当前位置:网站首页>Classes and objects
Classes and objects
2022-04-23 17:57:00 【*Flowers bloom on the street】
One 、 The concept of object
It is an entity used to describe objective things in the system , It is a basic unit used to form a system . An object consists of a set of properties and a set of behaviors .
attribute : A data item used to describe the static characteristics of an object .
Behavior : An operation sequence used to describe the dynamic characteristics of an object .
| Object name |
Belong to sex |
Method ( operation ) |
Object name |
Belong to sex |
Method ( operation ) |
… |
| Zhang San |
Gender : male Age :21 Education : Undergraduate major : Computer |
having dinner attend class;class begins experiment Exercise … |
Li Si |
Gender : Woman Age :20 Education : Undergraduate major : Computer |
having dinner attend class;class begins experiment Exercise … |
… |
Object is an objective entity in the real world , Its characteristics are :
> Every object has a name ;
> Use attributes ( Or state ) Describe some characteristics of the object ;
> Describe the various behaviors of objects through a set of operations .
State and behavior are the main attributes of objects .
1. The state of an object is also called the static property of the object , It mainly refers to all kinds of information contained in the object , That's the variable . Each individual object has its own internal variables , The values of these variables indicate the state of the object .
2 Object method ( Behavior ) On the one hand, wrap the internal variables of the object , encapsulation , Protect it , So that only the object's own methods can manipulate these internal variables , On the other hand , The method of an object is to interact with the external environment and other objects , Communication interface , The environment of the object and other objects can call the method of the object through this interface , Manipulate the behavior of objects and change the state of objects .
An object is an abstract representation of a real-world entity or concept in computer logic . In particular , An object is a collection of properties and operations with a unique object name and a fixed interface to the outside world , A factor or group of factors used to simulate or affect real-world problems .
Two 、 The concept of class
Ignore the non essential characteristics of things , Only pay attention to the essential characteristics related to the current goal , So as to find out the commonness of things , Divide things of common nature into one class , Come up with an abstract concept .
In object-oriented methods “ class ”
1> A collection obtained by abstracting a group of objects with the same properties and behavior .
2> Provides an abstract description of all objects belonging to this class , It includes two main parts: attribute and behavior .
The relationship between classes and objects :
Such as the relationship between mold and casting , An object belonging to a class is called an instance of that class .
Such as object “ Zhang San ”、“ Li Si ”、…… Have some of the same properties , operation , Abstract it into concrete data , Can be abstracted into a category —— class : That is, students
A class is an abstraction of an object
Object is an instance of a class , Class materialization
Class is a template for creating objects , It contains the description of the state and operation behavior of the created object ;
An object is an instantiation of a class ( Object variables 、 Object array, etc ).
class It is an abstraction of objects with the same properties and functions .
Class is an abstract concept , And the object is concrete , Class is just a data type , The object is a variable belonging to this class , Occupy A certain Of Storage unit .
:: scope resolution , Use it to indicate which function or data belongs to which class , Use the full name of the member in the class :
Class name :: Member name
3、 ... and 、 The most prominent feature of object-oriented system :
encapsulation 、 inheritance 、 polymorphism
1> Data abstraction and encapsulation
1. Data abstraction : It is the case analysis of data , Extract the results of their common properties .
Such as :“ Student “ object , First of all, some examples of students are analyzed , Identify their common or main characteristics ( full name 、 Gender 、 Age 、 Professional and so on ) Ignore differences or minor features that are not interesting ( Difference in appearance 、 Personality differences, etc ).
2. Encapsulation of data
The data structure and the operations acting on the data structure form an entity , Hide the presentation and operation details of data , The user operates the data through the interface .
such , The user only knows the operation interface to operate the data , Without knowing how to do it internally and how to represent the encapsulation of data .
2> Data inheritance
Definition : Objects of special classes have all the properties and services of their general classes , It is called the inheritance of a special class from a general class .
1. Code reusability can be realized and enhanced through inheritance , It is one of the important reasons why object-oriented technology can improve the efficiency of software development .
2. When creating a new derived class , As long as you specify which base class the derived class is derived from, you can automatically inherit the properties and methods of the base class .
3. It is not necessary to modify the original code when modifying or expanding the function of the program ( Just add a new code ).
3> Polymorphism of data
Definition : Referring to General Properties or behaviors defined in , By Special class inheritance after , Can have Different data types or behaviors . This makes the same attribute or behavior have different semantics in general classes and their special classes .
Such as : The addition of numbers : Addition of real numbers
Addition of complex numbers
Such as : max() Function call :( function overloading )
max(a,b)—— Find the maximum number between two numbers ;
max(a,b.c)—— Find the maximum number between three numbers ;
Four 、 The relationship between classes and objects
C++ The class is in C Extended from the structure of language . stay C++ in , The type of object is called class , A class is an abstraction of an object , It represents the commonness and characteristics of a group of objects , Object is a concrete instance of a class .
The basic structure of a class
1. name / Mark
2. Data members of class ( Class composition )
3. class ( Class action 、 Behavior )
object : A class variable is an instance of a class , They are called objects .
Structures and classes
| Data and operation are separated in the structure |
Data and operations in the class are encapsulated together |
| struct student { int number; char name[15]; float score; }; |
struct student { int number; char name[15]; float score; void display( )// Members of the function { cout<<”number: ”<< number; cout<<”name: ”<< name; cout<<”score: ”<< score <<endl; } }; |
| void display(Student * stu) { printf(”number:%d”,stu->number); printf(”name:%s”,stu->name); printf(”score:%f\n”,stu->score); } |
In the structure , Members who are not specified as public or private members , The default is Members of the public .
In class , Any member that is not defined as a public member (public) Or protect members (protected) The members of are Private member (private) —— The embodiment of encapsulation .
5、 ... and 、 The type of the class
Is a user-defined data type . If you want to use class types in your program , Must be defined according to actual needs , Or use a designed class .
C++ Define a class , The method is similar to defining a structure type ,
The general form is :
class Class name
{
Member list
};
explain
1. Class definition must give the data type declaration of each data member .
2. When defining a class , The computer does not allocate memory space to data members , Space is allocated only when objects are defined ;
3. You cannot assign an initial value to a member of a class when it is defined .
4. Data members can be basic data types , It can also be a complex data type ( Array 、 The pointer 、 quote 、 Structure , It can also be class variables, etc ).
Member visits
Whether data members or function members , Each member of the class has access control properties , have access to Member access qualifier explain :
●public ( public )
●private ( Private )
●protected ( The protection of )
Member access qualifier
1) Members of the public :public —— The defined members are open , Can be accessed anywhere ( Class and other parts of the program )
public Implements the external interface of the class .
2) Private member :private—— The defined members are hidden , Can only be accessed inside a class , Cannot be accessed elsewhere in the program ;
private Realize the concealment of private members .
3) Protection member : protected—— The defined members are semi open , Can be accessed inside the class , You can also access... In its derived classes , But it cannot be accessed in other parts of the program .
Member access control yes C++ Another important feature of classes and structs .
Add the access label , The more general form of class definition is :
class Class name
{ public :
Data member or member function
protected:
Data member or member function
private :
Data member or member function
};
explain :
In the definition of the class ,private、protected、public Can appear any number of times in any order ; But usually private On the front ,protected In the middle ,public Put it at the back .
In actual programming , In order to make the program clear , Each member access qualifier appears only once in the class body , Usually, members with the same access control attributes are written together .
Data members in a class are usually described as private members , To realize data hiding ; Member functions are usually set to public , To access data members via messaging , Protecting members is mainly used to inherit .
class student
{ private:
int number;
char name[15];
float score;
public:
void display( )
{ cout<<”number: ”<< number;
cout<<”name: ”<< name;
cout<<”score: ”<< score <<endl;
}
};
Member functions are introduced into class (member function) Or function members : That is, the function becomes data ( class ) A member of the . Class puts the data ( The nature of things ) And the function ( The behavior of things -- operation ) Encapsulate as a whole .
Four data members are declared private , The six function members are described as public ; That is to say, if you operate on four data members from the outside . It can only be done through six public functions , Data is well protected , Not susceptible to side effects . The public function set defines the interface of the class (interface).
Class is a data type , When defined, the system does not allocate storage space for classes , So you can't initialize the data members of a class . Nor can any data member in a class use keywords extern、auto or register Limit its storage type .
Member functions can directly use any member in the class definition , Can handle data members , You can also call function members . Definition of member function :
Previously, only one declaration was made for the member function ( Prototypes of functions ), There is no definition of the function . Function definitions are usually made after the description of the class , The format is as follows :
Return value type class name :: Function name ( Parameter table )
f…]// The body of the function
Where the operator "∵" It is called scope resolution operator (scope resolution operator), It indicates which class the function belongs to .
6、 ... and 、 Methods for defining objects
When defining a class , That is, it defines a specific data type . To use a class , You need to instantiate the class , That is, the object that defines this class .
Object definition :
1. In a statement ( Definition ) Class while defining objects
2. First of all ( Definition ) Class redefines the object
3. Class name does not appear , Define the object directly
1> In a statement ( Definition ) Class while defining objects
class student
{ private:
int number;
char name[15];
float score;
public:
void display( ) // Members of the function
{ cout<<”number: ”<< number;
cout<<”name: ”<< name;
cout<<”score: ”<< score <<endl;
}
} stu1, stu2;
2> First of all ( Definition ) Class redefines the object
Such as :class student stu;
3> Class name does not appear , Define the object directly
class
{ private:
int number;
char name[15];
float score;
public:
void display( ) // Members of the function
{ cout<<”number: ”<< number;
cout<<”name: ”<< name;
cout<<”score: ”<< score <<endl;
}
} stu1,stu2;
7、 ... and 、 class
The member function of the class can access any member of the class .
Introduced in class Member functions (member function) Or function members , That is, the function becomes data ( class ) A member of the . Class handle data ( The nature of things ) and function ( The behavior of things , operation ) encapsulation For a whole .
If four data members are declared private , The six function members are described as public , That is to say, if you operate on four data members from the outside . It can only be done through six public functions , Data is well protected , Not susceptible to side effects . The public function set defines the interface of the class (interface).
Class is a data type , When defined, the system does not allocate storage space for classes , So you can't initialize the data members of a class . Nor can any data member in a class use keywords extern、auto or register Limit its storage type .
Member functions can directly use any member in the class definition , Can handle data members , You can also call function members . Definition of member function :
Previously, only one declaration was made for the member function ( Prototypes of functions ), There is no definition of the function .
Function definitions are usually made after the description of the class , The format is as follows :
Return value type class name :: Function name ( Parameter table )
{···}// The body of the function
Where the operator "::" It is called scope resolution operator (scope resolution operator), It indicates which class the function belongs to .
Object oriented programming generally hides data , No direct external access , and Take the member function as the interface to the outside world , Access data through member functions . That is, data members are attributes , Member functions are methods , Access properties through methods .
1. Defined in class ( It's also a statement ) Member functions .
2. The declaration of member functions is in the class , Defined outside the class
1> Defined in class ( It's also a statement ) Member functions , In the form of :
class Class name
{ •••
Return type Function name ( List of formal parameters )
{
The body of the function
}
•••
} ;
class student
{ private:
int number;
char name[15];
float score;
public:
void display( ) // Member function definition
{ cout<<”number: ”<< number;
cout<<”name: ”<< name;
cout<<”score: ”<< score <<endl;
}
} ;
2> The declaration of member functions is in the class , Defined outside the class , In the form of :
class Class name
{ •••
Return type Function name ( type 1 Parameter name 1, type 2 Parameter name
Return type Function name ( type 1, type 2,...);
•••
};
Return type Class name :: Function name ( List of formal parameters )
{ The body of the function
}
class student
{ private:
int number;
char name[15];
float score;
public:
void display( ); // Member function declaration
} stu1,stu2;
void student :: display( ) // Member function definition
{ cout<<”number: ”<< number;
cout<<”name: ”<< name;
cout<<”score: ”<< score <<endl;
}
The member function prototype declaration of a class must appear before the member function definition , Otherwise, compilation will fail .
Declare member functions inside a class , And define member functions outside the class , this Is a good programming habit . Because it can not only reduce the length of class body , Make the class structure clear , Easy to read , and It helps to separate the interface and implementation of the class .
1. Built in member functions
The member function of the class can be specified as inline, Built in member functions .
By default , If the member function defined in the class body does not include control structures such as loops , When it meets the requirements of built-in functions ,C++ They are automatically treated as built-in functions ( Implicit inline) .
If member functions are defined inside and outside , Member functions must be explicitly declared as inline. Display definition refers to when defining built-in functions , Still put the function outside the class definition body , But in order to make it work as a built-in function , Add before function definition inline.
class student
{ private:
int number;
char name[15];
float score;
public:
inline void display( );
} stu1,stu2;
inline void student :: display( )
{ cout<<”number: ”<< number;
cout<<”name: ”<< name;
cout<<”score: ”<< score <<endl;
}
2. How member functions are stored
C++ The data members of each object will be allocated their own independent storage space , Like structure members .
Member function code has only a common section of storage space , When calling member functions of different objects, the same section of function code is executed .
8、 ... and 、 How to access members of an object
1> Access members in an object by object name
2> Accessing members in an object through an object pointer
3> Accessing members in an object through an object reference
One 、 Access... Through member operators : .
1. Use of data members
Format : Object name . Member name
2. Use of member functions
Format : Object name . Member function name ( Argument table )
or : Object name . Class name :: Member function name ( Argument table )
or (*p). Member name
The general form of calling the member function in the object is :
Object pointer name one > Member function name ( Argument list )
or (*p). Member function name ( Argument list )
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class time
{
public:
int hour;
int minute;
int sec;
};
int main()
{
time t1;
time *p = &t1;
cin >> p->hour >> p->minute >> p->sec;
cout << p->hour << ":" << p->minute << ":" << p->sec << endl;
cin >> (*p).hour >> (*p).minute >> (*p).sec;
cout << (*p).hour << ":" << (*p).minute << ":" << (*p).sec << endl;
return 0;
3、 ... and 、 Access members in an object through references to object members
The general form of data members in access objects is :
Object reference variable name . Member name
The general form of calling the member function in the object is :
Object reference variable name . Member functions name ( Argument list )
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class time
{ public:
int hour;
int minute;
int sec;
} ;
int main( )
{ time t1;
time &t2=t1;
cin>>t2.hour>>t2.minute>>t2.sec;
cout<<t2.hour<<”:”<<t2.minute<<”:”<<t2.sec<<endl;
return 0;
}
If a class defines two or more objects at the same time , Then these similar Objects can be assigned to each other .
Object name 1 = Object name 2( Assign the values on the right to the objects on the left one by one )
Nine 、 Class encapsulation and information concealment
1> Separation of public interfaces from private implementations
A common member function is a function of the class used by the user Common interface , That is, the external interface of the class .
The operation of data members through member functions is called Implementation of the function of class , The data manipulated in the class is private , The implementation details of the functions of the class are hidden , This implementation is called Private implementation . Class Separation of public interfaces from private implementations Information concealment is formed , The user is exposed to the public interface , Without access to hidden data and implementation details .
Separation of interface and implementation Is the most basic principle of software engineering , Information concealment Is a very important concept of software engineering .
advantage :
If you want to modify or expand the function of a class , Just modify the relevant data members in the class and its related member functions , Parts of the program other than classes do not need to be modified .
If you find errors in reading and writing data in the class during compilation , You don't have to check the whole program , Just check the member functions in this class that access this data .
If a class is used by multiple programs , In object-oriented program development , Often the declaration of a class ( Contains the declaration of member functions ) Put it in the header file .
Use in program #include Include the relevant class declaration header file into the program .
actually , One c++ The program consists of three parts :
1. Class declaration header file : suffix .h Or no suffix
2. Class implementation file : The suffix is .cpp, Definition of class member function
3. Class : Master file
版权声明
本文为[*Flowers bloom on the street]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204230547207492.html
边栏推荐
- Go language JSON package usage
- Future usage details
- Sword finger offer 22 The penultimate node in the linked list - speed pointer
- JS implementation private attribute
- ROS package NMEA_ navsat_ Driver reads GPS and Beidou Positioning Information Notes
- 122. The best time to buy and sell stocks II - one-time traversal
- 一些问题一些问题一些问题一些问题
- Halo 开源项目学习(二):实体类与数据表
- Listen for click events other than an element
- Element calculation distance and event object
猜你喜欢
Anchor location - how to set the distance between the anchor and the top of the page. The anchor is located and offset from the top
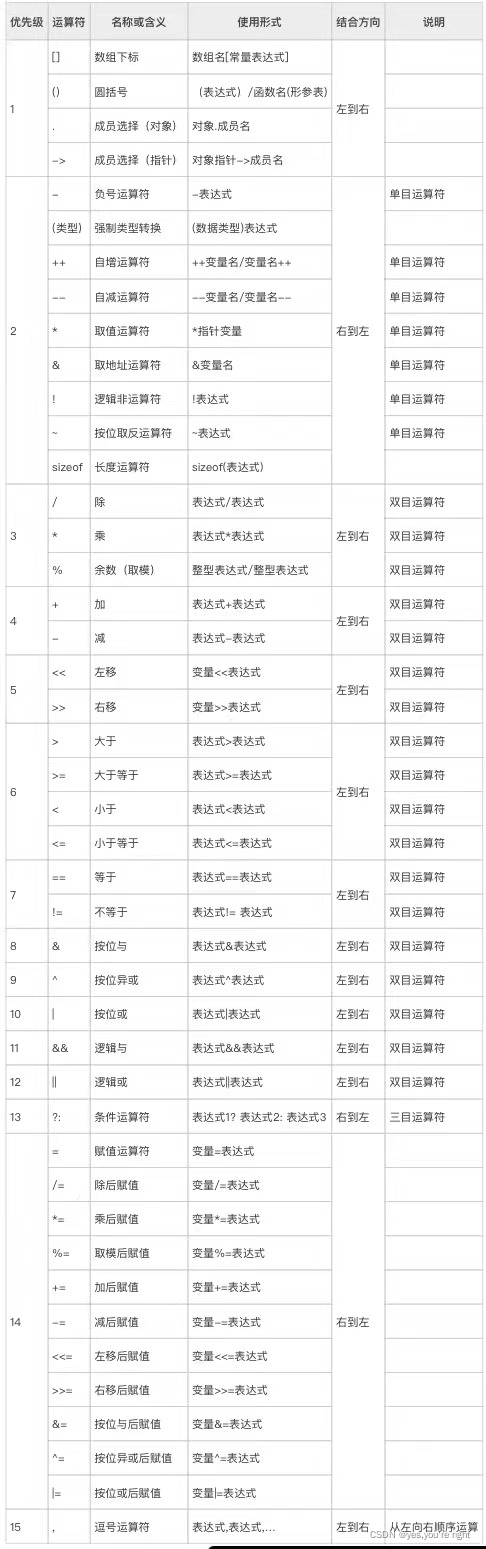
Operators in C language

Gets the time range of the current week
开源按键组件Multi_Button的使用,含测试工程
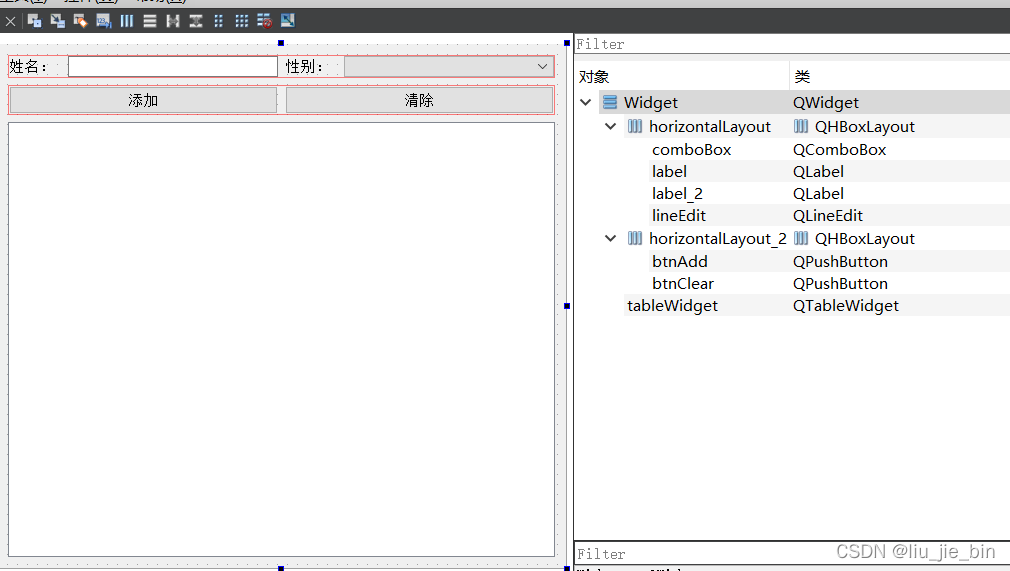
QTableWidget使用讲解
Auto.js 自定义对话框
Index: teach you index from zero basis to proficient use

Implementation of object detection case based on SSD
Laser slam theory and practice of dark blue College Chapter 3 laser radar distortion removal exercise
![SQL optimization for advanced learning of MySQL [insert, primary key, sort, group, page, count]](/img/60/e4d47d458dd98a0c6ba51874e07c30.png)
SQL optimization for advanced learning of MySQL [insert, primary key, sort, group, page, count]
随机推荐
Oil monkey website address
Notes on common basic usage of eigen Library
2022年流动式起重机司机国家题库模拟考试平台操作
122. The best time to buy and sell stocks II - one-time traversal
Submit local warehouse and synchronize code cloud warehouse
2022 Shanghai safety officer C certificate operation certificate examination question bank and simulation examination
MySQL_01_简单数据检索
Error in created hook: "referenceerror:" promise "undefined“
SystemVerilog(六)-变量
Eigen learning summary
Add animation to the picture under V-for timing
C#字节数组(byte[])和字符串相互转换
Use of list - addition, deletion, modification and query
Vite configure proxy proxy to solve cross domain
云原生虚拟化:基于 Kubevirt 构建边缘计算实例
Land cover / use data product download
958. Complete binary tree test
一些问题一些问题一些问题一些问题
386. Dictionary order (medium) - iteration - full arrangement
Client example analysis of easymodbustcp