当前位置:网站首页>C# Task. Delay and thread The difference between sleep
C# Task. Delay and thread The difference between sleep
2022-04-23 17:04:00 【begeneral】
We all know Task.Delay It's asynchronous waiting ,Thread.Sleep Is synchronization waiting , What's the difference between synchronous wait and asynchronous wait ?
Let's use an example to analyze , Create a new console application , The code is as follows :
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
var s = await MyTask();
Console.WriteLine(s);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
static async Task<string> MyTask()
{
var s = await Run();
Console.WriteLine("MyTask");
return s;
}
static async Task<string> Run()
{
await Task.Delay(5000);
Console.WriteLine("Run");
return await Task.FromResult("Run");
}The operation results are as follows :

Only the final running result can be seen here , Can't see the execution process . The execution process is : When the program runs , too 5 Second , Print out Run, And then it's printed MyTask and Run, Then cycle like this 4 Time . Now let's put Run Method Task.Delay Switch to Thread.Sleep, It is found that the execution process is the same . I won't write here , You can try it on your own .
Does that mean Task.Delay and Thread.Sleep It makes no difference , The answer must be No . Because we use 2 individual await,await The function of is to wait for the task to be completed , Don't believe it , We put Run Method Task.Delay(5000) Of await Get rid of , Run the program again , Found that the program didn't wait .
Let's put Run Method Task.Delay Replace with Thread.Sleep, The discovery program will still wait . because Thread.Sleep Is synchronization waiting , No matter where the program runs , Just meet Thread.Sleep Will block the current thread .
In fact, I feel that the above example can not well express my point of view , Let's look at another example :
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
Run2();
Console.WriteLine("after run2");
Console.ReadKey();
await Task.CompletedTask;
}
static async Task<string> Run2()
{
await Task.Delay(5000);
Console.WriteLine("Run2");
return await Task.FromResult("Run2");
}The output order of this example is : First, the output after run2, Then the output Run2. Let's take another look at the warnings generated by compilation :
![]()
This warning is because Run2 It's an asynchronous method , But in Main When the function is called , of no avail await To wait for asynchronous methods , So the program won't wait for the asynchronous method to finish executing , And then move on . Because the program didn't wait , So first output after run2.
Let's put Run2 Methods await Switch to Thread.Sleep, That is to output first Run2 了 .
When we use Delay When the method is used , We must add await, This truth is similar to Run2 The method should be preceded by await equally , because Delay Methods are also asynchronous .
We recommend using await Task.Delay To perform a wait operation , Because it's asynchronous , On the principle of asynchrony , I recommend you to read an official Microsoft document :
https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/dotnet/standard/async-in-depth
版权声明
本文为[begeneral]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204230554082223.html
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

TypeError: set_ figure_ params() got an unexpected keyword argument ‘figsize‘

ACL 2022 | DialogVED:用于对话回复生成的预训练隐变量编码-解码模型

How to choose the wireless gooseneck anchor microphone and handheld microphone scheme
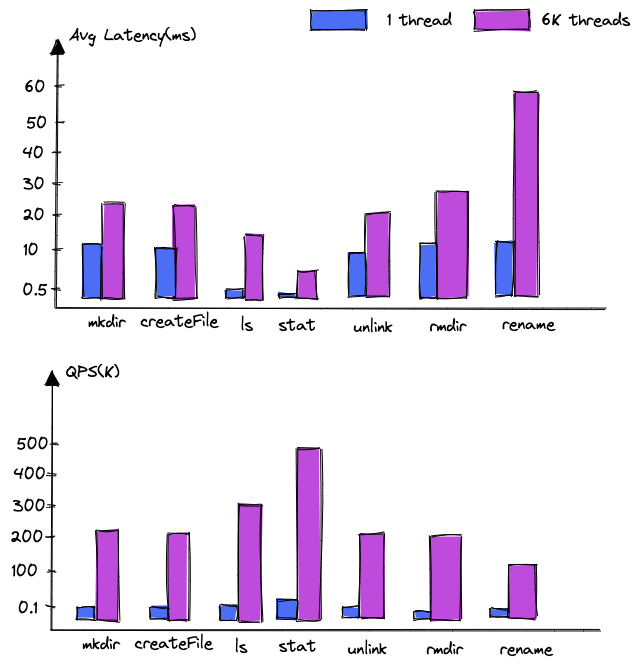
Dancenn: overview of byte self-developed 100 billion scale file metadata storage system
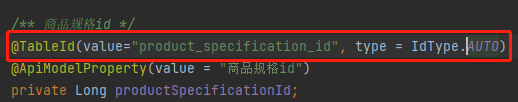
The new MySQL table has a self increasing ID of 20 bits. The reason is
Nodejs installation and environment configuration

Lock lock

Document operation II (5000 word summary)

ACL 2022 | dialogved: a pre trained implicit variable encoding decoding model for dialogue reply generation
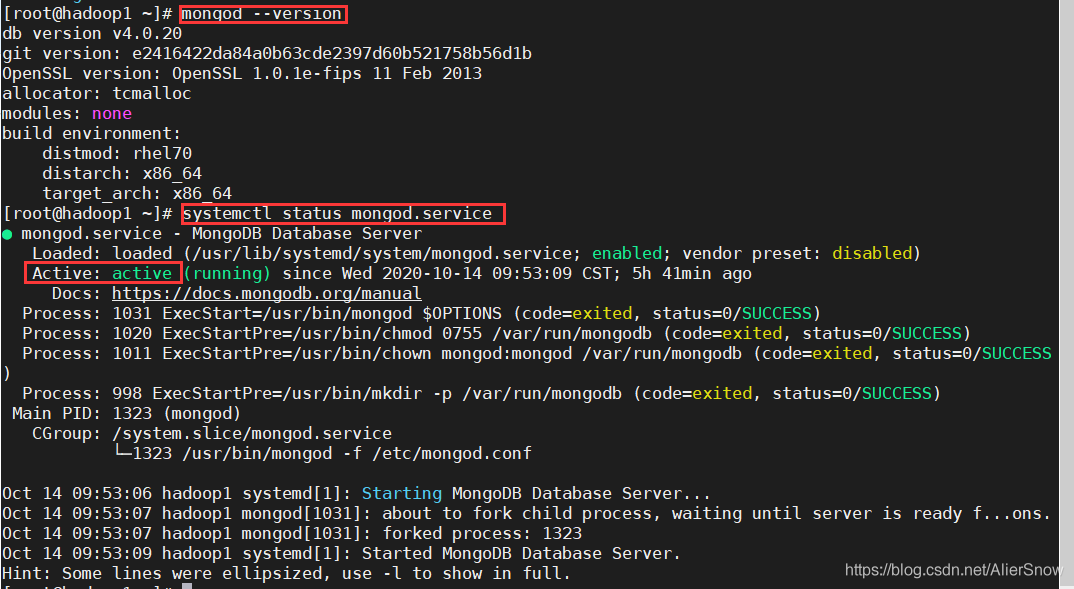
Quick install mongodb
随机推荐
Error in v-on handler: "typeerror: cannot read property 'resetfields' of undefined"
Linux MySQL data timing dump
Zhimeng dedecms security setup Guide
面试百分百问到的进程,你究竟了解多少
Quick install mongodb
New keyword learning and summary
Expression "func" tSource, object "to expression" func "tSource, object" []
SQL: How to parse Microsoft Transact-SQL Statements in C# and to match the column aliases of a view
Production environment——
线性代数感悟之1
文件操作《二》(5000字总结篇)
Aiot industrial technology panoramic structure - Digital Architecture Design (8)
Read a blog, re understand closures and tidy up
Talk about browser cache control
1-3 components and modules
Kunteng full duplex digital wireless transceiver chip kt1605 / kt1606 / kt1607 / kt1608 is suitable for interphone scheme
JSON deserialize anonymous array / object
蓝桥杯省一之路06——第十二届省赛真题第二场
Variable length parameter__ VA_ ARGS__ Macro definitions for and logging
Your brain expands and shrinks over time — these charts show how