当前位置:网站首页>Compact CUDA tutorial - CUDA driver API
Compact CUDA tutorial - CUDA driver API
2022-04-23 19:42:00 【Adenialzz】
Streamlining CUDA course ——CUDA Driver API
Driver API summary
CUDA The multistage of API
CUDA Of API There are multiple levels ( The figure below ), Details available :CUDA Environment details .
- CUDA Driver API yes CUDA And GPU The driving level of communication API. In the early CUDA And GPU Communication is directly through Driver API.
cuCtxCreate()etc.cuThe beginning is basically Driver API. Familiar to usnvidia-smiCommands are called Driver API. - Later I found out Driver API Too much , The details are too complicated , So it evolved Runtime API,Runtime API Is based on Driver API Developed , common
cudaMalloc()etc. API All are Runtime API.
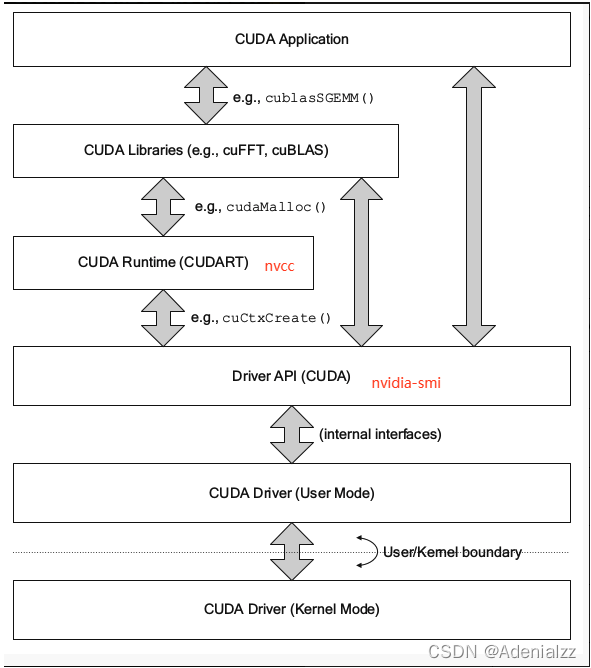
CUDA Driver
Environment related
CUDA Driver yes With the release of graphics card driver , want And cudatoolkit Look at it separately .
CUDA Driver Corresponding to cuda.h and libcuda.so Two documents . Be careful cuda.h Will be installed cudatoolkit It includes , however libcuda.so It is installed with the graphics card driver in our system ( and No Also follow cudatooklit install ). therefore , If you want to copy and move directly libcuda.so Note that the driver version needs to be adapted to the file .
How to understand CUDA Driver
This concise course is for the bottom Driver API The understanding of the , In order to Conducive to subsequent Runtime API Learning and error debugging .Driver API yes understand cudaRuntime The key to context . therefore , This abridged course is in CUDA Driver The main knowledge points of this part are :
- Context Management mechanism of
- CUDA Development habits of series interfaces ( Error checking method )
- Memory model
About context And memory classification
About context, There are two kinds of :
- Manually managed context:
cuCtxCreate, Manual management , In a stack push/pop - Automatically managed context:
cuDevicePrimaryCtxRetain, Automatic management ,Runtime API On this basis
About memory , There are two broad categories. :
- CPU Memory , be called Host Memory
- Pageable Memory: Pageable memory
- Page-Locked Memory: Page locked memory
- GPU Memory ( memory ), be called Device Memory
- Global Memory: Global memory
- Shared Memory: Shared memory
- … other
The above contents will be introduced later .
cuIint Drive initialization
cuInitThe meaning is , Initialize drive API, One global execution is enough , If not implemented , Then all API Will return an error .- No, Corresponding
cuDestroy, No need to release , Program destruction automatically releases .
Return value check
Version of a
Check correctly and friendly cuda The return value of the function , Conducive to the organizational structure of the program , Make the code more readable , Mistakes are easier to find .
We know cuInit The type returned is CUresult, The return value will tell the programmer whether the function succeeded or failed , What are the reasons for the failure .
The logic of the official version of the check , as follows :
// Use a parameterized macro definition to check cuda driver Whether it is initialized normally , And locate the file name of the program error 、 Number of lines and error messages
// Macro definition with do...while Loop can ensure the correctness of the program
#define checkDriver(op) \ do{
\ auto code = (op); \ if(code != CUresult::CUDA_SUCCESS){
\ const char* err_name = nullptr; \ const char* err_message = nullptr; \ cuGetErrorName(code, &err_name); \ cuGetErrorString(code, &err_message); \ printf("%s:%d %s failed. \n code = %s, message = %s\n", __FILE__, __LINE__, #op, err_name, err_message); \ return -1; \ } \ }while(0)
Is a macro definition , We're calling other API When , Check the return value of the function , And print out the error code and error information in case of error , Convenient debugging . such as :
checkDriver(cuDeviceGetName(device_name, sizeof(device_name), device));
If there are uninitialized and other errors , The error message will be clearly printed .
This version is also Nvidia The official version , But there are some problems , For example, the readability of the code is poor , Go straight back to int Type error code, etc . Version 2 is recommended .
Version 2
// Obviously , This kind of code encapsulation , More convenient to use
// Macro definition #define < Macro name >(< Parameter table >) < Macrobody >
#define checkDriver(op) __check_cuda_driver((op), #op, __FILE__, __LINE__)
bool __check_cuda_driver(CUresult code, const char* op, const char* file, int line){
if(code != CUresult::CUDA_SUCCESS){
const char* err_name = nullptr;
const char* err_message = nullptr;
cuGetErrorName(code, &err_name);
cuGetErrorString(code, &err_message);
printf("%s:%d %s failed. \n code = %s, message = %s\n", file, line, op, err_name, err_message);
return false;
}
return true;
}
The obvious , The return value of version 2 、 Code readability 、 The encapsulation is much better than version 1 . Use the same way :
checkDriver(cuDeviceGetName(device_name, sizeof(device_name), device));
// Or add a judgment , Exit in case of error
if (!checkDriver(cuDeviceGetName(device_name, sizeof(device_name), device))) {
return -1;
}
CUcontext
Manual context management
-
context Is a context , Association pair GPU All operations .
-
One context Associated with a graphics card , A graphics card can be used by more than one context relation .
-
Each thread has a stack structure to store context, The top of the stack is currently used context, The due push/pop Function operation context The stack , all API Are based on the current context For operational purposes
Just imagine , If you do anything, you need to pass a device Decide which device to send to perform , Much trouble .context Is to facilitate the management of the current API Where is it device A means of implementation , The stack structure is used to save the previous context device, Thus, it is convenient to control multiple devices .
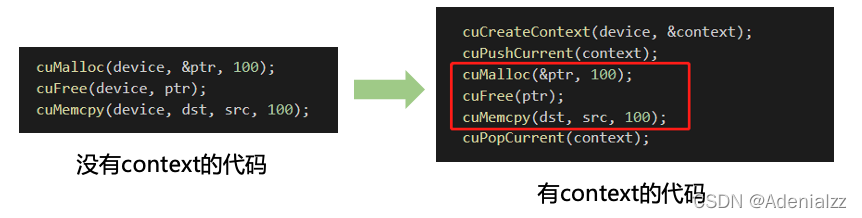
Automatic context management
- Since high-frequency operations are fixed access to a thread device unchanged , It's not often that the same thread accesses different data multiple times device The situation of , And only one context, Seldom use more context.
- That is, in most cases ,
CreateContext、PushCurrent、PopCurrentThis is more than context Management is troublesome - So it came out
cuDevicePrimaryCtxRetain, Associate the master for the device context, Distribute in this way 、 Set up 、 Release 、 The stack doesn't need us to manage it manually , It's a kind of automatic management context The way primaryContext: Give me the equipment id, Here you are. context And set it up. , here One device Corresponding to one primary context. Different threads , As long as the equipment id identical ,primary context It's the same , And context It's thread safe .- To be introduced later CUDA Runtime API in , Is to automatically use
cuDevicePrimaryCtxRetainOf .

DriverAPI memory management
- host memory Is the memory of the computer itself , It can be used CUDA Driver API To apply for and release , It can also be used. C/C++ Of
malloc/freeandnew/deleteTo apply for and release . - device memory It's the memory on the graphics card , That is, video memory , There are special ones Driver API To apply and release .
版权声明
本文为[Adenialzz]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204231923163837.html
边栏推荐
- 数据库查询 - 选课系统
- What is a message queue
- [report] Microsoft: application of deep learning methods in speech enhancement
- Physical meaning of FFT: 1024 point FFT is 1024 real numbers. The actual input to FFT is 1024 complex numbers (imaginary part is 0), and the output is also 1024 complex numbers. The effective data is
- C学习完结
- Possible root causes include a too low setting for -Xss and illegal cyclic inheritance dependencies
- Kubernetes入门到精通-裸机LoadBalence 80 443 端口暴露注意事项
- Go three ways to copy files
- 【h264】libvlc 老版本的 hevc h264 解析,帧率设定
- Pit encountered using camera x_ When onpause, the camera is not released, resulting in a black screen when it comes back
猜你喜欢

OpenHarmony开源开发者成长计划,寻找改变世界的开源新生力!

MySQL syntax collation

Possible root causes include a too low setting for -Xss and illegal cyclic inheritance dependencies
山东大学软件学院项目实训-创新实训-网络安全靶场实验平台(八)

Using oes texture + glsurfaceview + JNI to realize player picture processing based on OpenGL es
PHP reference manual string (7.2000 words)
Kubernetes introduction to mastery - ktconnect (full name: kubernetes toolkit connect) is a small tool based on kubernetes environment to improve the efficiency of local test joint debugging.

基于pytorch搭建GoogleNet神经网络用于花类识别
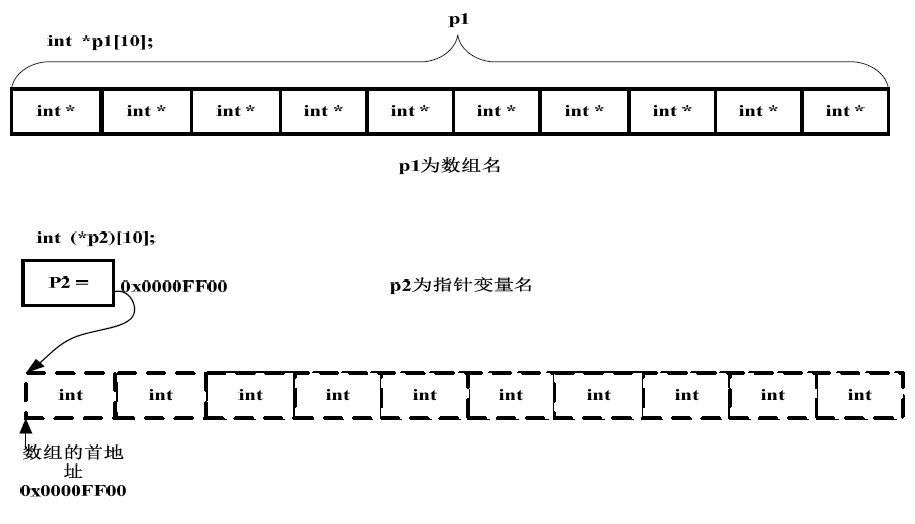
指针数组与数组指针的区分
How to create bep-20 pass on BNB chain
随机推荐
图书管理数据库系统设计
指针数组与数组指针的区分
C语言的十六进制printf为何输出有时候输出带0xFF有时没有
Some ideas about time-consuming needs assessment
An idea of rendering pipeline based on FBO
MySQL数据库 - 单表查询(三)
Inject Autowired fields into ordinary beans
山东大学软件学院项目实训-创新实训-网络安全靶场实验平台(七)
Kubernetes入门到精通-在 Kubernetes 上安装 OpenELB
Some speculation about the decline of adults' language learning ability
An algorithm problem was encountered during the interview_ Find the mirrored word pairs in the dictionary
uIP1. 0 actively sent problem understanding
【h264】libvlc 老版本的 hevc h264 解析,帧率设定
How to create bep-20 pass on BNB chain
How to select the third-party package of golang
A simple (redisson based) distributed synchronization tool class encapsulation
Speex Wiener filter and rewriting of hypergeometric distribution
Physical meaning of FFT: 1024 point FFT is 1024 real numbers. The actual input to FFT is 1024 complex numbers (imaginary part is 0), and the output is also 1024 complex numbers. The effective data is
TI DSP的 FFT与IFFT库函数的使用测试
MySQL syntax collation (3)