当前位置:网站首页>记录本项目中用到的系统调用与C库函数-2
记录本项目中用到的系统调用与C库函数-2
2022-08-09 12:45:00 【养猪去】
记录本项目中用到的系统调用与C库函数
syscall
getpw 函数组
getpw 都是用于获取用户的一组函数
相关函数:getpw, fgetpwent, getpwent, getpwuid
getpwnam
- 头文件:
#include <pwd.h>
函数说明:
函数说明:getpwnam()用来逐一搜索参数 name 指定的账号名称, 找到时便将该用户的数据以 passwd 结构体返回。
passwd 结构请参考 getpwent()。函数定义
struct passwd * getpwnam(const char * name);
返回值
返回 passwd 结构数据, 如果返回NULL 则表示已无数据, 或有错误发生。示例代码:
/** * @Author: 吉松阳 * @Date: 2021/9/23 * @Description: */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pwd.h>
int main() {
struct passwd *pw;
char *username = "jisongyang";
pw = getpwnam(username);
if (!pw) {
printf("%s is not exist\n", username);
return -1;
}
printf("pw->pw_name = %s\n", pw->pw_name);
printf("pw->pw_passwd = %s\n", pw->pw_passwd);
printf("pw->pw_uid = %d\n", pw->pw_uid);
printf("pw->pw_gid = %d\n", pw->pw_gid);
printf("pw->pw_gecos = %s\n", pw->pw_gecos);
printf("pw->pw_dir = %s\n", pw->pw_dir);
printf("pw->pw_shell = %s\n", pw->pw_shell);
return 0;
}
/* 输出结果: pw->pw_name = jisongyang pw->pw_passwd = ******** pw->pw_uid = 501 pw->pw_gid = 20 pw->pw_gecos = 吉松阳 pw->pw_dir = /Users/jisongyang pw->pw_shell = /bin/zsh */
时间相关
time
- 头文件:
#include <time.h>
- 函数说明:
C 库函数: 返回自纪元 Epoch(1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC)起经过的时间,以秒为单位。
如果 seconds 不为空,则返回值也存储在变量 seconds 中。 - 函数定义
time_t time(time_t *seconds)
- 返回值
以 time_t 对象返回当前日历时间。
localtime
- 头文件:
#include <time.h>
函数说明:
C 库函数 使用 timer 的值来填充 tm 结构。
timer 的值被分解为 tm 结构,并用本地时区表示。函数定义
struct tm *localtime(const time_t *timer)
- 返回值
该函数返回指向 tm 结构的指针,该结构带有被填充的时间信息。下面是 tm 结构的细节:
struct tm {
int tm_sec; /* 秒,范围从 0 到 59 */
int tm_min; /* 分,范围从 0 到 59 */
int tm_hour; /* 小时,范围从 0 到 23 */
int tm_mday; /* 一月中的第几天,范围从 1 到 31 */
int tm_mon; /* 月份,范围从 0 到 11 */
int tm_year; /* 自 1900 起的年数 */
int tm_wday; /* 一周中的第几天,范围从 0 到 6 */
int tm_yday; /* 一年中的第几天,范围从 0 到 365 */
int tm_isdst; /* 夏令时 */
};
strftime
- 头文件:
#include <time.h>
函数说明:
C 库函数,根据 format 中定义的格式化规则,格式化结构 timeptr 表示的时间,并把它存储在 str 中。函数定义
size_t strftime(char *str, size_t maxsize, const char *format, const struct tm *timeptr)
- str – 这是指向目标数组的指针,用来复制产生的 C 字符串。
- maxsize – 这是被复制到 str 的最大字符数。
- format – 这是 C 字符串,包含了普通字符和特殊格式说明符的任何组合。这些格式说明符由函数替换为表示 tm 中所指定时间的相对应值。
具体格式详见:
参考链接
- 返回值
如果产生的 C 字符串小于 size 个字符(包括空结束字符),则会返回复制到 str 中的字符总数(不包括空结束字符),否则返回零。
gettimeofday
- 头文件:
#include <sys/time.h>
- 函数说明:
返回当前距离1970年的秒数和微妙数,后面的tz是时区,一般不用(传 NULL 即可)。 - 函数定义
int gettimeofday(struct timeval *tv, struct timezone *tz);
clock_gettime
- 头文件:
#include <time.h>
函数说明:
根据时钟模式,获取多种时间。函数定义
int clock_gettime(clockid_t clock_id, struct timespec * tp );
CLOCK_REALTIME 0
Systemwide realtime clock. 系统实时时间,随系统实时时间改变而改变。
即从UTC1970-1-1 0:0:0开始计时,中间时刻如果系统时间被用户该成其他,则对应的时间相应改变CLOCK_MONOTONIC 1
Represents monotonic time. Cannot be set. 从系统启动这一刻起开始计时,不受系统时间被用户改变的影响
用的是相对时间,它的时间是通过jiffies值来计算的。该时钟不受系统时钟源的影响,只受jiffies值的影响。
也就是说它获得的时间戳是单调的。CLOCK_PROCESS_CPUTIME_ID 2
High resolution per-process timer. 本进程到当前代码系统CPU花费的时间CLOCK_THREAD_CPUTIME_ID 3
Thread-specific timer. 本线程到当前代码系统CPU花费的时间CLOCK_REALTIME_HR 4
High resolution version of CLOCK_REALTIME. 0
CLOCK_REALTIME 的 高精度版本CLOCK_MONOTONIC_HR 5
High resolution version of CLOCK_MONOTONIC.
CLOCK_MONOTONIC 的高精度版本返回值
时间结构struct timespec示例代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
int main() {
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
printf("gettimeofday : %ld, %d\n", tv.tv_sec,tv.tv_usec);
struct timespec ts;
clock_gettime(CLOCK_REALTIME, &ts);
printf("CLOCK_REALTIME: %ld, %ld\n", ts.tv_sec, ts.tv_nsec);
//打印出来的时间跟 cat /proc/uptime 第一个参数一样
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &ts);
printf("CLOCK_MONOTONIC: %ld, %ld\n", ts.tv_sec, ts.tv_nsec);
clock_gettime(CLOCK_PROCESS_CPUTIME_ID, &ts);
printf("CLOCK_PROCESS_CPUTIME_ID: %ld, %ld\n", ts.tv_sec, ts.tv_nsec);
clock_gettime(CLOCK_THREAD_CPUTIME_ID, &ts);
printf("CLOCK_THREAD_CPUTIME_ID: %ld, %ld\n", ts.tv_sec, ts.tv_nsec);
printf("\n%ld\n", time(NULL));
return 0;
}
值得一提的是,本项目使用的计时工具不能使用 time 以及 gettimeofday,否则有小概率发生"时间回溯现象",
具体可以参考 Linux的timedatectl —— 关闭或开启时间同步.
必须使用 clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, *timespec); 才可以先后两次拿到的时间戳是递增的。
边栏推荐
- WSA工具箱安装应用商店提示无法工作怎么解决?
- Bitmaps and bit operations
- jenkins api创建自定义pipeline
- About the handling of variable parameters in the Retrofit network request URL
- ftplib+ tqdm 上传下载进度条
- Customize VIEW to realize in-app message reminder to rotate up and down
- Flutter入门进阶之旅(五)Image Widget
- FPGA-近日工作总结
- Compensation transaction and idempotency guarantee based on CAP components
- telnet+ftp to control and upgrade the device
猜你喜欢
RTSP协议讲解

World's 4th mad scientist dies on his 103rd birthday
FFmpeg多媒体文件处理(ffmpeg处理流数据的基本概念)

5G 联通网管设计思路

我的2020年终总结
ansible-cmdb friendly display ansible collects host information
Go Affair, How to Become a Gopher and Find a Go Job in 7 Days, Part 1
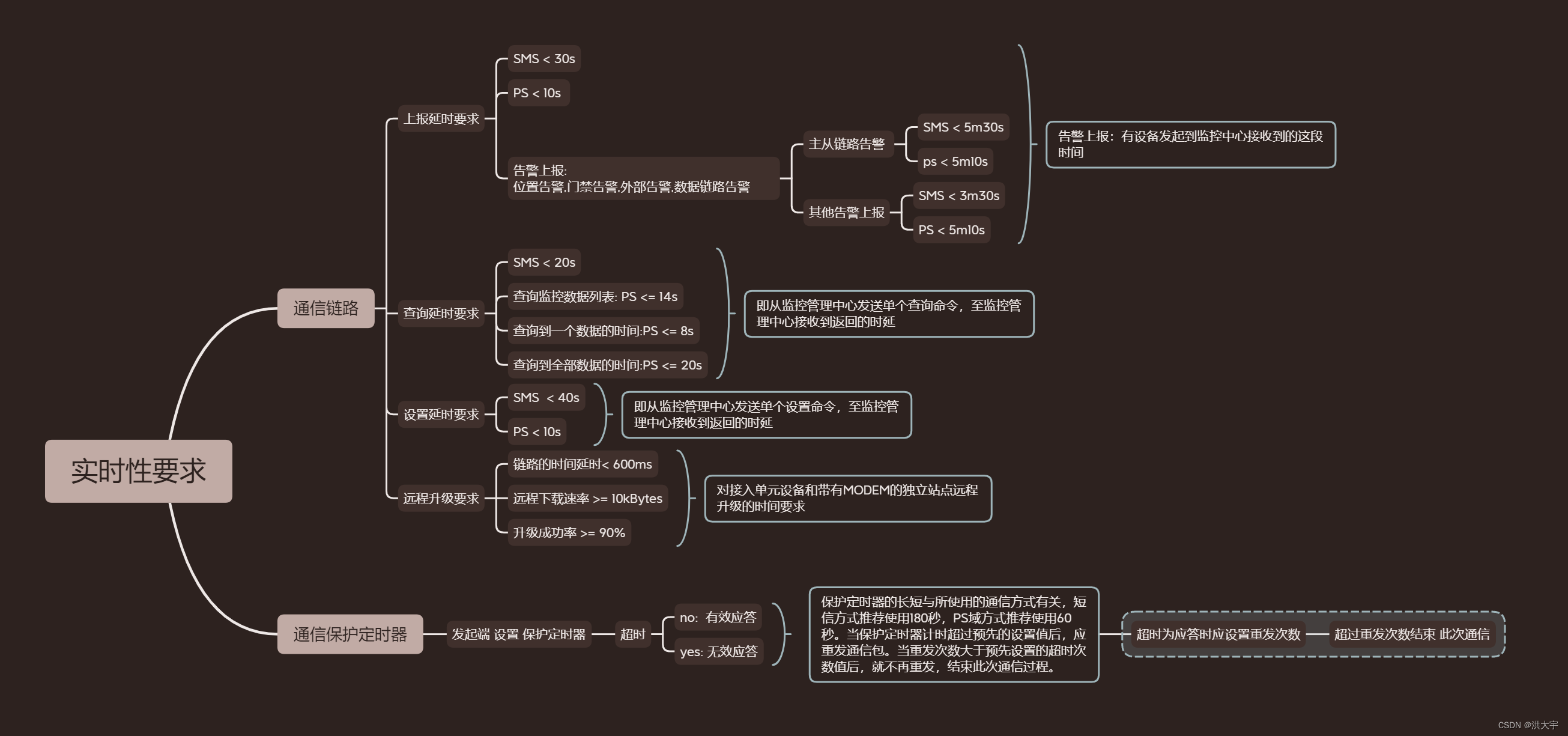
5G China unicom 直放站 网管协议 实时性要求
jenkins api create custom pipeline

ViewPager fragments of nested data blank page abnormal problem analysis
随机推荐
批量读取word docx文件指定表格内容,保存在excel文件中
SQL Server查询优化 (转载非原创)
leetcode 20. Valid Parentheses 有效的括号(中等)
绘制混合密度函数图以及添加分位数线
某高校的R语言数据分析期末作业
Use RecyclerView to implement three-level collapsed list
telnet+ftp 对设备进行 操控 和 升级
GIN中GET POST PUT DELETE请求
造自己的芯,让谷歌买单!谷歌再度开源 180nm 工艺的芯片
Redis源码剖析之字典(dict)
【TKE】GR+VPC-CNI混用模式下未产品化功能配置
5G China unicom AP:B SMS ASCII 转码要求
电脑重装系统还原0x80070005错误如何解决
透明tune proxy
用场景定义硬件,英码科技破解“边缘计算”密码
read stream special attention
leetcode 20. Valid Parentheses 有效的括号(中等)
kustomize入门示例及基本语法使用说明
Introduction to Flutter advanced trip Dialog&Toast (10)
Flutter Getting Started and Advanced Tour (7) GestureDetector