当前位置:网站首页>Future usage details
Future usage details
2022-04-23 17:36:00 【Flechazo`】
Future Usage details
Preface
Why does it appear Future Mechanism
Two common ways to create threads . One is direct inheritance Thread, The other is to realize Runnable Interface .
One drawback of both approaches is that : Unable to get execution result after task execution .
from Java 1.5 Start , Provided. Callable and Future, Through them, you can get the task execution result after the task execution .
Future The core idea of the pattern is to enable the main thread to use the time that it needs to wait synchronously to do other things .
Because the execution results can be obtained asynchronously , So you don't have to wait synchronously to get the execution result .
Future Usage details
It's easy to use
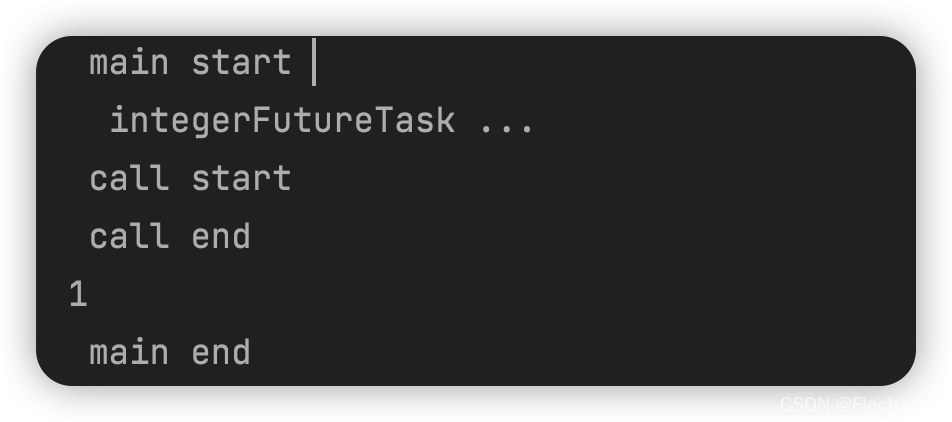
System.out.println(" main start ");
FutureTask<Integer> integerFutureTask = new FutureTask<>(new TestA());
new Thread(integerFutureTask).start();
System.out.println(" integerFutureTask ...");
Integer integer = integerFutureTask.get();
System.out.println(integer);
System.out.println(" main end ");
class TestA implements Callable<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println(" call start ");
Thread.sleep(10000);
System.out.println(" call end ");
return 1;
}
}
get It will always block access
Of course, you can also set the timeout
public V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
Future Simple principle
It's simple to use , Let's study the specific principle
We all know Thread Can only run Runable Interface
How does the return value return ?
FutureTask<Integer> integerFutureTask = new FutureTask<>(new TestA()); In this line of code, you can see FutureTask Realized RunnableFuture Interface

Continue to look at RunnableFuture The interface inherits our Runnable Interface And inherited a Future Interface
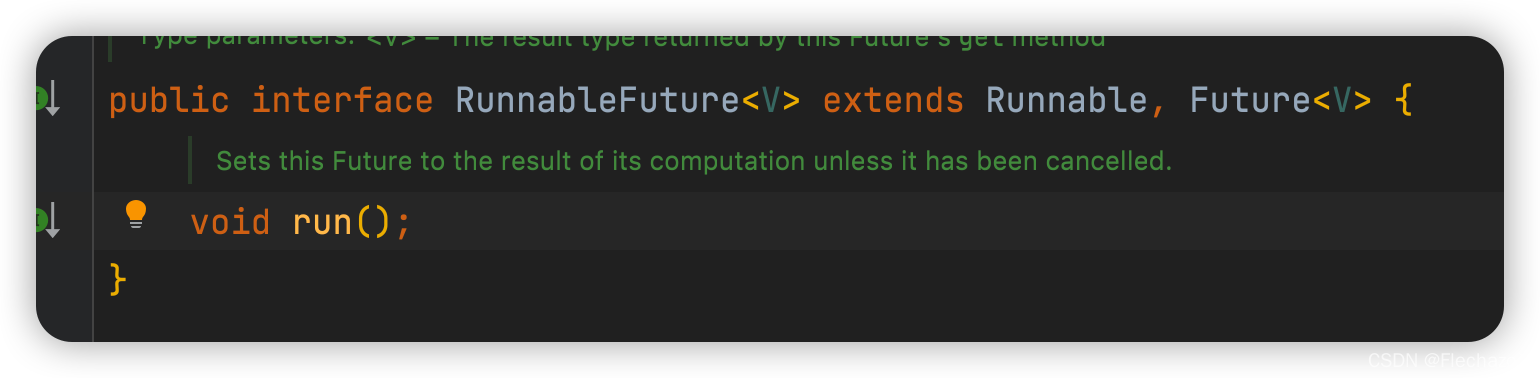
Future Interface
Defines some methods that return values
public interface Future<V> {
// Cancel
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
// Whether to cancel
boolean isCancelled();
// Whether to carry out
boolean isDone();
// obtain
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
// Timeout to get
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}
The principle and process are as follows
First step
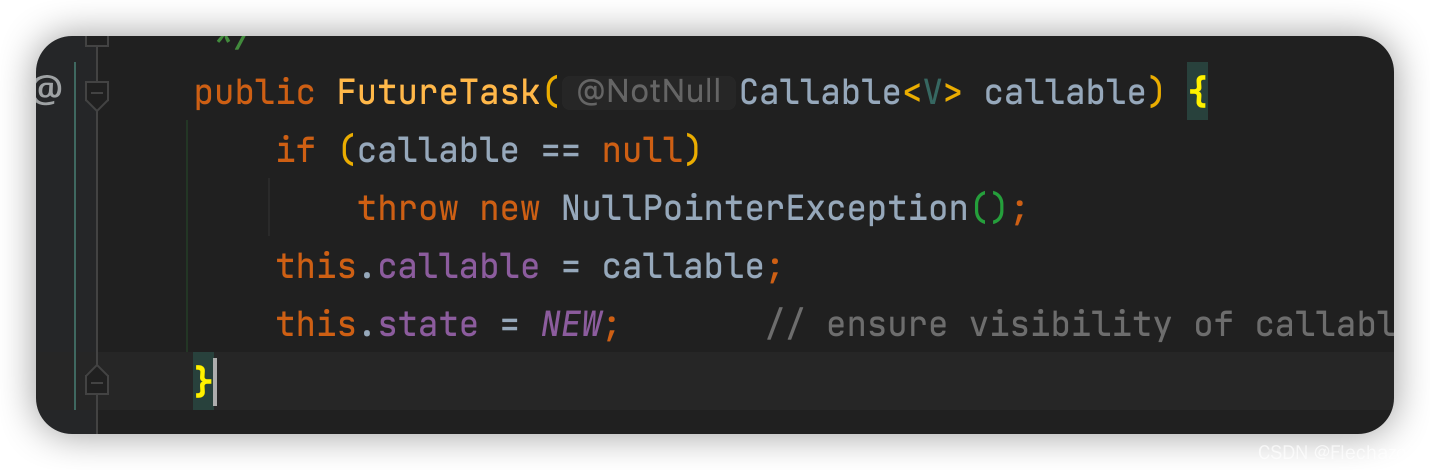
Initialization task , Set thread state
We can see several states of the thread and some states from start to end
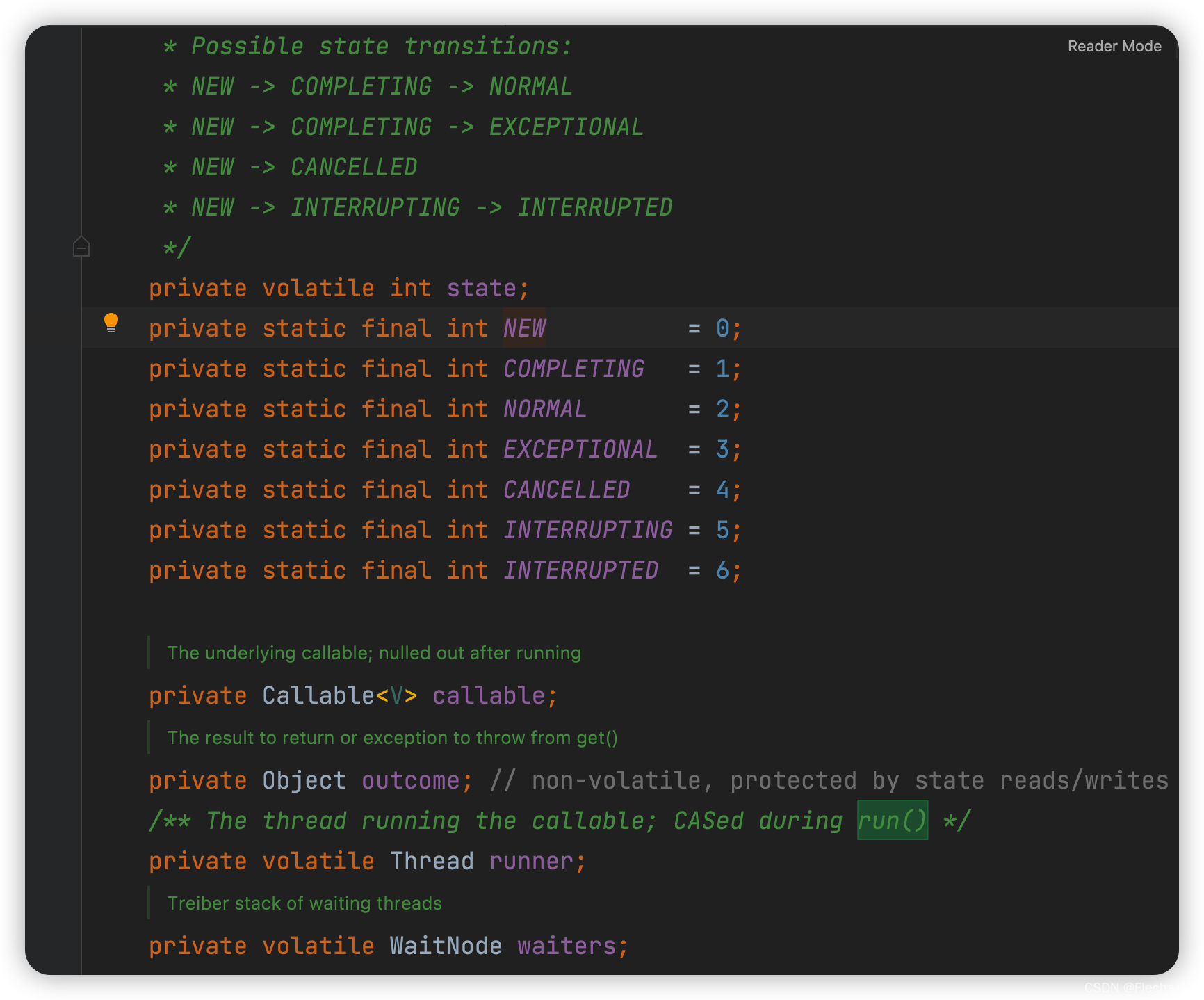
outcome Is the return value of the output
runner Indicates the running thread
waiters Indicates the waiting thread
The second step
run Method run
public void run() {
// Determine whether it is running
if (state != NEW ||
!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,
null, Thread.currentThread()))
return;
try {
//
Callable<V> c = callable;
if (c != null && state == NEW) {
V result;
boolean ran;
try {
// actual The bottom layer is still running call Interface
result = c.call();
// Running state
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
result = null;
ran = false;
// Handling exceptions
setException(ex);
}
if (ran)
//c.call() At the end of the run , Set result
set(result);
}
} finally {
// runner must be non-null until state is settled to
// prevent concurrent calls to run()
runner = null;
// state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent
// leaked interrupts
int s = state;
// If the thread is interrupted
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
}
The setting result sets the thread state to , Also set the value outcome
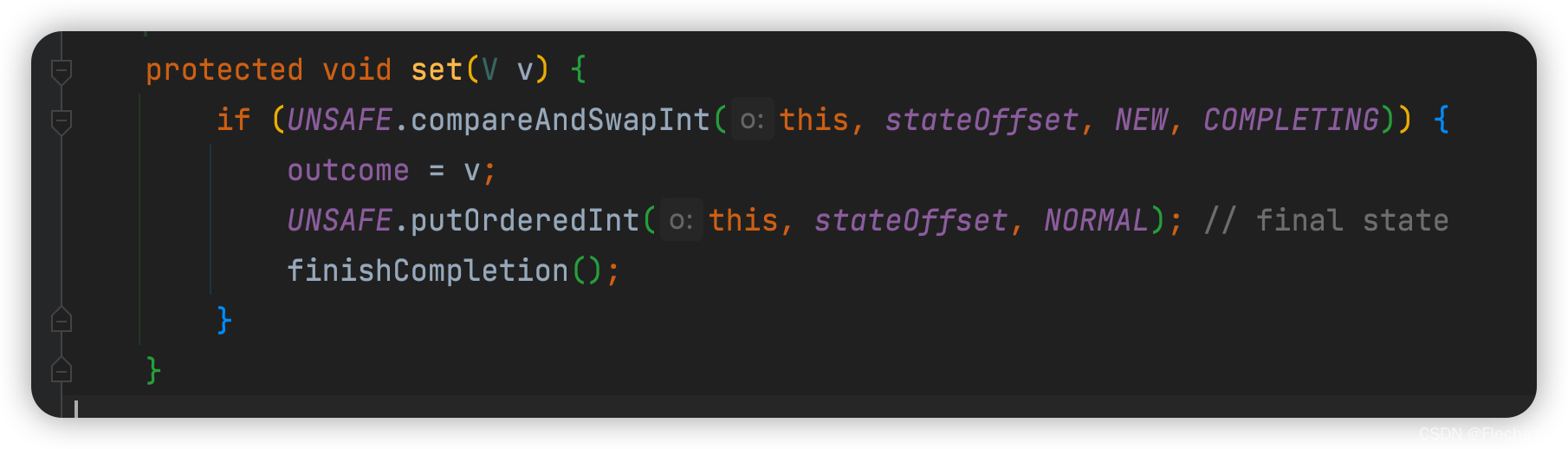
Third parts
get To get the results
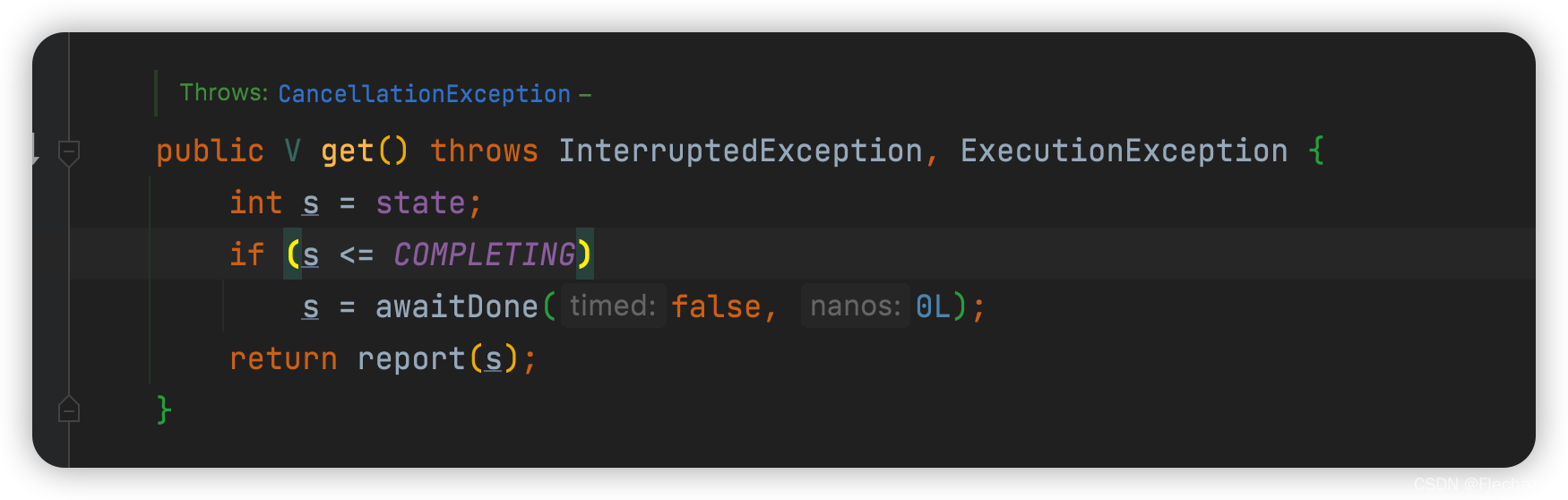
You can see that when the state is not greater than or equal to COMPLETING It will block
private int awaitDone(boolean timed, long nanos)
throws InterruptedException {
final long deadline = timed ? System.nanoTime() + nanos : 0L;
WaitNode q = null;
boolean queued = false;
for (;;) {
// If the thread is interrupted
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
// Waiting to be removed from the queue
removeWaiter(q);
throw new InterruptedException();
}
int s = state;
// Execution completed
if (s > COMPLETING) {
if (q != null)
q.thread = null;
return s;
}
else if (s == COMPLETING) // cannot time out yet
// hand over cpu Executive power Re competition
Thread.yield();
else if (q == null)
q = new WaitNode();
else if (!queued)
// Next thread Wake up the
queued = UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset,
q.next = waiters, q);
else if (timed) {
// Overtime
nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime();
if (nanos <= 0L) {
removeWaiter(q);
return state;
}
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanos);
}
else
LockSupport.park(this);
}
}
Return value Strong transition type
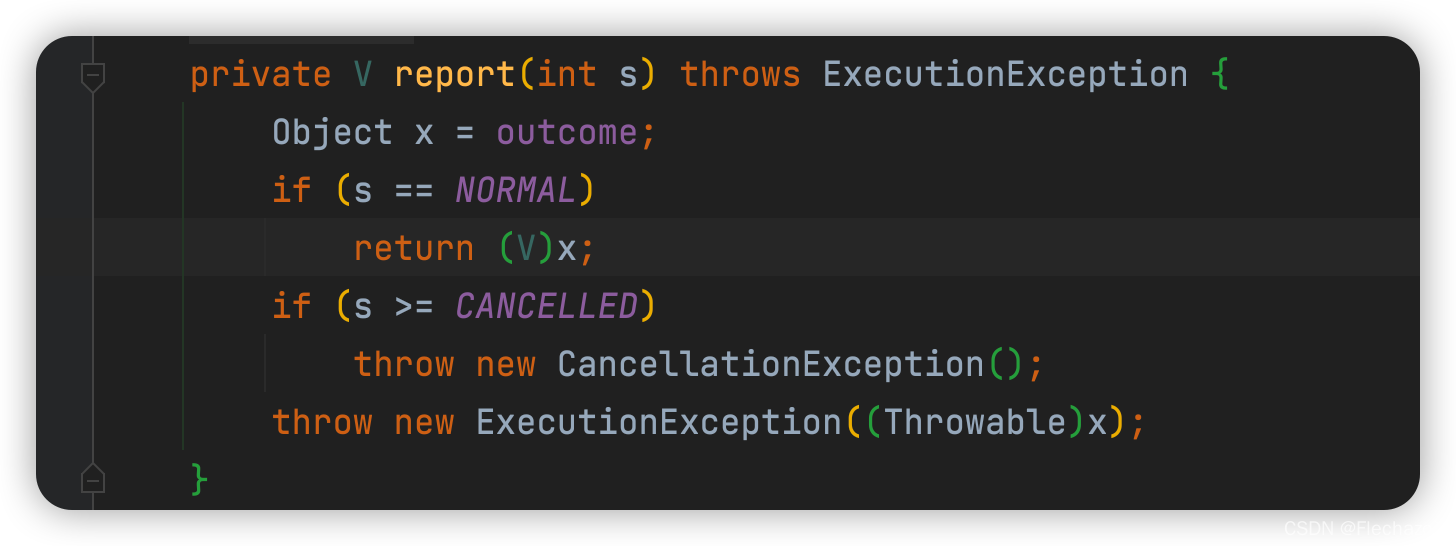
Thread pool return principle
Submit a return task with parameters
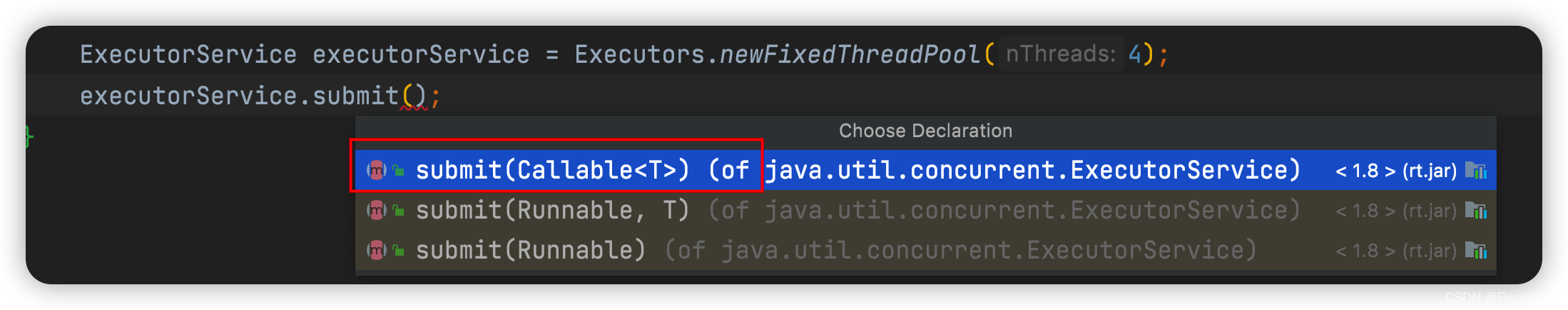
Submission code
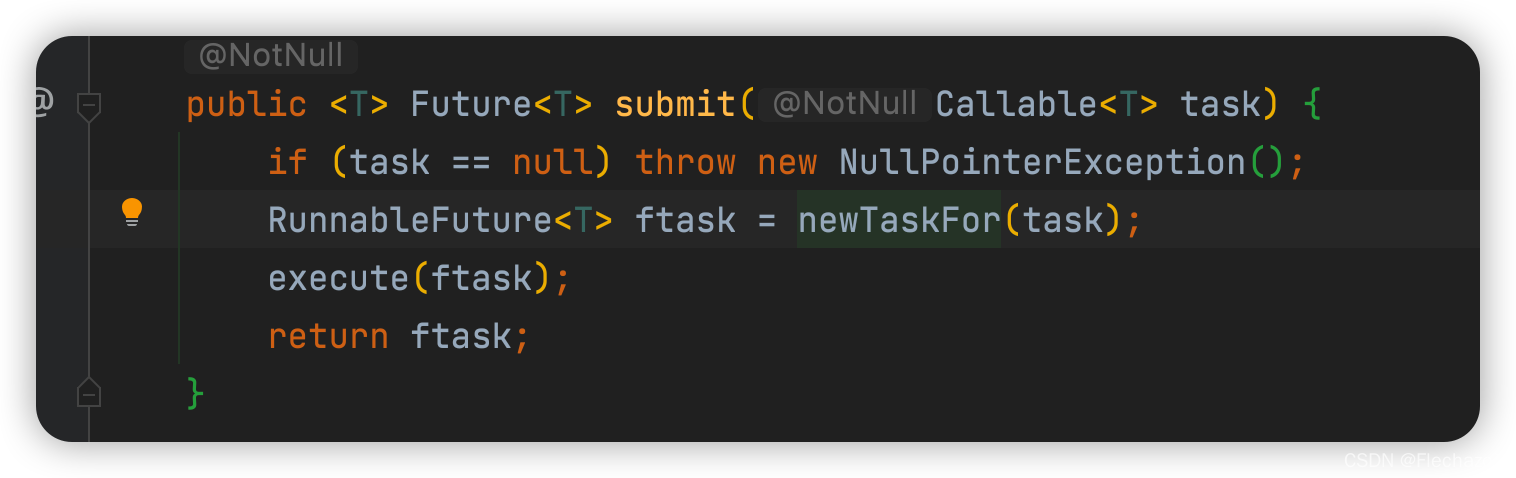
Also to FutureTask To carry out
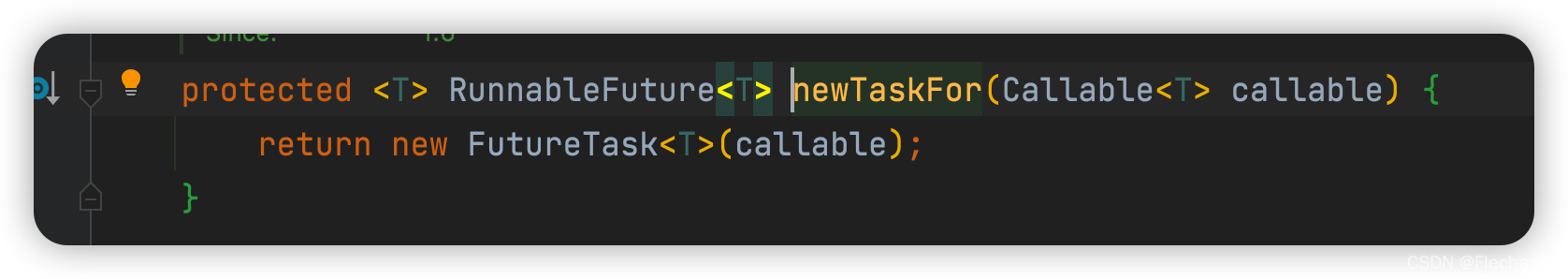
Custom return task value
You can refer to this to implement your own submission
Get data interface
public interface Future<T> {
T get() throws InterruptedException;
}
Do things interface
public interface FutureTask<T> {
T call();
}
Submit processing tasks asynchronously
public class FutureTaskService {
/** * Submit processing tasks asynchronously * @param futureTask * @param <T> * @return */
public <T> Future<T> submit(final FutureTask<T> futureTask){
// Asynchronous return
AysFutureTask<T> aysFutureTask = new AysFutureTask();
// Threads handle tasks
new Thread(()->{
// Perform tasks
T call = futureTask.call();
// Finish the task Notification return
aysFutureTask.done(call);
}).start();
// Asynchronous return
return aysFutureTask;
}
}
test
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
FutureTaskService futureTaskService = new FutureTaskService();
Future<String> submit = futureTaskService.submit(() -> {
// Submit tasks
return doThing();
});
System.out.println(" -------- return ------- ");
System.out.println(" --------- Do something else ----- ");
System.out.println(" --------- do other ----- ");
// obtain The task just submitted
System.out.println(submit.get());
}
/** * Simulate database reading and writing perhaps Network request * @return */
private static String doThing(){
try {
Thread.sleep(5_000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return " Do things ...";
}
}
test result

You can see the task we submitted first , Get the results after handling other things in front , During this period, the task is being carried out , Perform multiple tasks at the same time , Blocking the results at the last moment .
Last
FutureTask yes Future The concrete realization of .
FutureTask Realized RunnableFuture Interface .RunnableFuture The interface also inherits Future and Runnable Interface .
Thread You can submit FutureTask It's actually execution call Method
And then use cas Compare thread status and wait for results
Future Inheritance graph
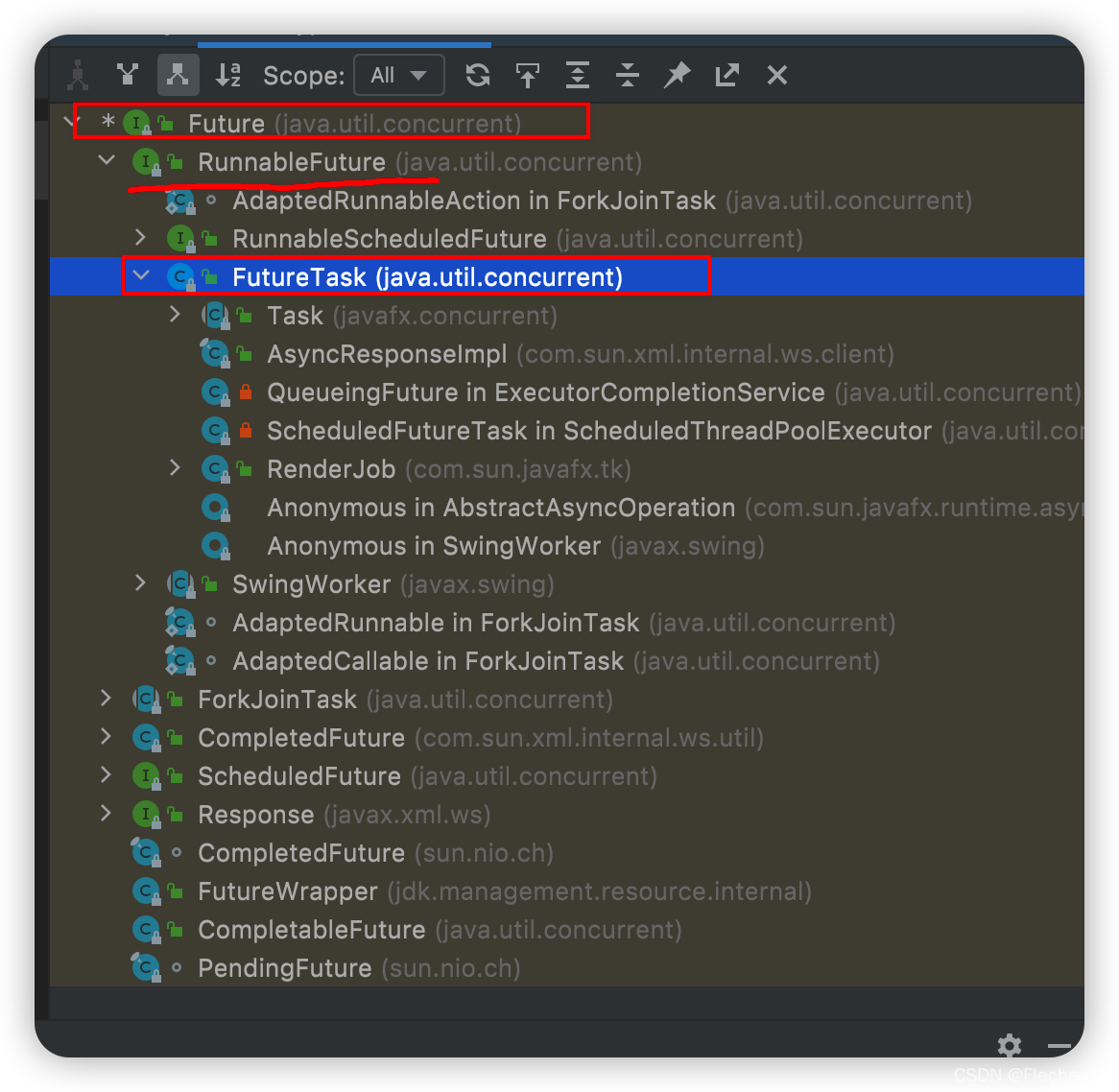
Of course Future There are other extended uses , Such as CompletableFuture etc.
版权声明
本文为[Flechazo`]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204231727205353.html
边栏推荐
- Why do some people say SCM is simple and I have to learn it so hard?
- 圆环回原点问题-字节跳动高频题
- 开期货,开户云安全还是相信期货公司的软件?
- [difference between Oracle and MySQL]
- PC uses wireless network card to connect to mobile phone hotspot. Why can't you surf the Internet
- 386. 字典序排数(中等)-迭代-全排列
- ASP. Net core JWT certification
- Exercise: even sum, threshold segmentation and difference (two basic questions of list object)
- 394. String decoding - auxiliary stack
- Change Oracle to MySQL
猜你喜欢
. net cross platform principle (Part I)
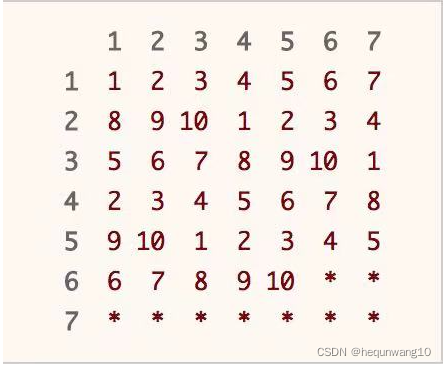
470. 用 Rand7() 实现 Rand10()
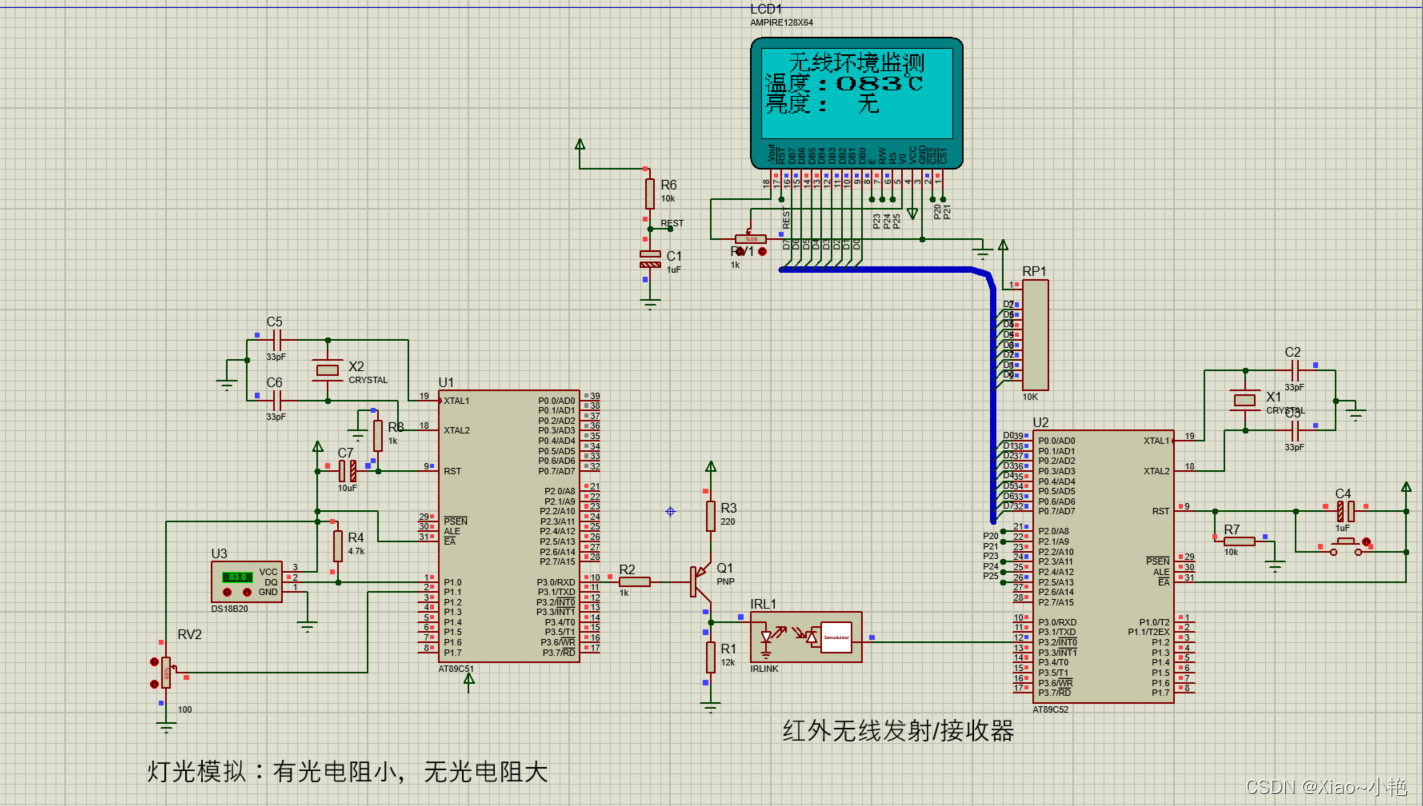
基于51单片机红外无线通讯仿真
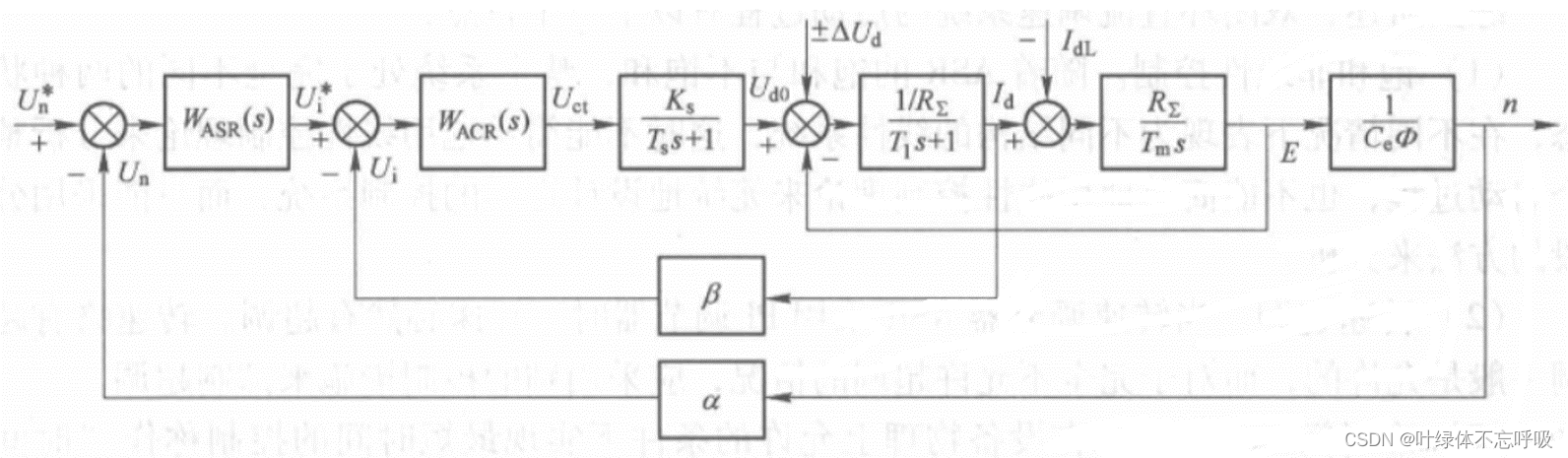
Matlab / Simulink simulation of double closed loop DC speed regulation system
Allowed latency and side output
In embedded system, must the program code in flash be moved to ram to run?
![Using quartz under. Net core - [1] quick start](/img/80/b99417e88d544ca6e3da4c0c1625ce.png)
Using quartz under. Net core - [1] quick start

470. Rand10() is implemented with rand7()
![[logical fallacy in life] Scarecrow fallacy and inability to refute are not proof](/img/71/14a17128dbe0f02edb4db3da479ef2.jpg)
[logical fallacy in life] Scarecrow fallacy and inability to refute are not proof
![Using quartz under. Net core -- job attributes and exceptions of [4] jobs and triggers](/img/ec/43dddd18f0ce215f0f1a781e31f6a8.png)
Using quartz under. Net core -- job attributes and exceptions of [4] jobs and triggers
随机推荐
XTask与Kotlin Coroutine的使用对比
Simulation of infrared wireless communication based on 51 single chip microcomputer
Generating access keys using JSON webtoken
.Net Core3. 1 use razorengine NETCORE production entity generator (MVC web version)
470. Rand10() is implemented with rand7()
Indexes and views in MySQL
ASP. Net core JWT certification
flink 学习(十二)Allowed Lateness和 Side Output
Use of todesk remote control software
[logical fallacy in life] Scarecrow fallacy and inability to refute are not proof
Ouvrir des contrats à terme, ouvrir des comptes en nuage ou faire confiance aux logiciels des sociétés à terme?
EF core in ASP Generate core priority database based on net entity model
Why do some people say SCM is simple and I have to learn it so hard?
Using quartz under. Net core -- a simple trigger of [7] operation and trigger
開期貨,開戶雲安全還是相信期貨公司的軟件?
ASP. NET CORE3. 1. Solution to login failure after identity registers users
ClickHouse-表引擎
C# Task. Delay and thread The difference between sleep
Exercise: even sum, threshold segmentation and difference (two basic questions of list object)
Router object, route object, declarative navigation, programmed navigation