案架构师和软件架构师有何不同