当前位置:网站首页>Command - sudo
Command - sudo
2022-04-23 19:26:00 【Little monster 55】
sudo It's a kind of authority management mechanism , It allows the system administrator to assign reasonable tasks to ordinary users " right ", Let them perform tasks that only super users or other authorized users can complete , such as : Run something like mount,halt,su Orders like that , Or edit some system configuration files , image /etc/mtab,/etc /samba/smb.conf etc. .
1.su
Switching users
Format
# Format
1)su
-[l]/--login username
2)su username
# Don't specify username The default is root
1 and 2 The difference between :1 After switching users , Also switch to the new user's work environment
2 After switching users , Do not change the original user's working directory , And other environment variable directories
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.

Example
[[email protected] ~]
# su openstack
[[email protected] root]
$ pwd
/root
[[email protected] root]
$ exit
exit
[[email protected] ~]
# su - openstack
Last login: Sat Apr
23
17:44:35 CST
2022 on pts/0
[[email protected] ~]
$ pwd
/home/openstack
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
2.sudo
package :sudo
help :man
5 sudoers
effect : Authorize the specified user , On the specified host , Run some commands ; If an unauthorized user attempts to use sudo, You will be prompted to contact the administrator
Provide logs , Record user usage sudo operation
Provide configuration files for system administrators , Manage user permissions and hosts
Use a timestamp file to accomplish something like
" Ticket checking " The system of , The default deposit period is 5min
# adopt visudo Command edit profile , It has the function of grammar checking
use visudo Command to edit /etc/sudoers
usage: visudo [-chqsV] [-f sudoers]
visudo
-c
# Syntax check
visudo
-f /etc/sudoers.d/test
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
2.1. file
The configuration file :/etc/sudoers /etc/sudoers.d/*
Time stamp file :/var/db/sudo
Log files :/var/log/secure
Profile support : wildcard glob
?
*
[wxc]
# Match one of the characters
[!wxc]
\x
# escape
[[alpha]]
# There are two types of profile rules :
1. The alias definition : It's not necessary
2. Authorization rules : must
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
2.2. Authorization rules
user host
= (runas) command
user Log in to the host
= ( On behalf of the user ) command
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
-
root ALL
= (ALL) ALL
user:
# The identity of the person who ran the command
host:
# Through which hosts
(runas):
# As which user
command:
# Which commands to run
# Example :
wang
192.168.37
.7
=(root) /bin/mount /dev/sr0 /mnt
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
2.3. Alias
#user and runas:
username
#uid
%group_name
%
#gid
user_alias|runas_alias
#host:
ip or hostname
network(/netmask)
host_alias
#command:
command name
directory
sudoedit
Cmnd_Alias
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
# There are four types of aliases
User_Alias
Runas_Alias
Host_Alias
Cmnd_Alias
# Alias format
[A-Z]([A-Z][0-9]_)*
# The alias definition :
Alias_Type
NAME1
=item1,item2,item3
:NAME2
=item4,item5
Example 1:
Student
ALL
=(ALL) ALL
%wheel
ALL
=(ALL) ALL
Example 2:
Student
ALL
=(root) /sbin/pidof,/sbin/ifconfig
%wheel
ALL
=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL
Example 3:
User_Alias
NETADMIN
= netuser1,netuser2
Cmnd_Alias NETCMD
= /usr/sbin/ip
NETADMIN
ALL
=(root) NETCMD
Example 4:
User_Alias
SYSADER
=wang,mage,%admins
User_Alias
DISKADER
=tom
Host_Alias
SERS
=www.magedu.com,172.16.0.0/24
Runas_Alias
OP
=root
Cmnd_Alias
SYDCMD
=/bin/chown,/bin/chmod
Cmnd_Alias
DSKCMD
=/sbin/parted,/sbin/fdisk
SYSADER
SERS
= SYDCMD,DSKCMD
DISKADER
ALL
=(OP) DSKCMD
User_Alias ADMINUSER
= adminuser1,adminuser2
Cmnd_Alias ADMINCMD
= /usr/sbin/useradd,/usr/sbin/usermod, /usr/bin/passwd [a-zA-Z]*, !/usr/bin/passwd root
ADMINUSER
ALL
=(root) NOPASSWD:ADMINCMD,PASSWD:/usr/sbin/userdel
Example 5:
Defaults:wang
runas_default
=tom
wang
ALL
=(tom,jerry) ALL
Example 6:
wang
192.168.1.6,192.168.1
.8
=(root) /usr/sbin/,!/usr/sbin/useradd
Example 7:
wang
ALL
=(ALL) /bin/cat /var/log/messages*
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
2.4.sudo command
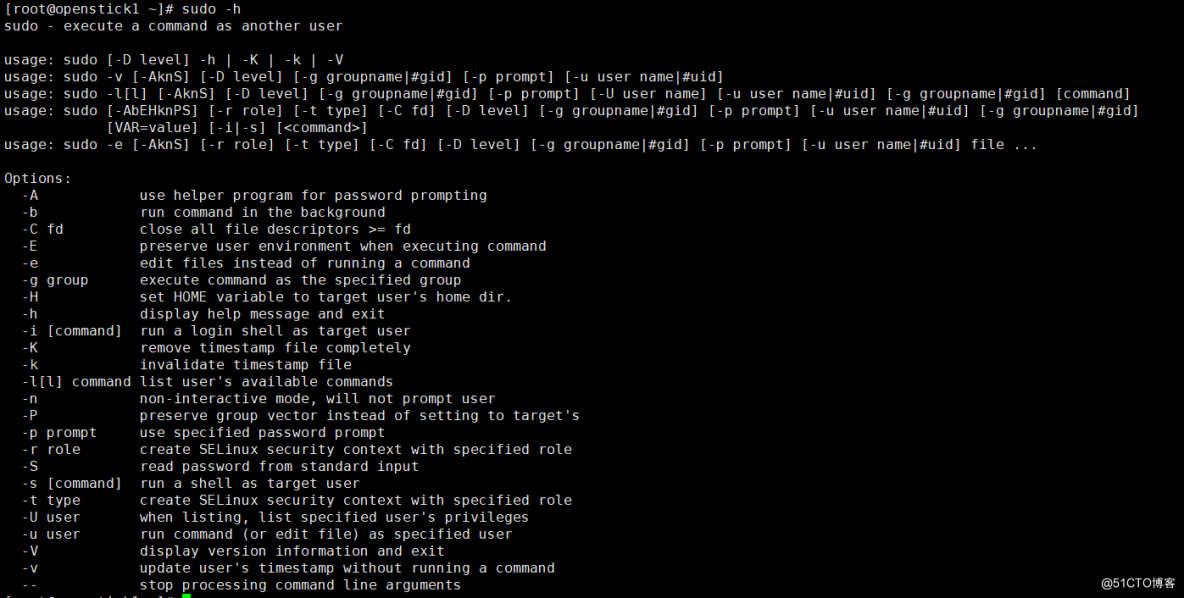
sudo –i –u wang Switch identities
sudo [-u user] COMMAND
-V
# Display configuration information such as version information
-u user
# Think root
-l,ll
# List the commands available and disabled on the host
-v
# Extend the validity of the password 5 minute , Update timestamp
-k
# Clear timestamp (1970-01-01), I need to retype the password next time
-K
#-k similar , Also delete the timestamp file
-b
# Execute instructions in the background
-p
# Change the prompt symbol for asking for the password
Example :-p
"password on %h for user %p:"
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
版权声明
本文为[Little monster 55]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204231859372099.html
边栏推荐
- MySQL syntax collation
- An example of using JNI to directly access surface data
- How to use go code to compile Pb generated by proto file with protoc Compiler Go file
- Application of DCT transform
- Main differences between go and PHP
- Speculation on the way to realize the smooth drag preview of video editing software
- Openlayers 5.0 discrete aggregation points
- How to uninstall easyton
- Encyclopedia of professional terms and abbreviations in communication engineering
- 精简CUDA教程——CUDA Driver API
猜你喜欢

RuntimeError: Providing a bool or integral fill value without setting the optional `dtype` or `out`
JVM的类加载过程
Kubernetes入门到精通-裸机LoadBalence 80 443 端口暴露注意事项
![[transfer] summary of new features of js-es6 (one picture)](/img/45/76dba32e4fa7ed44a42e5f98ea8207.jpg)
[transfer] summary of new features of js-es6 (one picture)
![[report] Microsoft: application of deep learning methods in speech enhancement](/img/29/2d2addd826359fdb0920e06ebedd29.png)
[report] Microsoft: application of deep learning methods in speech enhancement
Oracle配置st_geometry
The platinum library cannot search the debug process records of some projection devices
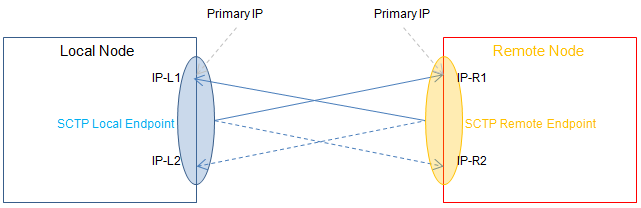
Network protocol: SCTP flow control transmission protocol
No, some people can't do the National Day avatar applet (you can open the traffic master and earn pocket money)

Common SQL commands
随机推荐
Common processing of point cloud dataset
What is a message queue
Pdf reference learning notes
Strange passion
How to use go code to compile Pb generated by proto file with protoc Compiler Go file
NiO related Basics
Openharmony open source developer growth plan, looking for new open source forces that change the world!
山大网安靶场实验平台项目-个人记录(五)
优先使用组合而不使用继承
Class loading mechanism
Machine learning catalog
Kubernetes入门到精通-裸机LoadBalence 80 443 端口暴露注意事项
SSDB foundation 2
SSDB foundation 1
Quick start to static class variables
Openlayers 5.0 thermal diagram
Zero base to build profit taking away CPS platform official account
arcgis js api dojoConfig配置
Customize the non slidable viewpage and how to use it
Prefer composition to inheritance