当前位置:网站首页>Creation of RAID disk array and RAID5
Creation of RAID disk array and RAID5
2022-04-23 16:27:00 【qjwthink】
Catalog
One 、RAID Disk array Introduction
2、RAID 0 Disk array Introduction
3、RAID1 Disk array Introduction
4、RAID 5 Disk array Introduction
5、RAID 6 Disk array Introduction
6、RAID 1+0 Disk array Introduction
3、 ... and 、RAID5 The creation of
One 、RAID Disk array Introduction
yes Redundant Array of Independent Disks Abbreviation , Chinese abbreviation is independent redundant disk array
Combine multiple independent physical hard disks in different ways to form a hard disk group ( Logical hard disk ), So as to provide higher storage performance than a single hard disk and provide data backup technology
The different ways to make up a disk array are called RAID Level (RAID Levels)
Two 、 frequently-used RAID
1、 frequently-used RAID Level
RAID0,RAID1,RAID5,RAID6,RAID1+0 etc.
2、RAID 0 Disk array Introduction
RAID 0
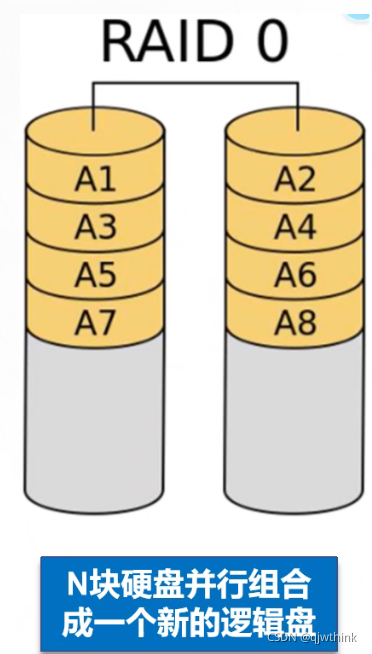
1、RAID 0 Divide data continuously in bits or bytes , Read in parallel / Write on multiple disks , Therefore, it has high data transmission rate , But it has no data redundancy
2、RAID 0 Just to improve the performance , There is no guarantee for the reliability of the data , And a disk failure will affect all data
3、RAID 0 It can't be used in the situation with high data security requirements
3、RAID1 Disk array Introduction
RAID 1
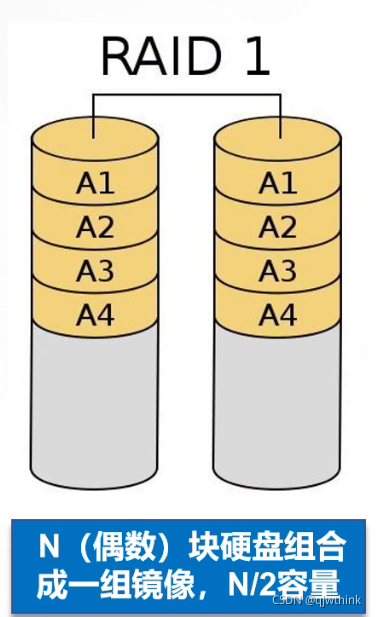
1、 Realize data redundancy through disk data mirroring , Generate backup data on a pair of independent disks
2、 When raw data is busy , Data can be read directly from the mirror copy , therefore RAID 1 Can improve read performance
3、RAID1 It's the highest cost per unit in a disk array , But it provides high data security and availability . When a disk fails , The system can automatically switch to read and write on the mirror disk , And there's no need to reorganize failed data
4、RAID 5 Disk array Introduction
RAID 5
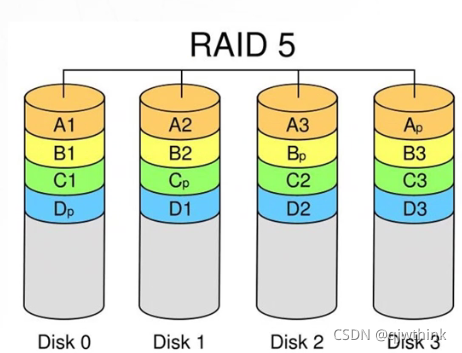
1、N(N>=3) The disks form an array , A data generation N-1 A strip , As well as 1 Check data , common N The data is in N Cycle balanced storage on the block disk
2、N Read and write at the same time , High reading performance , But because of the problem of checking mechanism , Write performance is relatively low
3、(N-1)/N Disk utilization
4、 High reliability , Allow bad 1 Block plate , It doesn't affect all the data
5、RAID 6 Disk array Introduction
RAID 6
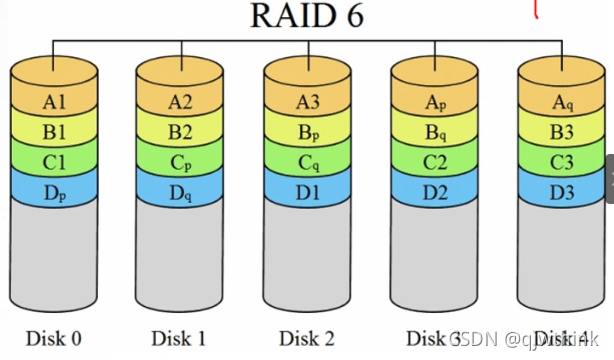
1、N(N>=4) The disks form an array ,(N-2)/N Disk utilization
2、 And RAID 5 comparison ,RAID 6 A second independent parity block is added
3、 Two independent parity systems use different algorithms , Even if two disks fail at the same time, data usage will not be affected
4、 be relative to RAID 5 There are bigger ones “ Write loss “, Therefore, the write performance is poor
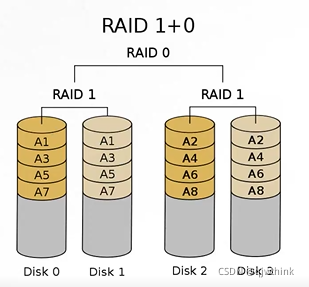
6、RAID 1+0 Disk array Introduction
RAID 1+0
1、N( even numbers ,N>=4) After two disks are mirrored , Then combine it into a RAID 0
2、N/2 Disk utilization
3、N/2 All disks are written simultaneously ,N All disks are read at the same time
4、 High performance , High reliability
7、 Array card introduction
Array cards are used to implement RAID Function board
Is usually I/O processor 、 Hard disk controller 、 It is composed of a series of components such as hard disk connector and cache
Different RAID Card supported RAID Different functions
For example, support RAIDO、RAID1、RAID5、RAID10 etc.
RAID The interface type of the card
IDE Interface 、SCSI Interface 、SATA Interface and SAS Interface
8、 Array card cache
1、 cache (Cache) yes RAID The place where the card exchanges data with the external bus ,RAID The card transfers the data to the cache first , Then the data is exchanged between the cache and the external data bus
2、 The size and speed of the cache are directly related to RAID The actual transmission speed of the card is an important factor
3、 Different RAID The memory capacity of the card is different when it is delivered from the factory , Generally, the capacity varies from a few megabytes to hundreds of megabytes
3、 ... and 、RAID5 The creation of
Start operation preparation first
Add four hard disks to the virtual machine
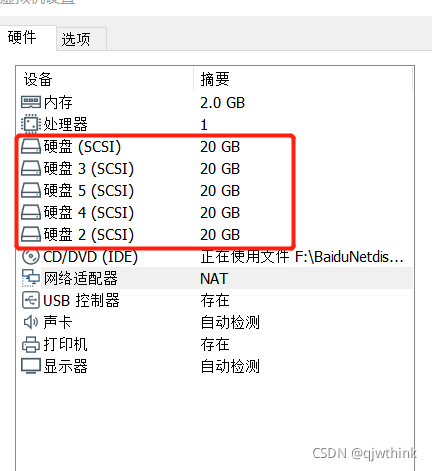
1、 Check that... Is installed mdadm software package
rpm -q mdadm
yum install -y mdadm
![]()
2、 Use fdisk. The tool will the new disk device /dev/sdb、 /dev/sdc、 /dev/sdd、 /dev/sde
Divide the main partition sdb1、sdc1、 sdd1、 sde1, also
Put the partition type ID Change the tag number to "fd”
fdisk /dev/sdb
fdisk /dev/sdc
fdisk /dev/sdd
fdisk /dev/sde
for example :fdisk /dev/sde

The establishment can be completed through fdisk -l Check it out.

3、 establish RAID equipment
# establish RAID5
mdadm -C -v /dev/md0 -15 -n3 /dev/sd[bcd]1 -x1 /dev/sde1
Command word raid name Level -n Number of disks /dev/sde1 /dev/sdd1 Hot standby Partition device of hot spare

-C: Means new ;
-v: Show details of the creation process .
/dev/md5: establish RAID5 The name of .
-l: Appoint RAID The level of ,15 Representation creation RAID5..
-n: Specify how many hard disks to use to create RAID, n3 Said the use of 3 Block hard disk creation RAID.
/dev/sd [bcd]1: Specify to use this 3 Block disk partition to create RAID.
-x: Specify how many hard disks to use RAID Hot spare for ,x1 Express reservation 1 Spare a spare hard disk
/dev/sde1: Specify the disk to use as a spare
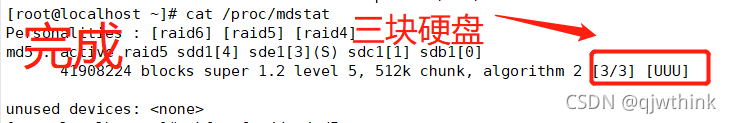
see RAID Disk details
cat /proc/mdstat # You can also view and create RAID Progress

perhaps
mdadm -D /dev/md0

# use watch Command to every - Refresh for a while /proc/mdstat The loss of Out
watch -n 10 ' cat /proc/mdstat '
# Check if the disk is EL do RAID.
mdadm -E /dev/sd[b-e] 1
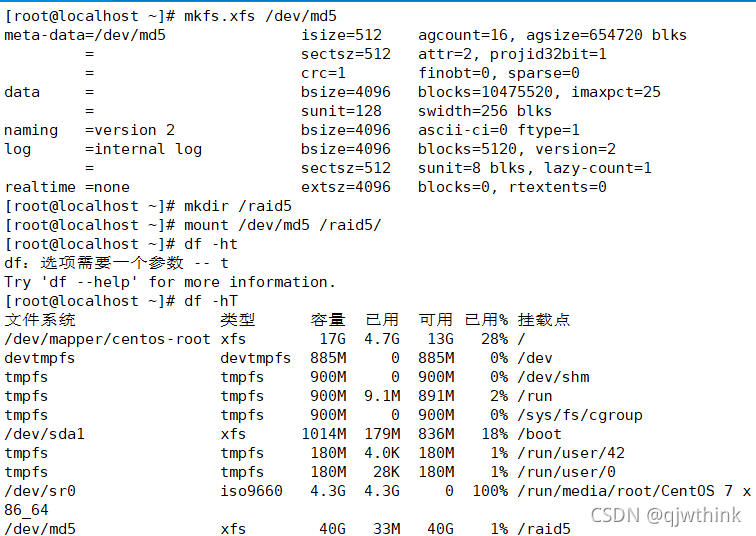
4、 Create and mount file systems
mkfs -t xfs /dev/imd0
mkdir /myraid
mount /dev/md0 /myraid/
df -Th
Or do permanent mount
cp /etc/ fstab /etc/fstab.bak Backup
vim /etc/fstab Get into /etc/fstab Enter the following
/dev/md0 /myraid xfs defaults 0 0
mount -a
df -Th
5、 Achieve fault recovery
mdadm /dev/md0 -f /dev/sdb1 # simulation /dev/sdb1 fault
![]()
mdadm -D /dev/md0 # View discovery sde1 Replaced sdb1, Be careful to wait a little
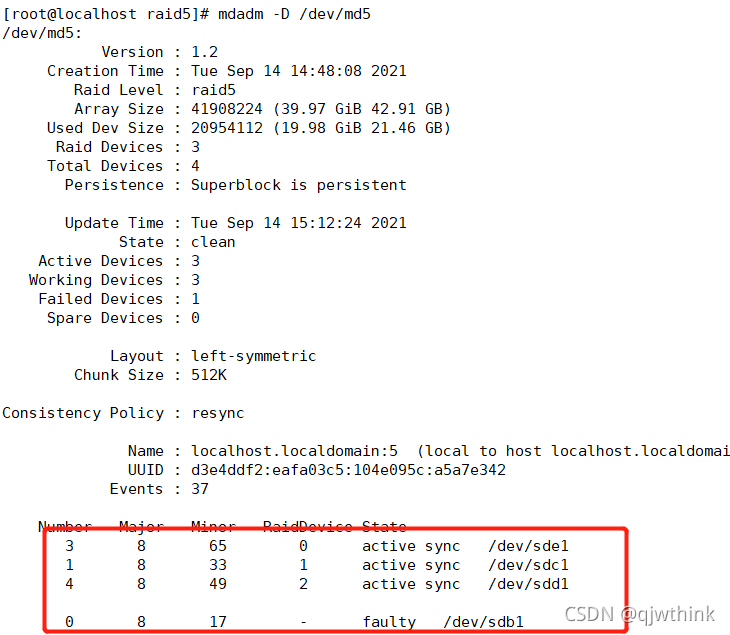
Repair process
mdadm /dev/md0 -r /dev/sdb1 Remove the device
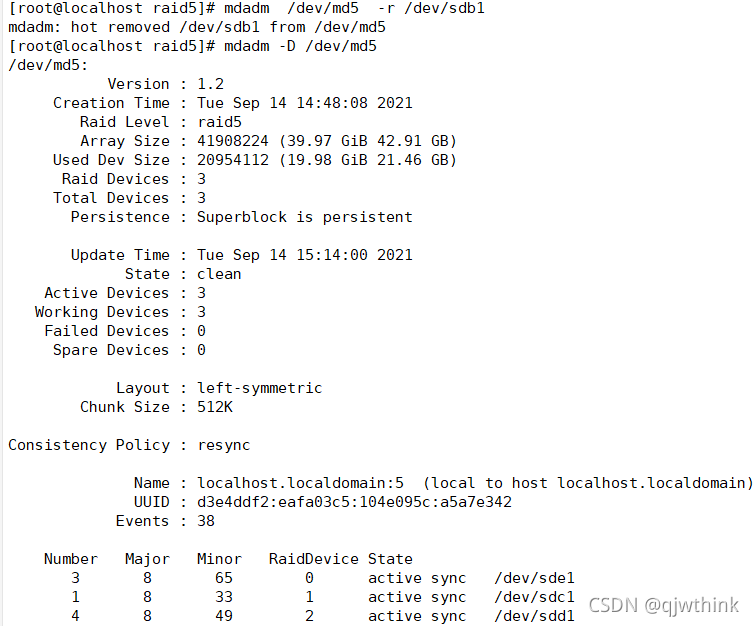
mdadm /dev/md0 -a /dev/ sdb1 Add equipment
![]()
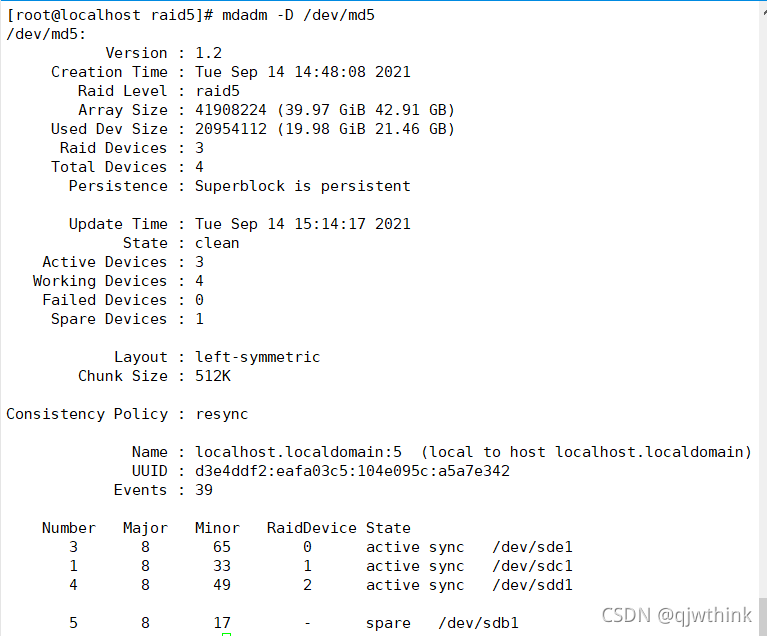
RAID summary
RAID
RAID Level Number of hard disks Disk utilization Whether there is verification The ability to protect Write performance
RAID0 N( It can be for 1) N nothing nothing Of a single hard disk N times
RAID1 N( even numbers ) N/2. nothing Allow one - Device failure You need to write two pairs of storage devices , Prepare for each other
RAID5 N>=3 (N-1) /N Yes Allow a device failure Need to write calculation verification
RAID6 N>=4 (N-2) /N Yes Two equipment failures are allowed Double write calculation verification is required
RAID10 N>=4( even numbers ) N/2 nothing Allow one of the two base groups to be bad N/2 block The disk is written simultaneously
The probability that two disks will not lose data at the same time is 3 Divided 2
版权声明
本文为[qjwthink]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204231624474087.html
边栏推荐
- 七朋元视界可信元宇宙社交体系满足多元化的消费以及社交需求
- 安装及管理程序
- 05 Lua control structure
- GRBL学习(二)
- 磁盘管理与文件系统
- Cartoon: what are IAAs, PAAS, SaaS?
- MySQL - execution process of MySQL query statement
- RecyclerView advanced use - to realize drag and drop function of imitation Alipay menu edit page
- Start Oracle service on Linux
- 100 deep learning cases | day 41 - convolutional neural network (CNN): urbansound 8K audio classification (speech recognition)
猜你喜欢
![[pyGame games] how did angry birds, a mobile game that became popular all over the world 10 years ago, dominate the list? Classic return](/img/f5/15b3731e75eb4d861bd9d29ae244da.png)
[pyGame games] how did angry birds, a mobile game that became popular all over the world 10 years ago, dominate the list? Classic return
Ali developed three sides, and the interviewer's set of combined punches made me confused on the spot
Ice -- source code analysis
JMeter setting environment variable supports direct startup by entering JMeter in any terminal directory
Phpstudy V8, a commonly used software for station construction 1 graphic installation tutorial (Windows version) super detailed
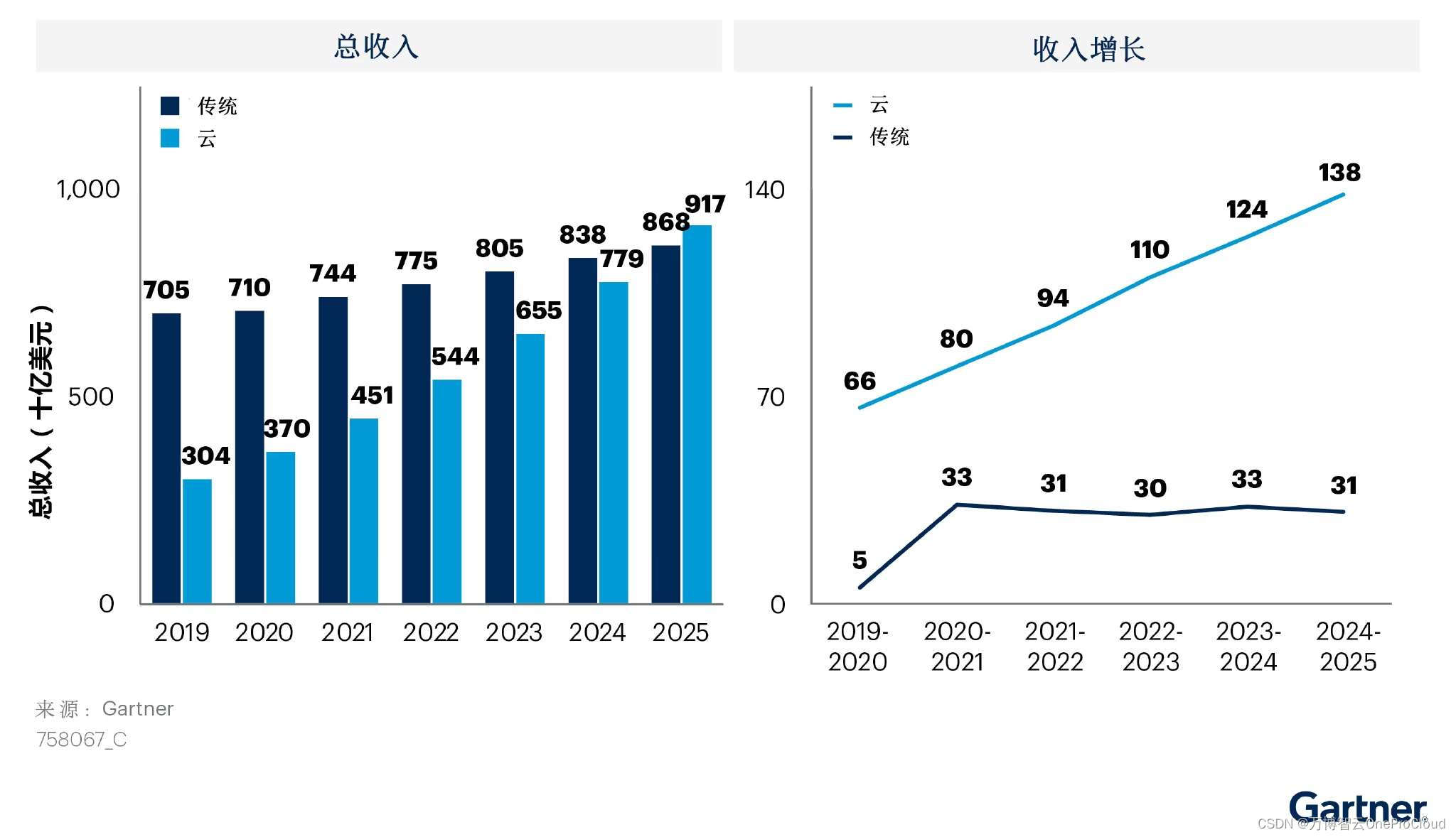
Gartner predicts that the scale of cloud migration will increase significantly; What are the advantages of cloud migration?
Matplotlib tutorial 05 --- operating images
Using JSON server to create server requests locally
Gartner 发布新兴技术研究:深入洞悉元宇宙
GRBL学习(一)
随机推荐
G008-hwy-cc-estor-04 Huawei Dorado V6 storage simulator configuration
RecyclerView advanced use - to realize drag and drop function of imitation Alipay menu edit page
What does cloud disaster tolerance mean? What is the difference between cloud disaster tolerance and traditional disaster tolerance?
VIM uses vundle to install the code completion plug-in (youcompleteme)
Hypermotion cloud migration completes Alibaba cloud proprietary cloud product ecological integration certification
【Pygame小游戏】10年前风靡全球的手游《愤怒的小鸟》,是如何霸榜的?经典回归......
撿起MATLAB的第(9)天
5分钟NLP:Text-To-Text Transfer Transformer (T5)统一的文本到文本任务模型
04 Lua 运算符
最詳細的背包問題!!!
TIA博图——基本操作
Download and install mongodb
C language self compiled string processing function - string segmentation, string filling, etc
Grbl learning (I)
JMeter setting environment variable supports direct startup by entering JMeter in any terminal directory
Day (3) of picking up matlab
Nacos detailed explanation, something
Change the icon size of PLSQL toolbar
Hyperbdr cloud disaster recovery v3 Release of version 3.0 | upgrade of disaster recovery function and optimization of resource group management function
Jour (9) de ramassage de MATLAB