当前位置:网站首页>Go语言切片,范围,集合
Go语言切片,范围,集合
2022-04-23 15:34:00 【世界尽头与你】
Go语言切片,范围,集合
1.Go 语言切片(Slice)
概述
Go 语言切片是对数组的抽象。
Go 数组的长度不可改变,在特定场景中这样的集合就不太适用,Go 中提供了一种灵活,功能强悍的内置类型切片(“动态数组”),与数组相比切片的长度是不固定的,可以追加元素,在追加时可能使切片的容量增大。
定义切片
你可以声明一个未指定大小的数组来定义切片:
var identifier []type
var si []int
或使用 make() 函数来创建切片:
var slice1 []type = make([]type, len)
也可以简写为
slice1 := make([]type, len)
也可以指定容量,其中 capacity 为可选参数。
make([]T, length, capacity)
这里
len是数组的长度并且也是切片的初始长度。
切片初始化
s :=[] int {
1,2,3 }
len() 和 cap() 函数
切片是可索引的,并且可以由 len() 方法获取长度。
切片提供了计算容量的方法 cap() 可以测量切片最长可以达到多少。
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var numbers = make([]int, 3, 5)
fmt.Println(len(numbers), cap(numbers), numbers)
}
-----------------------
输出:
3 5 [0 0 0]
空(nil)切片
一个切片在未初始化之前默认为
nil,长度为 0,实例如下:
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var numbers []int
if numbers == nil {
fmt.Println("切片为空")
}
}
--------------------------
输出:切片为空
切片截取
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
numbers := []int{
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
fmt.Println(numbers)
fmt.Println(numbers[1:4])
fmt.Println(numbers[:3])
fmt.Println(numbers[4:])
}
------------------------------
输出:
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
[1 2 3]
[0 1 2]
[4 5 6 7 8 9]
append() 和 copy() 函数
append()
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
numbers := []int{
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
/* 向切片添加一个元素 */
numbers = append(numbers, 521)
/* 同时添加多个元素 */
numbers = append(numbers, 11, 12, 13)
fmt.Println(numbers)
}
---------------------------------------------------
输出:
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 521 11 12 13]
copy()
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
numbers := []int{
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
/* 创建切片 numbers1 是之前切片的两倍容量*/
numbers1 := make([]int, len(numbers), (cap(numbers))*2)
copy(numbers1, numbers)
fmt.Println(numbers1)
}
-----------------------------------------------
输出:
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
2.Go 语言范围(Range)
Go 语言中 range 关键字用于 for 循环中迭代数组(array)、切片(slice)、通道(channel)或集合(map)的元素。在数组和切片中它返回元素的索引和索引对应的值,在集合中返回 key-value 对。
实例1:
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// 使用range去求一个slice的和。使用数组跟这个很类似
nums := []int{
2, 3, 4}
sum := 0
for _, num := range nums {
sum += num
}
fmt.Println(sum)
}
-----------------------------
输出:9
实例2:
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// 使用range去求一个slice的和。使用数组跟这个很类似
nums := []int{
2, 3, 4}
sum := 0
for i, num := range nums {
sum += num
fmt.Println(i)
}
fmt.Println(sum)
}
----------------------------------
输出:
0
1
2
9
实例3:range也可以用来枚举Unicode字符串。第一个参数是字符的索引,第二个是字符(Unicode的值)本身。
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
for i, c := range "hello" {
fmt.Println(i, c)
}
}
---------------------------------------
输出:
0 104
1 101
2 108
3 108
4 111
3.Go 语言Map(集合)
Map 是一种无序的键值对的集合。Map 最重要的一点是通过 key 来快速检索数据,key 类似于索引,指向数据的值。
Map 是一种集合,所以我们可以像迭代数组和切片那样迭代它。不过,Map 是无序的,我们无法决定它的返回顺序,这是因为 Map 是使用 hash 表来实现的。
实例1:
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var country map[string]string
country = make(map[string]string)
/* map插入key - value对 */
country["France"] = "巴黎"
country["beijing"] = "北京"
country["Japan"] = "日本"
/* 使用键输出地图值 */
for cou := range country {
fmt.Println(cou, "+", country[cou])
}
}
-------------------------------------------------
输出:
France + 巴黎
beijing + 北京
Japan + 日本
实例2:
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var country map[string]string
country = make(map[string]string)
/* map插入key - value对 */
country["France"] = "巴黎"
country["beijing"] = "北京"
country["Japan"] = "日本"
/* 查看元素在集合中是否存在 */
capital, ok := country["American"]
if ok {
fmt.Println(capital)
} else {
fmt.Println("American的首都不存在")
}
}
----------------------------------------
输出:
American的首都不存在
实例3:delete() 函数用于删除集合的元素
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var country map[string]string
country = make(map[string]string)
/* map插入key - value对 */
country["France"] = "巴黎"
country["beijing"] = "北京"
country["Japan"] = "日本"
delete(country, "Japan")
fmt.Println(country)
}
------------------------------------
输出:map[France:巴黎 beijing:北京]
版权声明
本文为[世界尽头与你]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://blog.csdn.net/Gherbirthday0916/article/details/124361772
边栏推荐
- 控制结构(二)
- JVM-第2章-类加载子系统(Class Loader Subsystem)
- The El tree implementation only displays a certain level of check boxes and selects radio
- G007-hwy-cc-estor-03 Huawei Dorado V6 storage simulator construction
- Educational codeforces round 127 A-E problem solution
- Deep learning - Super parameter setting
- The life cycle of key value in redis module programming
- Common interview questions of operating system:
- API gateway / API gateway (III) - use of Kong - current limiting rate limiting (redis)
- Byte interview programming question: the minimum number of K
猜你喜欢

Sword finger offer (2) -- for Huawei
setcontext getcontext makecontext swapcontext
Cookie&Session
The wechat applet optimizes the native request through the promise of ES6
G007-HWY-CC-ESTOR-03 华为 Dorado V6 存储仿真器搭建
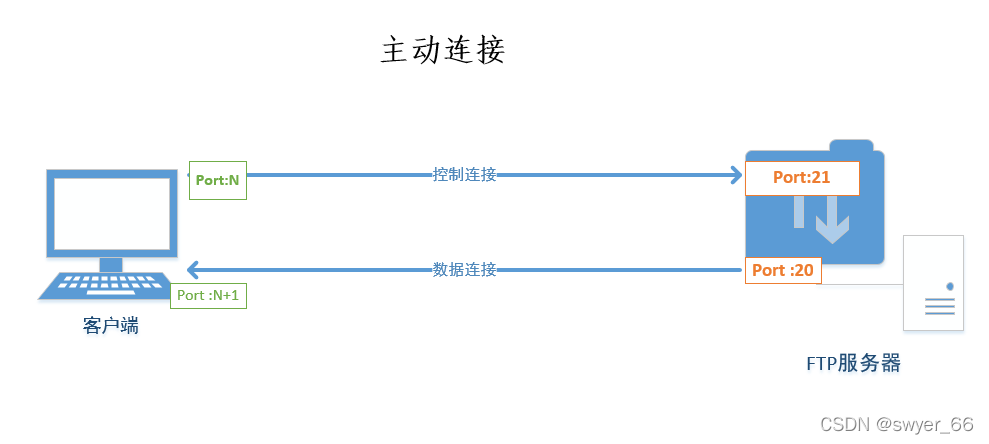
Analysis of common storage types and FTP active and passive modes
My raspberry PI zero 2W toss notes to record some problems and solutions
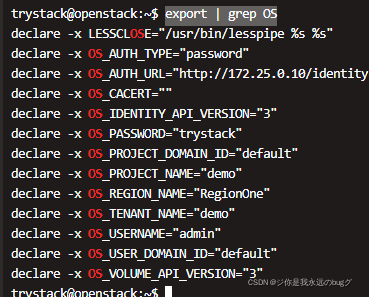
Openstack command operation
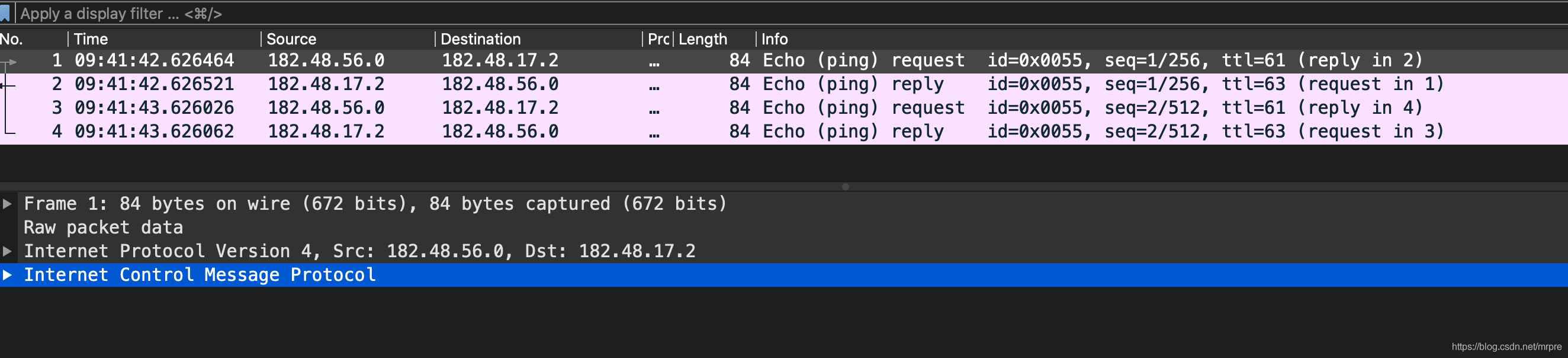
Tun model of flannel principle
How did the computer reinstall the system? The display has no signal
随机推荐
木木一路走好呀
通过 PDO ODBC 将 PHP 连接到 MySQL
adobe illustrator 菜單中英文對照
通過 PDO ODBC 將 PHP 連接到 MySQL
激活函数的优缺点和选择
MySQL query library size
My raspberry PI zero 2W toss notes to record some problems and solutions
Detailed explanation of kubernetes (IX) -- actual combat of creating pod with resource allocation list
PHP PDO ODBC loads files from one folder into the blob column of MySQL database and downloads the blob column to another folder
Baidu written test 2022.4.12 + programming topic: simple integer problem
Detailed explanation of redirection and request forwarding
MySQL InnoDB transaction
Elk installation
SSH connects to the remote host through the springboard machine
TLS / SSL protocol details (28) differences between TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1 and TLS 1.2
tcp_ Diag kernel related implementation 1 call hierarchy
编译,连接 -- 笔记
让阿里P8都为之着迷的分布式核心原理解析到底讲了啥?看完我惊了
Connectez PHP à MySQL via aodbc
基础贪心总结