当前位置:网站首页>Differences between SSD hard disk SATA interface and m.2 interface (detailed summary)
Differences between SSD hard disk SATA interface and m.2 interface (detailed summary)
2022-04-23 18:07:00 【Happy learning】
One 、 brief introduction
At present, the mainstream SSD Hard drives are SATA Interface or M.2 Interface . This paper mainly introduces SATA and M.2 The structure of the hard disk , The two kinds of hard disks are compared from many aspects .
Two 、SATA Interface details
SATA(Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) Hard disk , Also known as serial ATA, It's serial SCSI(SAS:Serial Attached SCSI) Twin brother , The arrangement of the two cables is compatible ,SATA The hard disk can be connected SAS Interface . It's a computer bus , Its main function is to be used as a main board and a mass storage device ( Such as hard disk and optical drive ) For data transmission between .
At present the mainstream SATA 3.0 passageway ,SATA 3.0 The biggest improvement , Is to increase the maximum transmission to 6Gbps, Due to the limitation of theoretical bandwidth, the reading and writing speed is 600MB/s.

3、 ... and 、M.2 Interface details
M.2 The name before the interface is what we often say NGFF(Next Generation Form Factor) Interface , because sata The limitation of the transmission speed of the interface itself , therefore M.2 Interface came into being , Such as PCI-E 3.0x4 The theoretical maximum bandwidth is 32Gbps, The upper limit of effective bandwidth is 4GB/s.
M.2 There are three types of interfaces B Key、M Key and B&M Key, The main difference is the direction of the power supply pins and the number of pins , Be careful B&M Key Is compatible B Key and M Key Common types of two interfaces .
 B Key and M Key The difference between the bus and protocol used is shown in the following figure :
B Key and M Key The difference between the bus and protocol used is shown in the following figure :
AHCI yes SATA Protocol standard corresponding to serial hard disk ( Logical device interface standard ), It can also be regarded as SATA Optimization driven , and NVME It is AHCI An advanced version of , It is also a protocol standard , It belongs to PCI-E Bus SSD A customized high-speed protocol , It should be noted that , use NVME Agreed M.2 SSD Must have used PCI-E 3.0x4 Bus standards , And used PCI-E 3.0x4 Bus M.2 SSD Not necessarily for NVME.
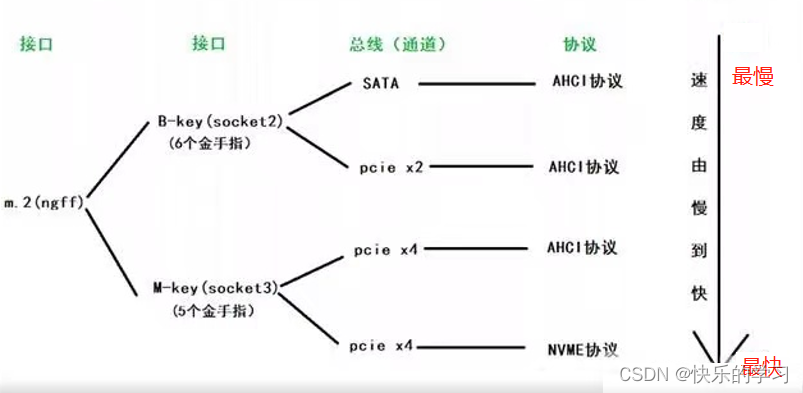
Four 、SATA Interface and M.2 Interface difference
The difference between buses :
Generally speaking NVME Adoption of the agreement M key or B&M key,SATA The agreement adopts B key or B&M key, therefore B&M key More versatility , So I'm buying M.2 If you encounter this kind of interface when hard disk , See whether the protocols supported by the hard disk correspond to those supported by the computer interface .SATA Due to the limitation of theoretical bandwidth (6Gbps), The ultimate transmission speed can only reach 600MB/s.NVME The theoretical bandwidth of the protocol is 10Gbps, The maximum transmission speed can reach 2000MB/s.
NVMe and AHCI The difference between :
These two are the transmission protocols of the hard disk , among NVME Is based on PCI-E Of ,AHCI Mainly based on SATA Of , So for SSD, If it is SATA Interface ( Include m.2 SATA) Yes, they all support AHCI Of , about PCI-E Interface ( Include m.2 PCI-E、 Standard plug-in card PCI-E、U.2), Yes, they basically support NVMe Of .
M.2 Interface and SATA The difference is that :
1、 The difference in transmission speed :SATA3 yes 6Gbps, Probably 600MB/s The transmission speed of .M.2 The theoretical maximum bandwidth is 32Gbps, The upper limit of effective bandwidth is 4GB/s.
2、 Price difference :M.2 Than SATA3 same-capacity SSD Prices vary widely .
3、 Agreement differences :M.2 Card slot interface protocol ,Sata3 It's a data protocol . There are three levels ,sata1 It's the first generation. The speed is 1.5Gbps,SATA2 Yes 3Gbps The speed of ,SATA3 yes 6Gbps The speed of .
PCI-E Than SATA Cause analysis of fast speed :
1、PCI-E It's full duplex mode
In fact, fundamentally speaking ,PCI-E Than SATA The biggest reason is because PCI-E Full duplex mode , and SATA In half duplex mode .
2、PCI-E More channels
PCI-E Can expand bandwidth by increasing the number of channels , As I said before , Up to 32 Number of channels , The more channels , The faster the speed. , Of course , And the higher the cost , It also consumes more electricity , In practice, you can decide how many channels to use according to your needs , It's flexible , Just like we can see different lengths on the motherboard PCIe It's the same as the slot , Yes x1 Yes x4 Yes x16 etc. , It can meet the requirements of different equipment .
We start with PCI-E 3.0x16(PCI-E 3.0 Standard bus , At the same time 16 passageway ) Let's talk about ,PCI-E 3.0x16 Slot length 89mm, Have 164 Root pin , Divided into two groups , The shorter slot in the front has 22 Root pin , Mainly used for power supply , A long set of slots at the back 142 root , Mainly used for data transmission .
Other disk Related Links :Flash Flash memory storage principle and NAND flash、NOR flash conclusion
版权声明
本文为[Happy learning]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204231801416761.html
边栏推荐
- Batch export ArcGIS attribute table
- Jenkspy package installation
- .105Location
- Logic regression principle and code implementation
- Queue solving Joseph problem
- Excel opens large CSV format data
- Calculation of fishing net road density
- C#的随机数生成
- 2022江西光伏展,中国分布式光伏展会,南昌太阳能利用展
- MySQL auto start settings start with systemctl start mysqld
猜你喜欢

2022 Jiangxi Photovoltaic Exhibition, China distributed Photovoltaic Exhibition, Nanchang solar energy utilization Exhibition

JS high frequency interview questions
![Yolov4 pruning [with code]](/img/09/ea4376d52edb7e419ace2cb1e0356b.gif)
Yolov4 pruning [with code]

Eigen learning summary

C network related operations
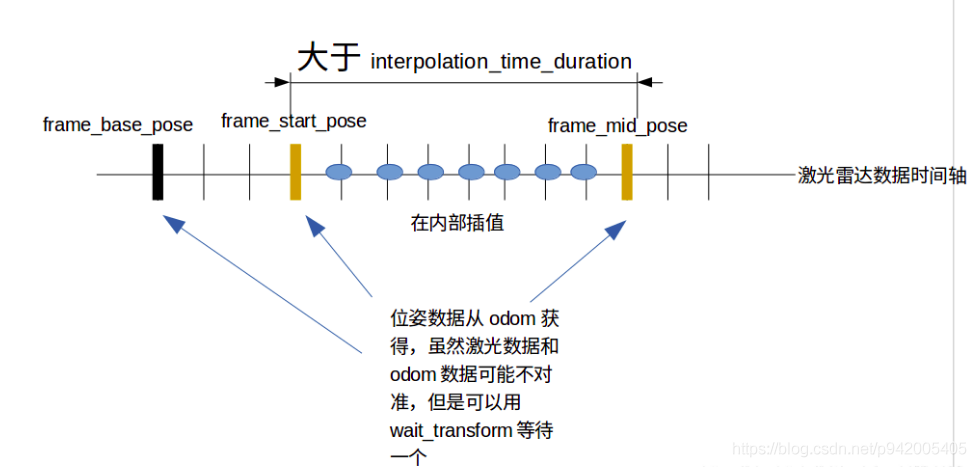
Laser slam theory and practice of dark blue College Chapter 3 laser radar distortion removal exercise
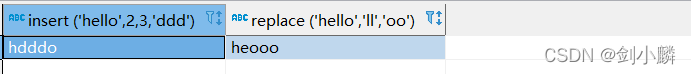
MySQL 中的字符串函数

Go language JSON package usage
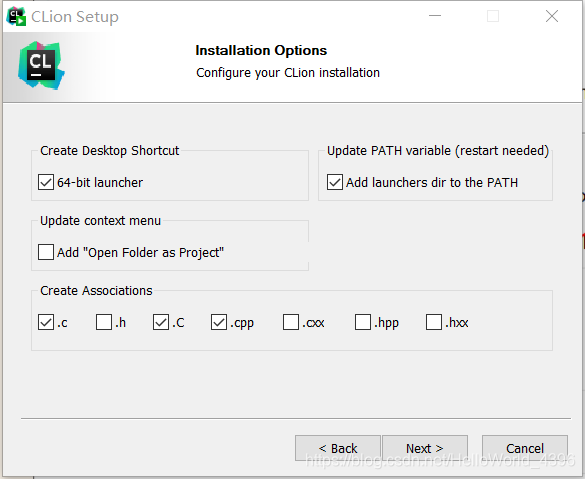
Clion installation tutorial
Auto. JS custom dialog box
随机推荐
Romance in C language
positioner
Implementation of object detection case based on SSD
Array rotation
Vulnérabilité d'exécution de la commande de fond du panneau de commande JD - freefuck
Theory and practice of laser slam in dark blue College - Chapter 2 (odometer calibration)
[UDS unified diagnostic service] v. diagnostic application example: Flash bootloader
C language input and output (printf and scanf functions, putchar and getchar functions)
ROS package NMEA_ navsat_ Driver reads GPS and Beidou Positioning Information Notes
Cells in rust share variable pointers
Rust: how to match a string?
MySQL_01_简单数据检索
Go's gin framework learning
Re regular expression
Serialization scheme of serde - trust
Summary of floating point double precision, single precision and half precision knowledge
Realization of consumer gray scale
Docker 安裝 Redis
Auto.js 自定义对话框
C# 的数据流加密与解密