当前位置:网站首页>Eigen learning summary
Eigen learning summary
2022-04-23 17:51:00 【ppipp1109】
Eigen It is provided to users in the form of source code , In use, you only need to include Eigen The header file can be used . The reason for this is , Because Eigen Use template to realize , Because the template function does not support separate compilation , Therefore, we can only provide source code instead of dynamic library for users to use .
Definition of matrix :Eigen In the template function of matrix class , There are six template parameters , Only the first three are commonly used . The first three parameters represent the types of matrix elements 、 Number of rows and columns .
When defining a matrix, you can use Dynamic To indicate that the number of rows and columns of the matrix is unknown .
Eigen Whether matrix or array 、 vector , The default constructor is provided for both static and dynamic matrices , In other words, these data structures can be defined without providing any parameters , Its size is determined by the runtime . Only the number of rows and columns is provided in the constructor of the matrix 、 Construction parameters of element type , Construction that does not provide element values , For smaller 、 A fixed length vector provides the definition of the initialization element .
Matrix type :Eigen Matrix types in are generally similar to MatrixXXX To express , You can judge the data type according to the name , such as ”d” Express double type ,”f” Express float type ,”i” Represents an integer ,”c” In the plural ;Matrix2f, It means a 2*2 Dimensional , Each of its elements is float type .
Some commonly used expressions :
1、 Rotation matrix (3X3):Eigen::Matrix3d
2、 Rotating vector (3X1):Eigen::AngleAxisd
The rotation vector is called the axis angle ;
3、 Four yuan number (4X1):Eigen::Quaterniond
4、 Translation vector (3X1):Eigen::Vector3d
5、 Transformation matrix (4X4):Eigen::Isometry3d
6、 Rotate counterclockwise around this axis angle(rad):AngleAxis(angle, axis)angle(rad) Indicates that the rotation angle is... By default : Radian system
7、 Transformation matrix :
Eigen::Isometry3d T;
T.matrix() Is the transformation matrix , You need to add .matrix() suffix ;
T.pretranslate() as well as T.rotate() You can assign values to the translation part and the rotation matrix , But if used in a loop , If the transformation matrix is not reset at the end , This setting will add up , Instead of covering .
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <ctime>
// Eigen part
#include <Eigen/Core>
// Algebraic operation of dense matrix ( The inverse , Eigenvalues, etc )
#include <Eigen/Dense>
#define MATRIX_SIZE 50
/****************************
* This program demonstrates Eigen Use of basic types
****************************/
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
// Eigen All vectors and matrices in are Eigen::Matrix, It's a template class . Its first three parameters are : data type , That's ok , Column
// Make a statement 2*3 Of float matrix
Eigen::Matrix<float, 2, 3> matrix_23;
// meanwhile ,Eigen adopt typedef There are many built-in types , But the bottom is still Eigen::Matrix
// for example Vector3d Is essentially Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 1>, Three dimensional vector
Eigen::Vector3d v_3d;
// It's the same
Eigen::Matrix<float,3,1> vd_3d;
// Matrix3d Is essentially Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 3>
Eigen::Matrix3d matrix_33 = Eigen::Matrix3d::Zero(); // Initialize to zero
// If you're not sure about the size of the matrix , Dynamic size matrices can be used
Eigen::Matrix< double, Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::Dynamic > matrix_dynamic;
// Simpler
Eigen::MatrixXd matrix_x;
// There are many more of this type , We don't list them one by one
// The following is true. Eigen Operation of array
// input data ( initialization )
matrix_23 << 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6;
// Output
cout << matrix_23 << endl;
// use () Access the elements in the matrix
for (int i=0; i<2; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<3; j++)
cout<<matrix_23(i,j)<<"\t";
cout<<endl;
}
// Matrix and vector multiply ( In fact, it is still matrix and matrix )
v_3d << 3, 2, 1;
vd_3d << 4,5,6;
// But in Eigen You can't mix two different types of matrices , It's wrong to be like this
// Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 1> result_wrong_type = matrix_23 * v_3d;
// You should explicitly convert
Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 1> result = matrix_23.cast<double>() * v_3d;
cout << result << endl;
Eigen::Matrix<float, 2, 1> result2 = matrix_23 * vd_3d;
cout << result2 << endl;
// Again, you can't get the dimensions of the matrix wrong
// Try to cancel the comment below , have a look Eigen What's wrong
// Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 3> result_wrong_dimension = matrix_23.cast<double>() * v_3d;
// Some matrix operations
// Four operations will not be demonstrated , Direct use +-*/ that will do .
matrix_33 = Eigen::Matrix3d::Random(); // Random number matrix
cout << matrix_33 << endl << endl;
cout << matrix_33.transpose() << endl; // Transposition
cout << matrix_33.sum() << endl; // The elements and
cout << matrix_33.trace() << endl; // trace
cout << 10*matrix_33 << endl; // Number multiplication
cout << matrix_33.inverse() << endl; // The inverse
cout << matrix_33.determinant() << endl; // determinant
// The eigenvalue
// Real symmetric matrix can guarantee the success of diagonalization
Eigen::SelfAdjointEigenSolver<Eigen::Matrix3d> eigen_solver ( matrix_33.transpose()*matrix_33 );
cout << "Eigen values = \n" << eigen_solver.eigenvalues() << endl;
cout << "Eigen vectors = \n" << eigen_solver.eigenvectors() << endl;
// solve equations
// We solve it matrix_NN * x = v_Nd This equation
// N The size of is defined in the previous macro , It is generated from random numbers
// Direct inversion is naturally the most direct , But the amount of inversion is large
Eigen::Matrix< double, MATRIX_SIZE, MATRIX_SIZE > matrix_NN;
matrix_NN = Eigen::MatrixXd::Random( MATRIX_SIZE, MATRIX_SIZE );
Eigen::Matrix< double, MATRIX_SIZE, 1> v_Nd;
v_Nd = Eigen::MatrixXd::Random( MATRIX_SIZE,1 );
clock_t time_stt = clock(); // timing
// Direct inversion
Eigen::Matrix<double,MATRIX_SIZE,1> x = matrix_NN.inverse()*v_Nd;
cout <<"time use in normal inverse is " << 1000* (clock() - time_stt)/(double)CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "ms"<< endl;
// Matrix decomposition is usually used to find , for example QR decompose , It's going to be a lot faster
time_stt = clock();
x = matrix_NN.colPivHouseholderQr().solve(v_Nd);
cout <<"time use in Qr decomposition is " <<1000* (clock() - time_stt)/(double)CLOCKS_PER_SEC <<"ms" << endl;
return 0;
}
data storage :Matrix The created matrix is stored by column by default ,Eigen It is more efficient when dealing with matrices stored by column . If you want to modify, you can add parameters when creating the matrix , Such as :
Matrix<int,3, 4, ColMajor> Acolmajor;
Matrix<int,3, 4, RowMajor> Arowmajor;
Dynamic matrix and static matrix : A dynamic matrix is one whose size is determined at run time , A static matrix is one whose size is determined at compile time .
MatrixXd: Indicates that the element type of any size is double Matrix variable of , Its size can only be known after it is assigned at run time .
Matrix3d: Indicates that the element type is double The size is 3*3 Matrix variable of , Its size is known at compile time .
stay Eigen The Bank of China priority matrix will include in its name row, Otherwise, it is column priority .
Eigen The vector in is just a special matrix , Its dimension is 1 nothing more .
Access to matrix elements : In the access to the matrix , The row index is always used as the first parameter ,Eigen Medium matrix 、 Array 、 The subscripts of vectors are from 0 Start . Matrix elements can be accessed through ”()” The operator completes . for example m(2, 3) Is to get the matrix m Of the 2 Xing di 3 Column elements .
For vectors, we also provide ”[]” The operator , Note that the matrix cannot be used in this way .
Set the elements of the matrix : stay Eigen It's overloaded ”<<” The operator , Through this operator, you can assign values one by one , You can also assign values one by one . In addition, subscripts can also be used for assignment .
Reset matrix size : The number of rows of the current matrix 、 Number of columns 、 The size can be determined by rows()、cols() and size() To get , For dynamic matrices, you can use resize() Function to dynamically modify the size of the matrix . Be careful :(1)、 Fixed size matrices cannot be used resize() To change the size of the matrix ;(2)、resize() Function will destruct the original data , So call resize() After the function, there is no guarantee that the value of the element will not change ;(3)、 Use ”=” When an operator operates on a dynamic matrix , If the matrices on the left and right are of different sizes , Then the size of the dynamic matrix on the left will be changed to the size on the right .
How to choose dynamic matrix and static matrix : For small matrices ( The general size is less than 16) Use a static matrix of fixed size , It can bring higher efficiency ; For large matrices ( Generally larger than 32) Dynamic matrix is recommended . Be careful : If a static matrix with a fixed size is used for a particularly large matrix, it may cause the problem of stack overflow .
Arithmetic operations of matrices and vectors : stay Eigen The arithmetic operation in is overloaded C++ Of +、-、*
(1)、 Matrix operation : Provide +、-、 Unary operators ”-”、+=、-=; Binary operators +/-, Represents the addition of two matrices ( The corresponding elements in the matrix are added / reduce , Return a temporary matrix ); Unary operators - Means taking a negative matrix ( The corresponding element in the matrix is negative , Return a temporary matrix ); Combined operation method += perhaps -= Express ( Do the corresponding operation for each element ); Matrices are also provided with scalars ( A single number ) Multiplication and division of , Indicates that each element multiplies and divides with the scalar ;
(2)、 Transpose matrix 、 Conjugate matrix 、 Adjoint matrix : You can use the member function transpose()、conjugate()、adjoint() To complete . Be careful : These functions return the results of the operation , Instead of directly manipulating the elements of the original matrix , If you want to convert the original matrix , You need to use the response InPlace function , Such as transpoceInPlace() etc. ;
(3)、 matrix multiplication 、 Matrix vector multiplication : Using operators *, share * and *= Two operators ;
(4)、 Block operation of matrix : There are two ways to use it :
matrix.block(i,j, p, q) : Represents the return from the matrix (i, j) Start , Fetch per line p Elements , Per column q A temporary new matrix object composed of elements , The elements of the original matrix remain unchanged ;
matrix.block<p,q>(i, j) :<p, q> It can be understood as a p That's ok q The submatrix of a column , This definition represents the first... From the original matrix (i, j) Start , Get one p That's ok q The submatrix of a column , Returns the temporary Matrix object composed of the sub matrix , The elements of the original matrix remain unchanged ;
#include <iostream>
#include <eigen3/Eigen/Dense>
using namespace Eigen;
using namespace std;
int main(int argc ,char** argv)
{
MatrixXf m(4,4);
m << 1,2,3,4,
5,6,7,8,
9,10,11,12,
13,14,15,16;
cout<<"Block in the middle"<<endl;
cout<<m.block<2,2>(1,1)<<endl<<endl;
for(int i = 1; i <= 3; ++i)
{
cout<<"Block of size "<<i<<" x "<<i<<endl;
cout<<m.block(0,0,i,i)<<endl<<endl;
}
return 0;
(5)、 Block operation of vector :
Get the front of the vector n Elements :vector.head(n);
Get the end of the vector n Elements :vector.tail(n);
Gets the number... From the vector i Elements start with n Elements :vector.segment(i,n);
Map class : In an existing matrix or vector , You don't have to copy objects , Instead, the operation is performed directly on the memory of the object .
Reference link :
https://eigen.tuxfamily.org/dox/
https://blog.csdn.net/lievech/article/details/115399862
版权声明
本文为[ppipp1109]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204230549076221.html
边栏推荐
- 122. 买卖股票的最佳时机 II-一次遍历
- Cross domain settings of Chrome browser -- including new and old versions
- JS get link? The following parameter name or value, according to the URL? Judge the parameters after
- 云原生虚拟化:基于 Kubevirt 构建边缘计算实例
- C1小笔记【任务训练篇二】
- Halo 开源项目学习(二):实体类与数据表
- vite配置proxy代理解决跨域
- Compilation principle first set follow set select set prediction analysis table to judge whether the symbol string conforms to the grammar definition (with source code!!!)
- 2021长城杯WP
- Vite configure proxy proxy to solve cross domain
猜你喜欢

440. The k-th small number of dictionary order (difficult) - dictionary tree - number node - byte skipping high-frequency question
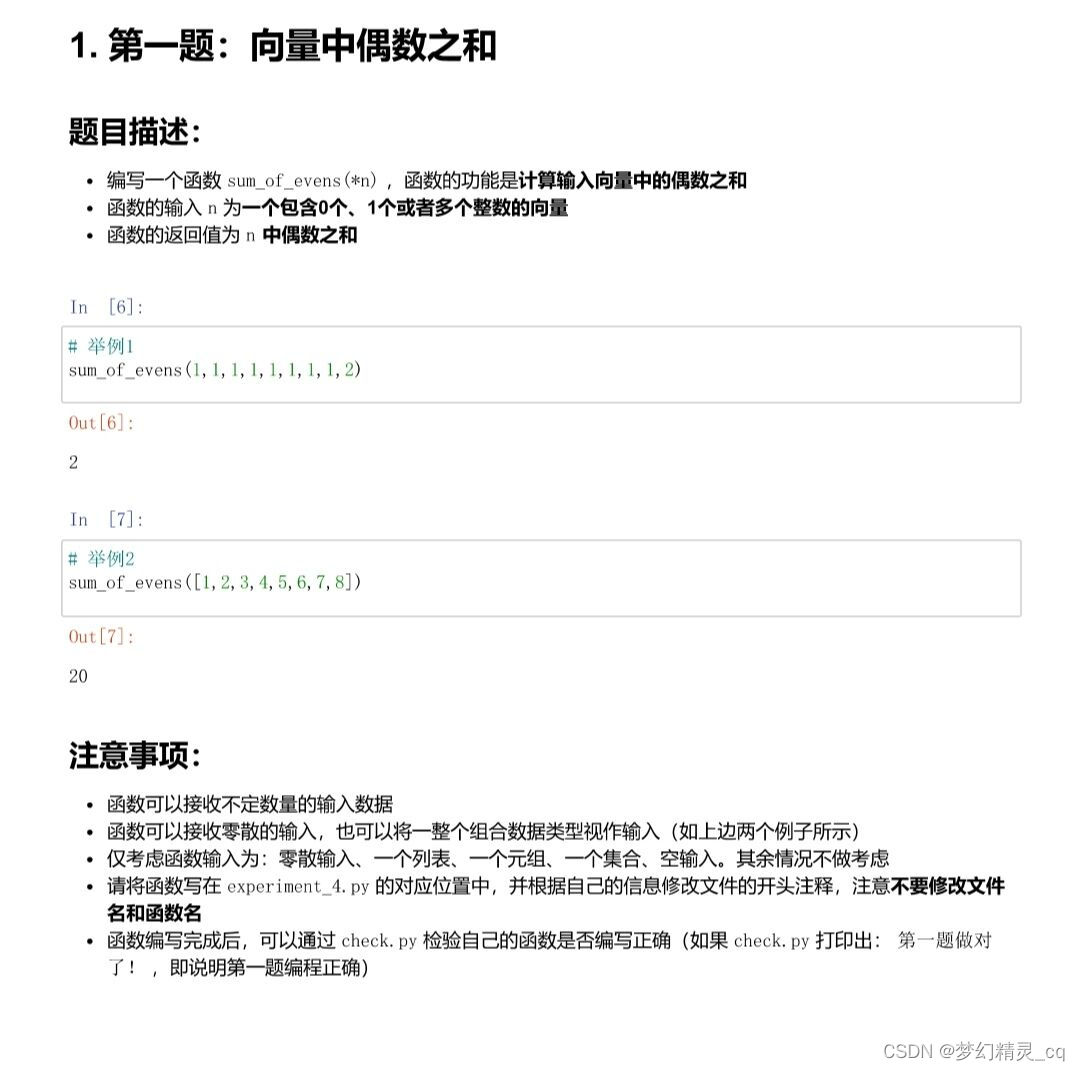
练习:求偶数和、阈值分割和求差( list 对象的两个基础小题)
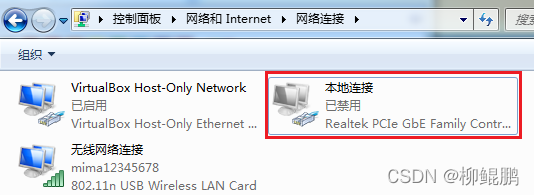
PC uses wireless network card to connect to mobile phone hotspot. Why can't you surf the Internet

Compilation principle first set follow set select set prediction analysis table to judge whether the symbol string conforms to the grammar definition (with source code!!!)
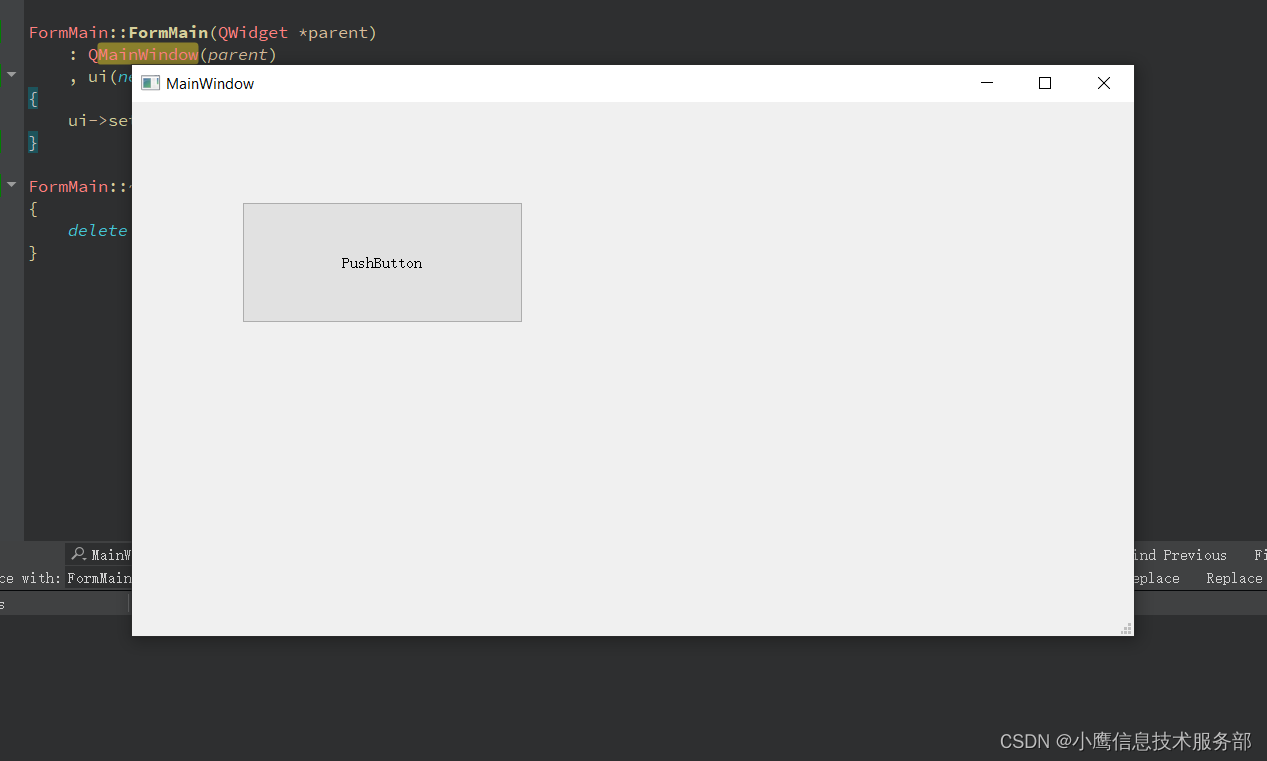
Qt 修改UI没有生效
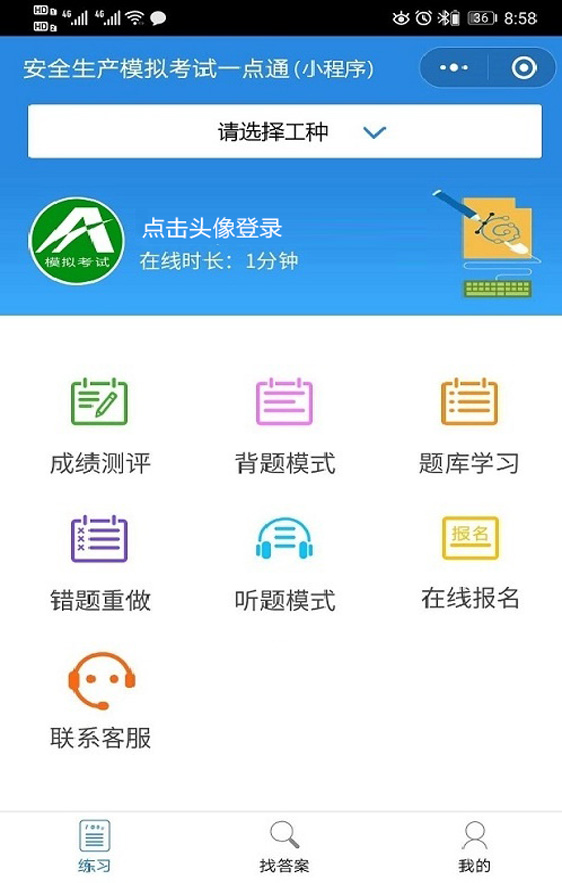
Operation of 2022 mobile crane driver national question bank simulation examination platform
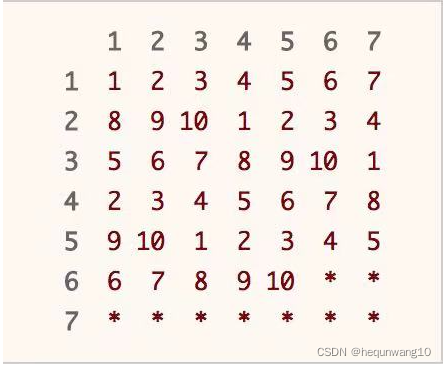
470. 用 Rand7() 实现 Rand10()

2022年流动式起重机司机国家题库模拟考试平台操作
C1小笔记【任务训练篇二】
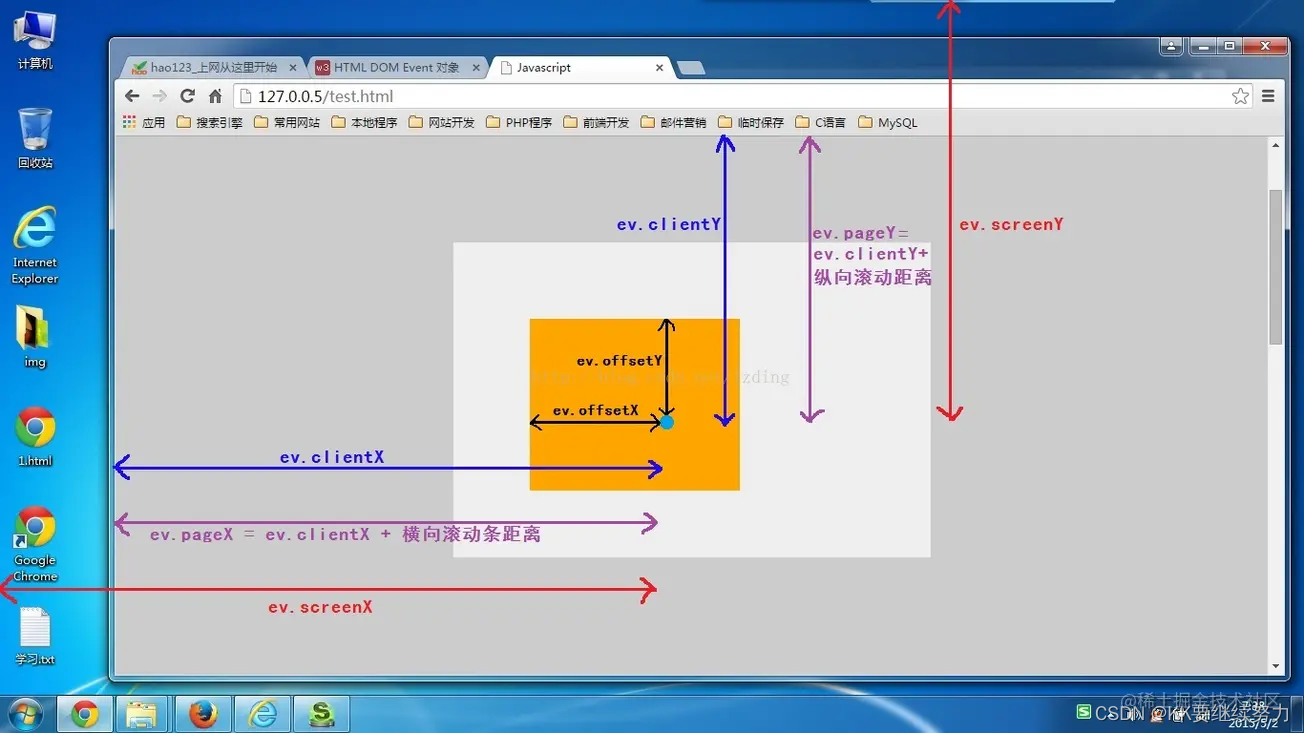
Element calculation distance and event object
随机推荐
1217_ Generating target files using scons
122. The best time to buy and sell stocks II - one-time traversal
開期貨,開戶雲安全還是相信期貨公司的軟件?
一些问题一些问题一些问题一些问题
2021长城杯WP
Exercise: even sum, threshold segmentation and difference (two basic questions of list object)
Write a regular
In ancient Egypt and Greece, what base system was used in mathematics
圆环回原点问题-字节跳动高频题
MySQL advanced index [classification, performance analysis, use, design principles]
102. Sequence traversal of binary tree
On the problem of V-IF display and hiding
Flask项目的部署详解
Qt error: /usr/bin/ld: cannot find -lGL: No such file or directory
386. 字典序排数(中等)-迭代-全排列
JS get link? The following parameter name or value, according to the URL? Judge the parameters after
双指针进阶--leetcode题目--盛最多水的容器
Halo open source project learning (II): entity classes and data tables
Special effects case collection: mouse planet small tail
Land cover / use data product download